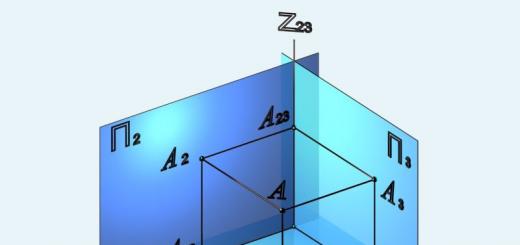
Consider a system of three mutually perpendicular projection planes (Fig. 5): P 1 horizontal projection plane, P 2 frontal projection plane and P 3 profile projection plane.
Rice. 5. Projection planes:
x 12 \u003d P 1 ∩ P 2;
y 13 = P 1 ∩ P 3;
z 23 = P 2 ∩ P 3
The point of intersection of the three planes O 123 is the origin of coordinates. The line of intersection of the horizontal and frontal planes is called the axis of projections x 12 \u003d P 1 ∩ P 2, the line of intersection of the horizontal and profile planes is called the axis of projections y 13 \u003d P 1 ∩ P 3, the line of intersection of the frontal and profile planes is called the axis of projections z 23 \u003d P 2 ∩ П 3 .
Since the projection planes are infinite, three planes will divide the entire space into eight parts - octants. The order of counting octants (see Fig. 5): to the left of the P 3 plane (counterclockwise) from the first to the fourth, to the right - from the fifth to the eighth.
The direction of the x,y,z axes in the first octant is considered positive. The signs of the axes extended beyond the origin are considered negative.
To obtain projections of point A on three planes (Fig. 6) P 1, P 2 and P 3, projecting rays are drawn through point A)