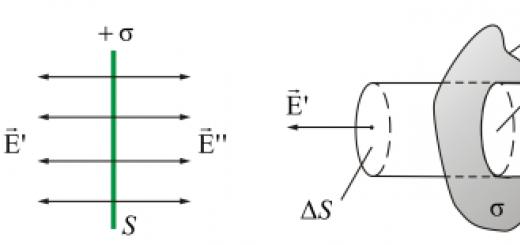
Conflictology today is preparing to be separated into a separate science. In this case, it is necessary to clearly define what it is, what types and types are, in other words, to designate the object of study of this science.
Going deeper, you need to understand the causes and differences of various disputes, on what basis they arise and in what ways they can be resolved. After all, everyone knows that there are no unsolvable situations, you just need to know what we are facing.
First, let's look at the very concept of conflict. Types of conflicts in society after that will become more understandable and obvious to us.
So, a conflict is often a discrepancy between the interests of two or more people whose interests do not coincide with respect to a particular case, event, goal, and so on. This is a situation where there is a difference of opinion that cannot be satisfied at the same time. As you know, such disagreements can have both positive and negative consequences that affect our lives and decisions.
Causes and types of disagreements
The causes and types of conflicts are closely interrelated. The former mainly influences how the situation will be resolved. It is the identification of the cause of the conflict that will help not only resolve it, but also prevent it in the future. It is clear that without knowing the true essence, we will not be able to fight this effectively, and, based only on theory, this cannot be done either. You will definitely need special knowledge of the psychology of the interlocutors, if we talk about interpersonal disputes.

Practice shows that it is not worth interfering in someone's dispute, since an attempt to resolve someone else's conflict can only aggravate it. Nevertheless, sometimes it can help resolve it: a fresh opinion and a look at the situation can lead conflicting interlocutors to a single solution, which will end the disagreement.
First of all, consider those types of social conflicts that are very familiar to us. We all live in society. Every day we communicate with dozens of people, and some people tend to spend their day exclusively among people. And for society, disagreement is a natural phenomenon, without which not one of our days can do.
There are two types of personality conflicts:
- Intrapersonal.
- Interpersonal.
- Personality and group.
- Group.
intrapersonal conflict
This type of conflict can be described as one's own, personal confrontation. In this case, only one person takes part in it - you. We are talking about our feelings, needs, certain goals and motives, which do not always work smoothly and together. After all, you see, often we have a desire that is not feasible for a number of reasons, and the point is not even in the availability of opportunities, but in certain of our thoughts and feelings.

Here a conflict arises with oneself, which pushes us to rash acts, or, conversely, to renunciation of action, which we may later regret. This is the inconsistency of the mind and heart, physical needs and moral principles, and so on.
Quite often, such a conflict can arise in connection with the work of a person. When his position or role in the organization makes too high demands that cannot be met for "own" reasons.
We can consider an example: the opposition of the role of "family man" and "good worker". It is present, and is characteristic of many of us. When you want to spend more time with your family, pay due attention to your relatives, work makes you stay up late, makes you stay late, which gives rise to an intrapersonal conflict.
interpersonal conflict
Different types of conflicts flow into our lives in different ways every day. But this view, one might say, is the most relevant and "popular" today.

An interpersonal dispute is a quarrel that occurs between two people for any reason, be it moral or material. If we talk about the sphere of work, then these are often disputes between managers and subordinates, colleagues or candidates for the same position, competition is also a kind of conflict.
The described situations can also be characterized as types of conflicts in the organization, since any organization has its own staff, which in essence are absolutely different people- individuals. Therefore, it is not surprising that disagreements and disputes arise quite often. It is common to argue that it is the differences in people that are the ground for the emergence of confrontations.
Conflict between the individual and the group

These types of conflicts are less common, but still present in our lives. In this case, the worldview or, more simply, the position of one person is contrary to the opinion of the rest of the group of people, for example, among employees of one team, or family members.
On the other hand, such a dispute may arise on the basis of non-compliance with established rules. As we know, each established team has its own rules and moral foundations that develop over time. When it comes new person, he is obligated to obey general rules, and any deviant behavior is regarded as an attempt to discord the team (of course, on a subconscious level), because of this, disagreement arises between people.
group conflict
If we call the types of conflicts in the organization and personal, then this type of disagreement can also be called general, which can occur everywhere.
This is a confrontation between groups, both formal and informal, which are present both in every company and in the whole society in general.
In this situation, different branches of the organization can resist, for example, management and subordinates, informal associations within the team (everyone is familiar with the situation when the team, during the discussion of a particular problem, is divided into several groups united by one opinion).
Other types of social divisions
The above are the main types of conflicts. These are the most common life situations, the way out of which, whether we like it or not, we often find on our own and on the basis of this we build our own personal experience and gain knowledge.
Types social conflicts also imply another classification, according to the spheres of human activity, according to which contradictions are divided into the following groups:
- Political.
- Socio-economic.
- National-ethnic.
- Interstate.
political conflict
Such a conflict can arise at moments of power sharing, achieving the desired heights in this area, the struggle for influence and authority. Just the same, these disagreements almost always arise, and we are all watching them.
The bottom line is that politicians are purposeful people who clearly formulate their goals and aspirations. And there is always competition and widespread struggle. It can take place both between certain branches of government, certain groups (which is the group conflict that we considered above), within the parliament itself, and so on.
Socio-economic conflict

These types of conflicts are connected, first of all, with the material well-being of every citizen of the country, and, in fact, of any person in the world.
They primarily concern employed people who are very concerned about the level of their wages, any payments, pension and social. In this case, the conflict is often caused by a discrepancy between wages and the forces invested in it, intellectual capabilities, personal qualities and ambition and so on.
National-ethnic conflict
Such disagreements arise on the basis of protecting the interests of races and nations. Here appears the concept of racism, which, unfortunately, will never be eradicated. There are and will be people in the world who despise other nations because of the difference in religions, skin colors, traditions and customs. This is very wrong, but nothing can be done about it. Fortunately, most people are absolutely peaceful and treat everyone equally.
It is also worth noting that these conflicts are conditionally divided into two subspecies - horizontal and vertical. Horizontal ones arise between ethnic groups, and vertical ones are disagreements between the state and a group, for example, Chechen.
Interstate conflicts

A separate group is to highlight the conflicts between states. The reasons for them can be all of the above conflicts, and other factors that together lead to a conflict of interests of two or more countries.
It's a shame, but such disputes, which often arise between the dominant branches of states, lead to the responsibility of all citizens. The consequences of such disagreements are wars, crises and defaults, limited cooperation between countries, and much more.
In this situation, the regulation of all such disagreements is handled by the UN, which is international and has the authority to do so. This organization is called upon not only to resolve conflict situations, but also to prevent them.
Now let's move on to the conflict resolution process. Based on the information provided above, we have gained knowledge of their possible types, and now it will be easier to work on one particular one. After all, the ability to distinguish between types and types of conflicts will greatly help us in this matter.
Basically, the classification of types of disagreement resolution is based on the behavioral strategies that a person uses for this purpose. You can follow different paths, but, accordingly, the result will be different.

Types of behavior in conflict
Behavior can also be different in the process of maturing, staying and resolving conflicts.
In a dispute, it is worth highlighting several behavioral strategies that entail different consequences.

What needs to be done to resolve the conflict
We will now present an indicative step-by-step outline for resolving interpersonal disagreements. It is important to remember that such situations are not resolved by shouting or assault. It is necessary to treat the person with understanding, because he may not even know that the conflict was brewing, and did everything not from evil.

You can describe specific actions through a banal situation: talking too loudly on the phone of your colleague in the office.
- Determine that the problem still exists for you, and it can provoke disputes (noise distracts from work).
- Consider what you will say. Remember that you need to speak absolutely calmly and measuredly, showing frustration rather than anger or hatred towards another person. The irritated tone has never led to a peaceful resolution of conflicts without consequences.
- Let the other person know that there is a problem that needs immediate resolution. Base on the three sides of the expression: behavior (when the phone rings and the conversation starts...), consequences (...you can't get yourself together and work efficiently...) and feelings (...which takes more effort and energy and ruins the mood).
- Do not let the person change the subject of the conversation, as he may begin to evade and not recognize the existence of a conflict, explaining in our situation that "everyone does it."
- Next, it is worth offering a way out of the situation, pointing out that this is unpleasant for any person. Say, for example, that a person can leave the room on personal matters. Take this as a rule in your team, agree together.
So, according to this situation, we can conclude that any conflict can be resolved through negotiations and reaching a compromise, common denominator, which brings the dispute to "no". In this way, any type of conflict can be resolved.
The article is devoted to the analysis of the phenomenon of "psychology of conflict". The characteristic is given psychological characteristics conflict, its functions, causes, types, structural components, methods of prevention, resolution and overcoming.
The concept of "conflict" acts as one of the varieties of human relationships. If it proceeds constructively, then it appears to us as the development of a connection between individuals from confrontation to communication: at first people do not find common language, but over time, in the course of searching for common ground, they are looking for a unified position and ways to overcome the conflict situation.
The conflict, from a psychological point of view, is designed to:
- show and display the contradictions that arise among people in the course of their communication or interaction in general;
- identify tension in relationships when incompatible positions, motives, goals and interests of people are affected.
As a social phenomenon, conflict has specific functions - a kind of indicators that indicate how conflict phenomena affect society, a group or an individual, which social, group or individual norms and approaches are affected, what are the consequences of such violations.
When considering the functions of conflict, the most extensive of them are the following types:
- positive(constructive, functional).
- Negative(destructive, dysfunctional).
The mentioned types of functions are also very broad in their content. Among the positive features, the most famous are:
- group integration(collective) - people tend to unite among themselves in the middle of the group against an external threat;
- balance of power and social control- the factor of redistribution of spheres of influence comes to the fore, when, under the influence of a conflict situation, changed, more adequate social ties and phenomena arise;
- informing about the situation- when participating in a conflict, there is a more objective orientation regarding social environment surrounding a person or group;
- structuring relationships between people- in the course of the conflict, it is possible to determine the ways and possibilities for establishing cooperation, to adapt to the new conditions of interaction.
Negative features include:
- destruction of a favorable psychological climate in a group (collective);
- reduction of interaction and cooperation between people - participants in the conflict;
- increased costs - both material and emotional;
- intensification of confrontation - the confrontation of the participants in the conflict makes them look for ways to their own victory, which increases the tension of the situation;
- inadequacy of the perception of the situation - the conflicting parties tend to attribute to each other the worst intentions, aspirations and goals.
Causes
Conflicts arise due to all sorts of reasons, which are divided in this way.
1. General, "global" reasons:
- socio-political and economic(contradictions of people regarding political and economic worldviews);
- socio-demographic(human contradictions related to gender, age, ethnic group);
- socio-psychological(associated with differences in various social groups ah about the motives of actions, moods, leadership and other things);
- individual psychological(display the causes of contradictions due to differences in personal characteristics and manifestations).
2. Specific reasons look like this:
- resources(contradictions about their shortage, distribution, absence);
- interdependence(in any situations - personal, business, emotional, when an individual is dissatisfied with this and tries to change);
- difference between goals and objectives(they do not coincide with conflicting personalities or even prevent them from realizing their own);
- values and perceptions(at various people may be antagonistic)
- communications(contradictions due to inadequacy of communication or non-constructive formation of communication skills, here - unreliability of information, omissions, distortions).
Types and structure
The specific differences of conflicts are very diverse and wide, their classification can be presented as follows.
1. Depending on the area in which conflicts arise:
- family(arise in the sphere of family relations, between parents, children, various relatives);
- production(exist in teams and groups about work processes and discipline, between managers, subordinates, employees in general);
- social(manifested in the tense interaction of various social groups and entities: government, people, public organizations).
2. According to the sources of occurrence, conflicts manifest themselves as:
- business- arise in the structure of various institutions and organizations due to shortcomings in the structure, distribution of responsibilities;
- emotional- appear due to the individual psychological characteristics of each person, when people are incompatible in terms of temperament or character types, manifestations of the emotional-volitional sphere.
3. From exactly how a person is on subjective level perceives conflicts, they are:
- erroneous- there are no real reasons for confrontation, but a person subjectively perceives the situation as a conflict;
- potential- when the prerequisites for the conflict have already appeared, but the conflict itself has not yet arisen;
- true(real) - a "classic" conflict with an open confrontation between its participants.
4. Based on the subjects that take part in the collision, conflicts are divided into:
- intrapersonal(conflicts with oneself);
- interpersonal(between two individuals);
- intragroup(between spheres of influence in a single group);
- intergroup(between different groups with conflicting positions and goals).
 The structural elements of the conflict process look like this:
The structural elements of the conflict process look like this:
- sides(subjects, participants) of the conflict - all those who are directly or indirectly involved in conflict interaction;
- flow conditions conflict - sharply and painfully, quietly and sluggishly;
- images conflict situation (the subject of the conflict) - the participants' ideas about what exactly caused the confrontation;
- results conflict situation - how the conflict ended, what are its consequences for each of the participants.
The problem of industrial and personal harm
The industrial harm from conflicts is obvious if we analyze a number of factors:
- Disciplinary(decrease due to the conflict situation of production discipline and performance).
- interpersonal(violation of positive connections, subordination between colleagues and in the structure of relations between the boss and subordinate).
- Information and communication(violations in the field of work with information - distrust of sources, silence of important information, its unreliability and bias, etc.).
- Social(may be distorted by the prevailing in the team social structure, interactions between people in groups of different interests, there are opposing groups with opposite goals, with their adherents and opponents).
Personal harm is manifested through emotional negativism; conflicting people have:
- lowering mood;
- focusing on emotions with a "-" sign;
- depression;
- aggressiveness and excessive irritability;
- inability to establish adequate communication;
- excessive focus on the problem of conflict.
Methods for resolution and prevention
Ways to overcome conflicts become clear through consideration of various strategies and procedures for working in the event of conflict interaction.
Each stage (pre-conflict, initial, active confrontation, final) of the conflict will have its own specific ways of resolving (depending on the depth of contradictions).
At the pre-conflict stage, it is important to carefully monitor the structure of social (individual-psychological) ties and the prerequisites for their violation. If people are incompatible, their joint activities should not be organized, or clear and understandable rules of interaction should be outlined for them.
The following are subject to analysis in the process of conflict prevention:
- personal characteristics of each member of the team;
- quality of personal interaction;
- relations in the group, their specificity, leadership of individual participants (formal and informal);
- group culture (dominant points of view, traditions and attitudes in the team, inconsistent positions of individuals).
In the later stages of conflict interaction, you can use:
- Behavioral Approach(involves the formation of consistent rational and constructive actions - acts of behavior that will step by step bring the conflict participants closer to its resolution).
- Analytical approach(based on a detailed analysis of the structural components of the conflict, the stages of the course of the conflict, environment and developing on this foundation an analytical model for getting out of the situation).
- Situational approach(provides for the solution and overcoming of conflicts depending on the specific situation that develops during interpersonal interaction, taking into account its specific characteristics and influencing exactly those points that allow you to reduce tension and reduce contradictions).
Video: Ways to behave in conflict
Everyone knows what conflict is. This concept has many synonyms: quarrel, dispute, scandal, etc. It is quite natural for people to conflict, which is why conflicts come in various forms. Depending on the number of participants and the issues that are discussed during a quarrel, they are social, intrapersonal, interpersonal, political, etc.
Many people have experienced intrapersonal and interpersonal conflicts. Only at the level of groups or the whole state can one enter into a social or political conflict.
A feature of conflicts is that they can be observed from the outside, you can enter them when they are already flaring up, and also go out when they do not stop. Conflict can arise between two people and between entire states that number millions of people.
At all times people have had conflicts. What kind of "beast" is this? This will be discussed in the article, which will also consider the topic of how to resolve conflicts, which is also necessary for every person to be able to do.
What is conflict?
Most main question: What is conflict? All people know what it is, because they could be in it more than once. Conflict has many concepts:
- Conflict is a method of resolving differences in goals, worldview, ideas that arise during interaction with society.
- A conflict is an emotional dispute where the participants express negative feelings towards each other, going beyond the norm.
- A conflict is a struggle between its participants.
In rare cases, a quarrel begins on impartial grounds. Usually the conflict is emotional state when a person begins to experience negative emotions, which push him to raise his voice and express rude words to other people. Thus, conflict is mental condition negative and subjective.
What is a dispute, quarrel, conflict between people? This is a war of opinions. A man and a woman do not quarrel, but each one tries to prove his case. Friends do not conflict, but each try to defend their opinion. People do not argue, but provide evidence and arguments for their points of view.
Everyone has their own opinion on a particular issue. This is fine. There is some exact knowledge that does not require its proof. So, for example, everyone agrees to unconditionally perceive knowledge in mathematics, physics or anatomy. No one argues or refutes this knowledge, unless there is good evidence. And there is an opinion, a view, which is often confirmed by what a person has gone through. This is due to the fact that events can occur for various reasons.
Each of the participants in the dispute is right. Surprisingly, two opposite opinions are correct, although the disputants themselves do not think so. When you are in conflict with someone, you consider your behavior and look to be the only correct ones. So does the opponent. The most amazing thing is that you are both right.
The same situation can be formed for different reasons. Everyone has their own experience of experiencing certain situations. People are different, as well as their attitude to what is happening. That is why everyone has a personal opinion on the same event. And all these opinions will be correct.
Conflict is a war of opinions. It's just that each of the opponents wants to prove his case. And the important thing to remember in the moment of an argument with another person is that you and your opponent are right, despite the fact that your opinions do not coincide. You're right! Your opponent is right! If you remember this, then the war will stop. No, you won't change your point of view. You will simply have a chance not to fight for whose opinion is more correct, but to start a conversation in order to find a solution to the problem that takes into account the interests of both parties.
As long as there is a war going on, the problem will not be solved. Once you admit that both are right, then there is a chance to start a conversation that is aimed at finding a solution to your common problem.
Conflict functions
A person usually sees only the negative side of conflicts. However, personality is naturally given a tendency to conflict. This is dictated by the functions to which conflict situations lead. Negative side becomes obvious only when people do not reach the goal, because of which, in principle, the dispute flared up.
The functions of the conflict can be called:
- The pursuit of excellence. Only through the struggle of the old and the new, where the new wins, can something better be achieved.
- Striving for survival. There are a limited number of material resources. A person who is struggling is trying to get as many resources as possible for himself in order to survive.
- Striving for progress. Only through a conflict of interest, where some want to keep and others change, is progress possible when something new is created.
- The pursuit of truth and stabilization. A person is not yet completely moral and highly spiritual. That is why there is so much debate about what is moral and immoral. Such discussions are capable of finding truth.
Not every conflict brings positive results. There are numerous cases where the outcome was negative. The positive result of any conflict is finding a solution to the problem, which is implemented and helps the participants become better, stronger, more perfect. The negative result of the conflict is observed when the participants cannot find a common solution, their actions lead to destruction, decline, degradation.
An unsuccessful conflict can be called any dispute when people tried to agree on something, but did not agree. There are many reasons why people just quarrel, and as a result of this action they get emptiness.
Is conflict beneficial in and of itself? For the conflict to be useful, you need to set a goal when entering into a dispute - what do you want to achieve as a result of the conflict? After that, act only within the framework of this goal. Since people rarely set themselves a goal they want to reach, they simply express their emotions, indignation, wasting their time and energy.
Often people just want to show their dissatisfaction. But what after that? What do you want from the other person to receive or hear? It’s not enough just to dissatisfy and criticize, you also need to argue your dissatisfaction and say what you want to get from a person.
People quite often do not agree, but force them to accept their point of view. It seems to each of the opponents that his opinion is the only correct one. But everyone involved in the process thinks so. And while people are trying to force opponents to go over to their side, it will be like a tug of war, where everyone will remain a winner and a loser. People will quarrel, and it will not end with anything more.
The cause of unsuccessful conflict is sometimes the habit of conflict. A person is used to communicating with others in a raised voice, which they perceive as an attack. A person speaks loudly with other people, they perceive it as an attack against them, which causes an unreasonable conflict. And all because a person simply does not understand that you can express your thoughts and desires in a calm tone.
People often conflict with each other. But what is the use of conflict? It does not exist, because sometimes people simply conflict, discussing a certain problem, without any clear goal of solving it.
Main types of conflicts
The classification of conflicts can be very diverse. This includes the number of participants, and the topic of the conversation, and the consequences that occur, and ways of conducting the conflict, etc. The main types of conflicts are intrapersonal, interpersonal and group (by the number of conflicting):
- Intrapersonal conflicts are the struggle of several opinions, desires, ideas within a person. Here comes the question of choice. A person must sometimes choose between equally attractive or unattractive positions, which he cannot do. This conflict can still arise when a person cannot find a solution, how to please himself and other people (their requirements). Another factor is getting used to one role, when a person cannot switch to another.
- Interpersonal conflicts are mutually directed disputes and reproaches of people against each other, where everyone wants to defend their needs and desires. They have their own classification:
— By spheres: household, family, property, business.
- By consequences and actions: constructive (when opponents achieve goals, find common decision) and destructive (the desire of opponents to defeat each other, to take a leading position).
- According to the criteria of reality: genuine, false, hidden, random.
- Group conflicts are confrontations between separate communities. Each of them considers itself exclusively with positive side, and opponents - with negative.
Genuine conflict is a quarrel that really exists and the participants adequately perceive it. False conflict occurs when there is no reason to argue. There is no contradiction.
Displaced conflict occurs when people quarrel for a reason other than the actual conflict between them. So, they may quarrel over what furniture to buy, although in fact they do not like the lack of a lot of money.
A misattributed conflict develops when a person argues over what the opponent did, although he himself asked him to do it, but forgot.
Types of intrapersonal conflicts

Sometimes a person does not need a partner for conflict to arise. Often people themselves begin to conflict within themselves. This is the surest way to become unhappy - not being able to choose, not knowing what to do, doubting and hesitating. Types of intrapersonal conflicts are as follows:
- Role - this is a conflict of roles that a person can and should play. Sometimes a person is required to behave that he cannot or does not want to play, but is forced to. Sometimes a person has more opportunities, but is forced to limit himself, because it does not fit into social norms behavior. Sometimes there is difficulty with switching roles, for example, from work to family.
- Motivational - often we are talking about the opposition of instinctive desires and moral needs. Tension is reduced when a person finds a solution to satisfy both parties.
- Cognitive is a collision of two knowledge, ideas, ideas. A person is often faced with the inconsistency of the desired and the actual, the real. When a person does not get what he wants, based on the ideas that he is guided by, then it becomes necessary to study other knowledge that contradicts the existing ones. It is sometimes difficult for a person to accept what contradicts his views.
The surest way to become an unhappy person is to have internal conflicts, that is, to conflict with oneself in views, opinions, desires. Often such a person who is not able to make decisions is influenced by public opinion, which is ready to tell him what to do in this or that situation. However, this will not solve his problem, but will only allow him to temporarily reduce the level of tension within himself.
Types of interpersonal conflicts
The most common conflict is interpersonal. A person interacts with individual members of society, where one can inevitably encounter conflicting beliefs, desires, needs, interests. This type of conflict flares up very often, which makes people avoid it even more. However, this is not possible. Between people, as between integral individual systems, disputes will always arise, since everyone has their own opinions, needs, aspirations, etc.
Quarrels and scandals in the family are normal in society. Of course, spouses may be unhappy with the current state of affairs. However, if this dissatisfaction comes to shouting and even physical assault, this only indicates that the partners do not have constructive communication. They are focused on achieving only their desires, which they defend, and not on finding a compromise that will take into account the interests of both parties.
No one is obviously worried about the fact that there are quarrels and scandals in the family. However, all these conflict situations do not go unnoticed. They leave a wound in the soul of each of the partners, give rise to doubts, insecurity in feelings and union. No need to saw, itch, grumble. When this happens, the spouse is not sawing his opponent, but his own relationship. It is necessary to learn to be more calm and sometimes even positive about what events happen.
One of the reasons that breeds discontent is ingratitude. Spouses focus on what they do not like, rather than on the positive sides of each other and what they had. They want to achieve the relationship that is presented to them in their heads. And each of them represents something different. It is the clash of these ideas that leads to quarrels. They are not grateful for the union that they have built in reality, because they want to live in the relationship that they imagine.
Keep in mind that if you consider your spouse to be bad, then soon you may not have any spouse at all. If you love your wife (husband) and strive to create a strong family, then only you owe, and your wife (husband) owes nothing. Learn to demand from yourself, not from your partner. Quarrels and scandals are usually based on this: you want some changes and actions on the part of your loved one, but you yourself are not going to do or change anything. Learn not to demand anything from your partner, let him decide what he should do for your relationship. Demand only from yourself. Otherwise, you will not cut your spouse (wife), but your relationship with him.
Types of interpersonal conflicts:
- Value, interests, normative - what is affected in a quarrel?
- Acute, lingering, sluggish - how quickly does a quarrel develop? Acute events take place here and now in direct confrontation. Lingering ones last several days, months, years and affect significant values and topics. Sluggish are low-intensity, occur periodically.
Types of conflicts in the organization
Conflicts that arise in an organization can be perceived both positively and negatively. Much depends on the level at which they occur and how they are resolved. If conflicts arise between colleagues who are trying to harm each other, then the clash can lead to a decrease in the efficiency and productivity of people. If the conflict occurs in the process of solving a labor issue, then it can become productive due to the expression of different points of view and the possibility of finding a solution. Types of conflicts in the organization:
- Horizontal, vertical and mixed. Horizontal conflicts arise between colleagues of equal status. Vertical conflicts, for example, occur between subordinates and superiors.
- Business and personal. Business concerns only work issues. Personal affect people's personalities and their lives.
- Symmetrical and asymmetrical. In symmetrical conflicts, the parties equally lose and gain. In asymmetric conflicts, one of the parties loses, loses more than the other.
- Hidden and open. Hidden conflicts arise between two people who may not express their dislike for a long time. Open conflicts are often manifested and even managed by management.
- Destructive and constructive. Destructive conflicts develop when the result, development, progress of work is not achieved. Constructive conflicts lead to progress, development, advancement towards the goal.
- Intrapersonal, interpersonal, between an employee and a group, intergroup.
- Violent and non-violent.
- Internal and external.
- Intentional and spontaneous.
- Long term and short term.
- Recurring and one-time
- Subjective and objective, false.
The essence of social conflicts
Why do people conflict? On the this question people have already found the answer, but they continue to clash, because the problem is often not “why?”, but “what contributes?”. The essence of social conflicts lies in the fact that each person has his own established system of views, opinions, ideas, interests, needs, etc. .
A quarrel is not a clash of two opinions, but the desire of opponents to win in their views.
Quarrels, scandals, disputes, wars, conflicts - we are talking about a confrontation between two or more parties, where each tries to defend its opinion, prove its case, gain power, force rivals to submit, etc. Peace-loving readers may have a question: is it possible Is it possible to live at all without such clashes? Psychologists note that everything is possible, but not in the situation that is developing in society.
First, you should decide on the mechanism by which any conflict situations occur. There is a topic, a question, people can get some useful resource. If people have different goals, opinions and plans, then they begin to conflict with the intention to prove their superiority and get a useful resource for themselves or make others live at their behest. A conflict is a confrontation of different opinions, where everyone is trying to achieve something beneficial for themselves.
Quarrels can not exist among people only in one case: when everyone starts to think the same way, when collective thinking reigns.
The modern world is the era of individualization. Selfishness, “life for your own good”, freedom are actively promoted. Each person is individual, and he must cultivate it in himself. It is an individual person who can think differently than everyone else. Here there is no collectivism, compromises, humility.
Quarrels occur because each person thinks of himself. In a scandal, each side seeks to prove that it is the best, correct, and smartest. In the era of individuality, no relationship can do without quarrels and scandals.
Things are quite different when people think the same way. They have nothing to defend. There is no "mine", there is only "ours". Here everyone is equal, the same. In such a society, there simply cannot be confrontation. Collectivism leads to the creation of one large organism, which is stronger than any individual. However, here a person must give up individuality, selfishness, his own Self and desires.
Let's take a family as an example. If partners act together, make concessions, think alike, strive for the same goal, then quarrels rarely occur in their relationship. They live for a common family. If the partners take care of themselves, insist on being right, strive for different goals, then conflicts become an obligatory attribute. Each partner will try to "bend under himself", adjust. Here everyone will want to win back power and force the other to live for the sake of personal desires.
The conflict begins when external circumstances indicate the impossibility of realizing a certain human need. To take part in the conflict can:
- Witnesses are those who observe the quarrel.
- Instigators - those who push, inflame even more quarrel.
- Accomplices - those who inflame the quarrel through advice, tools, recommendations.
- Mediators are those who try to resolve, pacify the conflict.
- Participants in a conflict are those who are directly arguing.
Types of political conflicts
Various types of political conflicts have existed at all times. People fought wars, conquered foreign lands, robbed and killed other nations. All this is part of the conflict, which, on the one hand, is aimed at the development and strengthening of one state, on the other hand, at the infringement of the freedom and rights of another country.
Conflicts between countries arise at the level that one state in one way or another begins to infringe on the existence and activities of another. When mutual understanding is not achieved, then political wars begin.
Types of political conflicts:
- Interstate, domestic political, foreign policy.
- The struggle of totalitarian regimes, democratic systems.
- Status-role struggle, confrontation of values and identification, clash of interests.
Sometimes states may argue over different government devices to which they adhere, as well as the goals and directions of their activities.
Conflict Management

Conflicts have always existed and will continue to arise. No two are the same thinking people, groups, states that would not encounter opposing opinions or needs. That is why conflict management becomes important if the participants are willing to get out of the current situations with the least loss for themselves.
The resolution of the conflict is understood as the fact that all parties came to a common conclusion, decision or opinion, after which they calmly left the situation. Often this is either agreeing on some opinion, reaching a compromise, or understanding that it is necessary to disperse and not cooperate further. These methods can be called positive methods of conflict resolution. The negative way to resolve the dispute is the destruction, degradation, destruction of one or all parties to the conflict.
Website psychological help the site insists that people learn to resolve conflict situations, do not delay their elimination and do not develop them. This can be done in the following ways:
- Negotiation.
- Avoiding confrontation.
- Finding a compromise.
- Smoothing questions.
- Solution.
Answer the question: do you want to quarrel or solve a problem? This gives an understanding that a person begins to behave differently when he wants to quarrel or when he wants to solve a problem.
When you seek to quarrel, you are trying to find flaws in your interlocutor in order to criticize them and make them guilty. You start doing only those things that will offend your interlocutor. You scream with pleasure because your emotions are raging.
When you want to solve a problem, you deliberately act calm. You don't scream, even if you're being shouted at. You are ready to listen to the interlocutor, to be silent in order to think over his words. You are nervous, but you understand that emotions will not help you now. You should try to think as clearly as possible, realizing what you want, and hearing the opinion of your opponent.
Watch yourself or your partner - and notice what the person is striving for. The one who quarrels only "muddles the waters": there is no conversation, there is only a verbal contest - who will win? The one who tries to solve the problem behaves calmly in a stressful situation, because he wants to think about the issue and solve it. In which case will the dispute be resolved faster? Only when both you and your opponent will strive to solve the problem, and not to verbal victory, any issues will be resolved quickly and without serious losses.
How to quickly end a quarrel? There are many options for how to do this. But often the question is not how to do it, but whether at least one of the disputing parties wants to end a useless conversation.
The fact that a quarrel is a useless dialogue has to be said. People often forget that when they are under the influence of negative emotions and indignation, they do not seek to solve the problem, but want to prove their opinion, deed, point of view is right. It seems to them that they did everything right, so they enter into a loud conversation, trying to prove it. Their opponents prove that they were right in their actions and decisions, and everyone else was wrong. Thus, a quarrel is a conversation where everyone considers himself right, tries to achieve only this goal and does not seek to hear the other person.
People don't always want to end a fight. Until they achieve their goal, that is, the recognition of their innocence, they will not retreat. Therefore, you first need to want to get away from the quarrel, and then take the appropriate steps.
How to quickly end a quarrel?
- You can go to another place where your opponent will not be.
- You can say: "Do as you like" or "Do as you like." Thus, you do not agree with the correctness of your interlocutor, but do not reject the fact that he is right.
Other methods are less effective, because the opponent may not want to end the argument with you. Your task is to be at a remote distance from your interlocutor, so that neither you see him, nor he sees you.
Outcome
Conflict is inherent in all people. Everyone knows how to quarrel with others. However, managing and resolving conflicts is an art that not everyone has been taught. If a person knows how to calm conflicts, then he knows how to manage people, which requires a lot of knowledge and effort. The result is the ability to organize one's own life, to make it happier and more orderly.
People have already ruined a lot of relationships because they did not want to stop the quarrel. Often people died because of conflicts that flared up between groups and even entire states. The forecast becomes unpredictable when people start to conflict. However, the result depends entirely on what decisions they will make and actions they will take.
You can lead the dialogue in a constructive direction, if there is a desire to solve the problem, and not to prove your case. You can lead the argument in a destructive direction, when there is no desire to cooperate and find a compromise. Often people refuse to take responsibility for the results achieved as a result of the conflict. Although in fact they achieved everything on their own.
The concept of conflict.
The word conflict comes from the Latin verb, which, translated into Russian, means to resist, to oppose. Like many concepts in management theory, conflict has many definitions. In psychology, conflict is understood as "a collision of oppositely directed goals, interests, positions, opinions or views of opponents or subjects of interaction." In this regard, it is possible to give the definition of conflict as one of the forms of human interaction, which is based on various kinds of real or illusory, objective and subjective, to varying degrees, perceived contradictions between people, with attempts to resolve them against the background of the manifestation of emotions.
Types of conflicts.
Conflicts are very diverse, and they can be classified according to various criteria. At present, there are:
Intrapersonal;
interpersonal;
Between the individual and the group (intra-group);
Between two or more groups of people (intergroup). Intra-personal conflict. It can appear when production requirements are in conflict with personal needs or values. For example, an employee plans to spend the weekend at home with his family, and the boss asks to get out to work to solve a difficult issue. Intrapersonal conflict may also be related to the degree of job satisfaction.
The structure of the conflict.
Each conflict also has a more or less clearly defined structure. In any conflict, there is an object of a conflict situation, associated either with technological and organizational difficulties, peculiarities of wages, or with the specifics of business and personal relations of the conflicting parties.
The second element of the conflict is the goals, the subjective motives of its participants, due to their views and beliefs, material and spiritual interests.
And, finally, in any conflict it is important to distinguish the immediate cause of the collision from its true causes, often hidden.
It is important for a practitioner to remember that as long as all the listed elements of the conflict structure exist (except for the reason), it cannot be eliminated. Trying to stop conflict situation forceful pressure or persuasion leads to its growth, expansion by attracting new individuals, groups or organizations. Therefore, it is necessary to eliminate at least one of the existing elements of the conflict structure.
conflict functions.
Constructive (positive) functions of the conflict. These include:
the function of discharging tension between antagonists, the “exhaust valve”;
"communicative-informational" and "connecting" functions, during the implementation of which people can check each other and get closer;
function as a stimulator and driving force of social change;
the function of promoting the formation of a socially necessary balance;
guarantees of the development of society by revealing opposing interests, the possibilities of their scientific analysis and determining the necessary changes;
assisting in the reassessment of old values and norms;
assisting in strengthening the loyalty of members of this structural unit.
Destructive (negative) functions of the conflict, i.e. conditions that hinder the achievement of goals. These are such as:
dissatisfaction, poor state of mind, increased staff turnover, reduced labor productivity;
a decrease in the degree of cooperation in the future, a violation of the communication system;
absolute loyalty to one's group and unproductive competition with other groups in the organization;
the idea of the other side as an enemy, of one's own goals as positive, and of the other side's goals as negative;
curtailment of interaction between the conflicting parties;
an increase in hostility between the conflicting parties as communication decreases, an increase in mutual hostility and hatred;
shifting emphasis: giving more importance to winning the conflict than solving the problem;
the possibility of preparing for a new round of conflict; consolidation in the social experience of an individual or a group of violent ways of solving problems.
However, when evaluating the constructiveness and destructiveness of conflict functions, it is necessary to keep in mind the following:
lack of clear criteria for distinguishing between constructive and destructive conflicts. The line between constructive and destructive functions sometimes loses its unambiguity when it comes to assessing the consequences of a particular conflict;
the vast majority of conflicts have both constructive and destructive functions;
the degree of constructiveness and destructiveness of a particular conflict may change at different stages of its development;
it should be taken into account for which of the participants in the conflict it is constructive, and for which it is destructive. It is not the opposing sides themselves that may be interested in the conflict, but other participants (instigators, accomplices, organizers). Therefore, the functions of the conflict from the standpoint of different participants can be assessed differently.