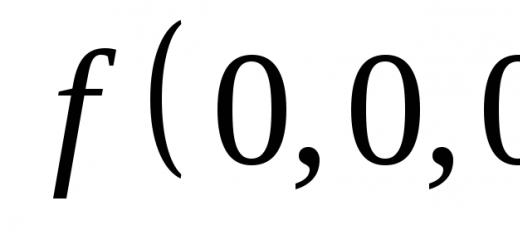Application
to the letter from the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
dated February 25, 2014 N 01-25/1139
I. General provisions
1. These methodological recommendations on the registration of children and the procedure for recruiting educational organizations implementing the basic educational program of preschool education on the territory of the Udmurt Republic were developed in order to implement the provisions of the Federal Law of December 29, 2012 N 273-FZ "On Education in Russian Federation"and order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated August 30, 2013 N 1014 "On approval of the procedure for organizing the implementation educational activities on basic general educational programs- educational programs for preschool education."
Guidelines propose a unified approach to accounting for children declared by their parents (legal representatives) for a place in educational organization implementing preschool education programs, and also determine uniform deadlines for the formation of a register of applications for a place in a preschool educational organization.
In order to obtain objective information on the number of children registered for enrollment in an educational organization, as well as on the number of children in need of a place in an educational organization, the Ministry of Education and Science of the Udmurt Republic is creating a single information resource (hereinafter referred to as EIR), accumulating data on the number of children registered in all municipal districts and urban districts located on the territory of the Udmurt Republic.
When establishing the procedure for staffing an educational organization, the rights of citizens in the field of education established by the legislation of the Russian Federation are ensured. Educational organizations implementing the main educational program of preschool education on the territory of the Udmurt Republic are staffed with children registered to provide a place in the educational organization.
1) registration of children declared by parents (legal representatives) for a place in an educational organization implementing the basic educational program of preschool education (hereinafter referred to as registration, educational organization) - a state (municipal) service for registering children who need a place in an educational organization, on the regional portal of state and municipal services of the Udmurt Republic (hereinafter referred to as RPGU UR), specially created on the Internet, recording the date of registration of the child, the desired date of granting the child a place in an educational organization, the age of the child. The result of registering children is the formation of an “electronic queue” - a list of names of children declared by parents (legal representatives) to receive preschool education and supervision and care in an educational organization and (or) other forms;
2) priority in an educational organization - a list of children registered for a place in an educational organization in the current academic year, but not provided with such a place at the start of the school year (September 1 of the current academic year);
3) priority indicator - the number of children registered for provision of a place in an educational organization;
4) current demand - the number of children applied by parents (legal representatives) for a place in an educational organization in the current academic year;
5) deferred demand - the number of children applied by parents (legal representatives) for a place in an educational organization in subsequent years;
6) the procedure for staffing an educational organization - the sequence of actions of the education management body and the educational organization when forming the contingent of students (pupils) of the educational organization, carried out, among other things, through the EIR.
3. Ministry of Education and Science of the Udmurt Republic in order to ensure the implementation of a regional information resource that ensures the acceptance of applications, registration of children in the queue (electronic queue), registration and enrollment of children in educational organizations implementing the basic educational program of preschool education in the territory of the Udmurt Republic Republic, additionally ensures the development of user instructions for maintaining EIR.
4. When registering children who need a place in an educational organization implementing preschool education programs, in accordance with federal legislation, lists of children of citizens who have benefits (the right to extraordinary or priority enrollment of a child in an educational organization) are formed:
1) the following categories of children have the right to priority enrollment of a child in an educational organization:
children of citizens exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (Law of the Russian Federation of May 15, 1991 N 1244-1 “On the social protection of citizens exposed to radiation as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant”);
children of citizens from special risk units, as well as families who have lost their breadwinner from among these citizens (Resolution of the Supreme Council of the Russian Federation of December 27, 1991 N 2123-1);
children of prosecutors (Federal Law of January 17, 1992 N 2202-1 “On the Prosecutor’s Office of the Russian Federation”);
children of judges (Law of the Russian Federation of June 26, 1992 N 3132-1 “On the status of judges in the Russian Federation”);
children of employees of the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation (Federal Law of December 28, 2010 N 403-FZ “On the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation”).
2) the following categories of children have the right to priority enrollment of a child in an educational organization:
children from large families(Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 5, 1992 N 431 “On measures for social support of families”);
disabled children and children, one of whose parents is disabled (Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of October 2, 1992 N 1157 “On additional measures of state support for disabled people”);
children of military personnel performing military service under a contract, discharged from military service when they reach age limit stay on military service, health status or in connection with organizational and staffing measures (Federal Law of May 27, 1998 N 76-FZ “On the status of military personnel”);
children of police officers (Federal Law
children of a police officer who died as a result of injury or other damage to health received in connection with the performance of official duties (Federal Law of February 7, 2011 No. 3-FZ “On the Police”); children of a police officer who died as a result of an illness acquired during his service in the police (Federal Law of February 7, 2011 No. 3-FZ “On the Police”);
children of a citizen of the Russian Federation who was dismissed from police service due to injury or other damage to health received in connection with the performance of official duties and which excluded the possibility of further service in the police (Federal Law of February 7, 2011 No. 3-FZ “On the Police”) ;
children of a citizen of the Russian Federation who died within one year after dismissal from police service as a result of injury or other damage to health received in connection with the performance of official duties, or as a result of an illness received during the period of service in the police, which excluded the possibility of further service in the police (Federal Law of February 7, 2011 N 3-FZ “On the Police”);
children of employees of internal affairs bodies who are not police officers (Federal Law of February 7, 2011 No. 3-FZ “On the Police”);
children of employees with special ranks and serving in institutions and bodies of the penal system, the federal fire service of the State Fire Service, authorities for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and customs authorities of the Russian Federation (Federal Law
children of an employee who had a special rank and served in institutions and bodies of the penal system, the federal fire service of the State Fire Service, authorities for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and customs authorities of the Russian Federation, who died due to injury or other damage health received in connection with the performance of official duties (Federal Law of December 30, 2012 N 283-FZ “On social guarantees for employees of certain federal bodies executive power and amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation");
children of an employee who had a special rank and served in institutions and bodies of the penal system, the federal fire service of the State Fire Service, authorities for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and customs authorities of the Russian Federation, who died due to a disease acquired during the period of service in institutions and bodies (Federal Law of December 30, 2012 N 283-FZ “On social guarantees for employees of certain federal executive authorities and amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation”);
children of a citizen of the Russian Federation who had a special rank and served in institutions and bodies of the penal system, the federal fire service of the State Fire Service, authorities for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and customs authorities of the Russian Federation, dismissed from service in institutions and authorities due to injury or other damage to health received in connection with the performance of official duties and excluding the possibility of further service in institutions and bodies (Federal Law of December 30, 2012 N 283-FZ "On social guarantees for employees of certain federal executive bodies and amendments in certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation");
children of a citizen of the Russian Federation who had a special rank and served in institutions and bodies of the penal system, the federal fire service of the State Fire Service, authorities for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and customs authorities of the Russian Federation, who died within one year after dismissal from service in institutions and bodies due to injury or other damage to health received in connection with the performance of official duties, or as a result of an illness received during service in institutions and bodies, which excluded the possibility of further service in institutions and bodies (Federal Law of December 30 2012 N 283-FZ "On social guarantees for employees of certain federal executive authorities and amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation").
5. Inside one preferential category(the right to extraordinary or priority enrollment of a child in an educational organization) applications are arranged according to the date of submission of the application.
II. Recommendations for the registration of children declared by parents (legal representatives) for a place in an educational organization implementing the basic educational program of preschool education in the territory of the Udmurt Republic
6. Registration of children is carried out in order to ensure “transparency” of the procedure for admitting children to an educational organization and to avoid violations of the rights of the child during admission to an educational organization, planning to ensure the necessary and sufficient number of places in an educational organization on a specific date to meet the needs of citizens in preschool education, as well as supervision and care of children up to school age.
7. Registration of children is carried out in a uniform manner established by the authorities local government municipal districts and urban districts of the Udmurt Republic in accordance with these methodological recommendations. Accounting is carried out by the education management body(s). Registration can be carried out on electronic and (or) paper media indicating the child’s last and first name, his age (date of birth), date of registration and the desired date of provision of a place in the educational organization. The form of the accounting document is approved by the relevant local government bodies of municipal districts and urban districts of the Udmurt Republic.
8. Child registration includes:
compiling a name list (register) of children in need of a place in an educational organization, in accordance with the date of registration and the existence of the right to provide a place in an educational organization in a priority or extraordinary manner (if any). Depending on the date from which the child is planned to attend an educational organization, the register is differentiated into lists of annual registration of children in need of a place in an educational organization in the current academic year (from September 1 of the current calendar year) (current demand) and in subsequent years (deferred demand);
monthly updating of the register taking into account the provision of places for children in an educational organization;
formation of a “waiting list” of children who need a place in an educational organization in the current academic year, but who are not provided with such a place at the start of the school year (September 1 of the current academic year).
9. The registration of children is organized through the EIR, to which all municipal districts and urban districts of the Udmurt Republic are connected. Registration is carried out by filling out an interactive application form for the RPGU UR by parents (legal representatives), or by specialists of the education management body based on a personal appeal from parents (legal representatives), or upon their written application to the education management body. A written application can be sent by post or to the email address of the education authority.
10. The application for registration of children must indicate the date of birth of the child, the date from which the child plans to begin attending an educational organization, the address of the child’s actual residence, and the desired educational organization(s). When registering children in person, parents (legal representatives) present a passport or other document certifying the identity of the parents (legal representatives), the child’s birth certificate, documents certifying the right to be provided with a place in an educational organization on an extraordinary or priority basis (if any available).
When filling out the interactive application form, the EIR generates a list of institutions from which parents (legal representatives) can choose no more than seven educational organizations: the first educational organization chosen by parents (legal representatives) is a priority, the others are additional.
11. RPGU UR provides the possibility of separate registration of children with disabilities health to provide a place in an educational organization in a group of compensatory, combined or health-improving orientations for the timely correction of deficiencies in physical and (or) mental development.
After registering an application at the RPGU UR, a child with disabilities is sent for examination to the Republican Medical-Psychological-Pedagogical Commission (hereinafter referred to as PMPC) at the State Treasury educational institution for children in need of psychological, pedagogical and medical and social assistance "Republican Center for Diagnostics and Consulting", which decides on the need to provide the child with a place in an educational organization in a group of compensatory, combined or health-improving areas.
After providing all necessary documents to the educational authorities and based on the decision of the PMPC, the child is included in the list of children with disabilities who must be provided with a place in an educational organization in a group of compensatory, combined or health-improving areas.
12. The education management body issues a notification to the parent (legal representative) who has submitted documents on registration of the child (children) in person; when submitting documents through the EIR, an electronic version of the notification is sent to e-mail or in Personal Area RPGU UR.
The notification contains information:
about the registration number of the application for registration of children;
about the contact numbers or website of the education authority, where (on which) parents (legal representatives) can find out about the progress of the queue;
about variable forms of preschool education that can be provided to a child temporarily starting from the desired start date of attending an educational organization for a set time (but not longer than a calendar year from the desired date) if it is impossible to provide a place in an educational organization (short-term groups, non-state educational organizations, preschool education in the form of psychological and pedagogical support for keeping a child in the family).
13. The education management body, through the EIR, compiles lists of children registered for provision of a place in an educational organization in the current academic year and in subsequent years, in accordance with the date of registration and taking into account the right to provide a place in an educational organization in an extraordinary or priority manner ok.
14. The list of children for provision of a place in an educational organization from September 1 of the current calendar year is formed on a certain date (no later than the start date of recruitment of educational organizations) established by the founder (for example, on June 1 of the calendar year, but no later than August 1, for provision place for the child from September 1 of the calendar year). After the established date, only children who have the right of priority or priority admission to the educational organization can be additionally included in the list of children for provision of a place in an educational organization from September 1 of the current calendar year.
Children whose parents filled out an application for registration after the established date are included in the list of children who must be provided with a place in an educational organization from September 1 of the next calendar year.
After the established date, changes may also be made to the list of children regarding the postponement of the date of admission to the educational organization for subsequent periods and changes in the child’s data.
15. Parents (legal representatives) have the right, before the date established by the education management body, to make the following changes to the application while maintaining the date of registration of the child:
change the previously selected year of admission of the child to the educational organization;
change previously selected educational organizations;
in case of moving from one city district or municipal district of the Udmurt Republic to another, change the previously selected educational organizations at the place of move;
if you wish to change the educational organization that the child is already attending to another one located on the territory of a city district or municipal district of the Udmurt Republic if there are free places in it;
change information about the benefit;
change data about the child (change of last name, first name, patronymic, address).
Parents (legal representatives) can make changes to the application by personally contacting the educational authority or educational organization.
16. Recruitment into educational organizations is carried out annually within a specified period of time, distributing among educational organizations children registered for a place in an educational organization and included in the list of children who need a place in an educational organization from September 1 current year.
17. The rest of the time, the educational organization is recruited for free (vacated, newly created) places.
18. If, during the recruitment process, places in an educational organization are not provided to all children registered for a place from September 1 of the current year, these children become “on the waiting list.” They are provided with places in an educational organization for free (vacant, newly created) places during the academic year or are taken into account in the list of children who will be provided with a place in an educational organization from September 1 of the next calendar year.
19. The education management body systematically (at least once a month) during the calendar year summarizes and analyzes through the EIR information on the availability of free places in the educational organization (vacant places and newly created places), providing free places to children registered for provision places in the current academic year.
20. If there are no free places in the selected educational organizations, parents (legal representatives) are offered free places in other educational organizations in accessible proximity to the child’s place of residence. Information is sent to parents (legal representatives) in the personal account of the RPGU UR or by email. Parents (legal representatives) are invited to choose an educational organization from those offered within 14 calendar days.
21. If parents (legal representatives) refuse or in the absence of their consent/refusal from the proposed (proposed) educational organizations, the desired date of admission to the next academic year maintaining the date of registration.
22. To make changes to the desired date of admission of the child to the educational organization, the parent (legal representative) contacts the education management body.
23. If educational authorities do not provide a place in an educational organization to a child from the list registered from September 1 of the current year, education authorities, before providing such a child with a place in an educational organization, provide the opportunity to receive preschool education in one of the variable forms, including : in preschool groups created in educational organizations of other types and types; in the form of family education through the provision of methodological, psychological, pedagogical, diagnostic and advisory assistance in educational organizations; in a non-state educational institution; in family preschool groups; in short-stay groups; in other forms and organizations.
In this case, the child is included in the list of children in need of a place in an educational organization and is not deregistered in order to be provided with a place. He must be provided with a free (vacated or newly created place) in the current academic year or a place in an educational organization from September 1 of the next year.
24. If, during the recruitment process, places are provided to all children from the name list of children in need of a place in an educational organization in the current academic year, free places can be provided to children included in the name list of children registered for a place next year.
25. The education management body notifies parents (legal representatives) of children:
about the time of granting a child a place in an educational organization;
about the opportunity to familiarize yourself with the rules of admission to an educational organization, approved by the head of the educational organization, in particular, about the documents that must be submitted to the head of the educational organization for admitting a child to the educational organization, and about the deadlines for the head of the educational organization to accept these documents.
Information is sent to parents (legal representatives) in the personal account of the RPGU UR or by email.
1. Relevance
Currently, the region continues to face a complex of problems in the sphere of life and legal protection of children, causing serious concern to government agencies and society as a whole. Current problems include an increase in the number of families and children in socially dangerous situations, neglect, and drug addiction among children and adolescents. Over the past two years, the number of homeless and neglected children in the region has increased (2008 - 387, 209-417). The problem of children who find themselves outside of education remains unresolved. As of September 1, 2009, 11 students aged from 6.6 to 18 years had not started their studies (7 in 2008).
Article 43 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation provides for the general availability and free of charge of basic general education.
Federal Law - Federal Law “On Amendments and Additions to the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education” and the Federal Law “On Higher and Postgraduate Education” vocational education» part 2 art. 31 of the Law of the Russian Federation -1 “On Education” was supplemented by clause 12, which established the powers of local governments to register children who are subject to education in educational institutions of basic general education.
The order of Rosstat approved the form of the federal state statistical observation No. 1 – ND “Information on the number of children aged 7–18 years who are not studying in educational institutions as of October 1.”
The Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation sent a letter dated January 1, 2001 No. 419/28-5 “On measures to identify and register children aged 6–15 years who are not studying in educational institutions,” containing recommendations aimed at organizing work on conducting registration school-age children subject to education.
Federal Law - Federal Law “On general principles organizations of local self-government in the Russian Federation" included within the competence of local self-government bodies the organization of the provision of public and free primary general, basic general, secondary (complete) general education, with the exception of the powers to financially support the educational process, which are within the competence of the bodies state power subjects of the Russian Federation.
Federal Law of 01.01.2001 No. 194-FZ “On amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation in connection with the establishment of compulsory general education” corresponding amendments to the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education”, which declared compulsory general education, including three levels - primary general, basic general and
secondary (complete) general education, and established that the requirement of compulsory general education in relation to a specific student remains in force until he reaches the age of 18 years.
Identification of students who do not attend, as well as those who systematically miss classes at an educational institution for unexcused reasons, is referred to the powers of the educational institution by the Federal Law of January 1, 2001 “On the fundamentals of the system for the prevention of neglect and juvenile delinquency.” Education authorities keep records of such minors.
3. Organization of registration of children on the territory municipality
The problem of registering children is of an interdepartmental nature and can be solved only if there is effective interaction not only between bodies that manage education and the educational institutions under their jurisdiction, but also through the active inclusion in this work of all bodies, organizations, and institutions located on the territory of the municipality.
In order to cover the maximum number of different categories of children subject to education in the accounting system, it is advisable to main sources information about children indicate the following:
1) registration data, including registration at the place of residence, carried out by bodies and organizations of housing and communal services (city) (copies of registration cards, house (apartment) books, etc.);
2) data from the census and (or) medical examination of the child population, compiled by local pediatricians of health care institutions about children actually living on the territory of the health care institution, regardless of registration at the place of residence (stay);
3) data from district police officers obtained as a result of door-to-door (door-to-door) visits, including information about children who are not registered, but actually live in the administrative area.
As additional sources Information about children is proposed to be used:
XIstage– clarification by the authorized body of primary information, taking measures to place those categories of children in education or employment, taking measures in relation to which it is within its competence, or sending information about such children, including children about whom information could not be established, to other bodies, organizations, institutions to take the necessary measures in accordance with the law.
XII stage– monitoring the placement of minors in education and/or their employment and their continuation of education in forms other than full-time, regardless of whether measures for placement were taken by the local government independently or transferred under jurisdiction to another body (organization).
XIIIstage– analysis of the reasons and conditions that contribute to students’ non-attendance or abandonment of educational institutions, analysis of the effectiveness of measures taken by educational institutions to involve children in the learning process. Development of a set of measures aimed at eliminating the reasons contributing to students’ non-attendance or abandonment of educational institutions, and at carrying out activities aimed at involving children in the learning process. Creating conditions for children to receive education in various forms in the presence of objective obstacles to their receiving full-time education. Organization of a comprehensive system of individual preventive work in relation to minors who do not attend an educational institution and their parents (legal representatives). Preparation of proposals on the provision of necessary measures aimed at implementing the principle of universal secondary (complete) general education.
4. Organization of registration of children in educational institutions
General education institutions annually organize and carry out current records of students of their institution, regardless of their place of residence. General information about the contingent of students are formalized by general education institutions (Appendix No. 3) and submitted to the authorized body annually:
In case of absence from classes for 1-3 days or individual lessons, the class teacher finds out the reasons for the absence from the student and his parents (legal representatives). If classes were missed without good reason and parents did not know about this, they should be warned about the need to strengthen control over the child’s behavior and school attendance.
2. If the parents have not responded properly to the information about truancy, and the student continues to miss classes (more than 5 days), the educational institution, together with representatives of the KDN and ZP, organizes a home visit to the child. During the visit, the family's living conditions, relationships with parents and the reason for absence from school are clarified. A home visit should be documented with a housing inspection report.
If it is known that parents abuse alcoholic beverages, drugs, or are prone to antisocial behavior, an inspector from the police department of the Department of Internal Affairs should be invited to visit the family.
If it was not possible to establish contact with the parents, and the neighbors do not know anything about the location of the family, you should contact the Police Department of the Department of Internal Affairs.
In-school registration is carried out, socio-psychological and pedagogical assistance is organized, and measures are taken to educate and receive general education.
The school administration sends information to the Department of Internal Affairs of the Department of Internal Affairs about the identification of students who systematically miss classes at the educational institution for unexcused reasons and the measures taken.
3. If parents do not take appropriate measures to return the child to school (absences total more than 7 days), the school administration warns them in writing about the administrative responsibility of parents of minors (legal representatives) for improper performance or failure to fulfill responsibilities for maintenance, education, education, protection of the rights and interests of minors.
4. Information about the student is sent to the local government body that manages the field of education (absences from classes total more than 7 days).
Information about the student (registration card for a minor in a socially dangerous situation) is sent to the social protection department of the municipal administration.
5. Local government bodies exercising management in the field of education inform the in writing KDN and ZP about parents (legal representatives) who do not pay due attention to the upbringing and education of the child.
If parents (legal representatives) do not fulfill their responsibilities for the upbringing, education, maintenance of minors, negatively influence their behavior or abuse them, it is necessary to inform the Department of Internal Affairs in writing.
6. The local government body that manages the field of education sends information about students who systematically miss classes in educational institutions for unexcused reasons for more than 20 days (in total) to the department of additional education and upbringing of the department of education and science of the region every month before the 25th day .
Timely identification of the causes of “truancy”, persistent work with “difficult children”, the ability to find an individual pedagogical approach to them, to prevent their rejection from school, to resolve problems of conflicts with classmates is a great contribution to the prevention of delinquency and juvenile crime and the key to effectiveness legal education of students.
Preventative work is carried out with all students who are registered within the school, aimed at preventing or reducing the likelihood of school absences:
constant, daily monitoring and recording of student attendance;
organization by the school’s psychological and social service of individual and group work with students and their parents to overcome the reasons for absences training sessions;
organization of individual work with students who have difficulties in mastering educational programs, eliminating gaps in students’ knowledge;
timely and immediate notification of institutions and bodies of the prevention system for minors who are maliciously evading education, not attending classes, as well as parents who are interfering with education or evading the upbringing and education of their children (Article 9 of the Federal Law “On the Basics of Preventing Neglect and Juvenile Delinquency” ").
on organizing children's registration,
subject to training
in educational institutions
Approximate structure of a normative legal act
1. General provisions (the legal grounds and purposes of registering children who are subject to basic general education programs of general education are determined; the age of children who are subject to registration in order to ensure the right to general education).
2. Determination of the authorized body coordinating the organization of registration of children in the territory of the municipality.
3. The competence of the local government body in the field of organizing and conducting registration of children subject to training in basic general education programs of general education.
4. Bodies, organizations, institutions involved in the registration of children in the territory of the municipality, their powers, duties and responsibilities (indicating the mandatory responsibility for ensuring information security in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of 01.01.01 “On Information, information technology and on the protection of information" and the Federal Law of 01/01/01 "On Personal Data").
5. Sources of information about children subject to education in basic general education programs; categories of children in respect of whom information is provided; obligation to provide information about children.
6. The main stages of organizing work on registering children.
7. Requirements for the content of information databases.
year of reaching the age for admission to secondary (complete) general education programs;
educational institution implementing general education programs which the child attends (non-state educational institution);
reason for not attending a general education institution (health status / receiving education at home (or in another (except full-time) form) / systematically missing classes / not studying in violation of the law / expelled from an educational institution / could not be determined / other);
the body whose competence includes taking measures in relation to a child who is not studying;
measures taken in relation to a child who is not studying (placement for study in another educational institution/transition to another form of education/employment/other);
the body/organization from which the information about the child was received;
dates of entry/change/exclusion of information about the child.
1. An alphabetical student record book is maintained in each educational institution (legal entity).
2. All students of a general education institution are recorded in the book. Every year the list is updated with new admission students.
Students are included in the list in alphabetical order, regardless of the classes in which they study.
3. Separate pages are allocated for each letter of the alphabet, and each letter has its own serial numbering. Serial number The student's entry in the book is also the number of his personal file.
On personal file For the student, this number is entered in the form of a fraction. For example, No. B/15 means that the student is recorded in the alphabet book with the letter “B” under No. 15.
4. Particular care must be taken to keep records of the departure of students from a general education institution. Dropouts should be considered students who have graduated educational institution who stopped attending a general educational institution due to a change of place of residence, moved to another general educational institution or other educational institution, as well as those expelled from general education institutions. Temporary cessation of studies (for example, due to illness) is not noted in the alphabet book.
The student's departure is formalized by order of the school director indicating the reason for the departure; at the same time, in column 11 of the alphabetical book the number and date of the order are entered, and in column 13 the reason for the departure is precisely indicated. If a student who previously left a general education institution, whose departure was formalized by order, returns to it again, then the data about him is recorded as for a newly admitted student, with the date of the student’s return marked “return.” is recorded in the column “Date of admission to school.”
5. When using all the pages of an alphabet book for a particular letter, the entries are continued in a new book in the order of subsequent numbers for each letter.
6. All entries in the alphabet book must be kept clearly and accurately. Corrections in the book are sealed with the signature of the director and the seal of the educational institution.
7. The book is numbered page by page, laced and sealed with the signature of the director and the seal of the educational institution.
on working with students who miss or
systematically not attending training sessions.
The problem of helping children and adolescents who miss or systematically do not attend school is acute. Particular attention is drawn to the growing number of students with pathologies of the reproductive system who need psychological, pedagogical and medical and social assistance. Factors that negatively affect the development and behavior of children and adolescents are: processes occurring in society, the state of the family and its atmosphere, risk factors coming from the organization within school life, internal factors of the child’s personality.
What is the reason for children and adolescents to lose interest in learning and refuse to attend school?
The main reasons underlying this form of desocialization:
Influence of the social environment:
deprivation of parental rights or removal of children by court;
chronic alcoholism of parents;
mental illness of parents;
stay of parents in places of deprivation of liberty;
parents' reluctance to raise their children;
influence of bad company, environment.
Learning difficulties of various etiologies:
insufficient stimulation mental development a child due to low social and material status and family dysfunction;
deficiencies in the development of the cognitive sphere due to defects in mental development;
Violation of parent-child relationships:
the child does not attend school, thus trying to attract the attention of too busy parents or using such actions as blackmail;
parents’ excessive demands regarding the academic performance of a child with a disability leads to the child beginning to hate school and then stop attending it;
Unfavorable personal relationships with peers and teachers.
In the educational institution, the number of students who miss or systematically do not attend classes remains stable - 1 - 2 students. These students require special control from class teachers, social educators, educational psychologists, and school administration.
These students require special control from class teachers, social educators, educational psychologists, and school administration.
One of the main areas of work of educational authorities and institutions is the identification and registration of children who do not attend or systematically miss school classes for unjustified reasons. The task of each educational institution is to ensure the rights of all citizens to receive secondary (complete) general education, to maintain the number of students until they graduate from the educational institution.
Timely identification of the causes of “truancy”, patient, persistent work with “difficult children”, the ability to find an individual pedagogical approach to them, to prevent their rejection from school, to resolve problems of conflicts with classmates is a great contribution to the prevention of delinquency and juvenile crimes and the key to the effectiveness of legal education of students.
Algorithm of work of specialists
Classroom teacher: Conducts daily monitoring of students' attendance at lessons and provides a report on missed lessons indicating the reasons for absence, involves them in club activities, visits the student at home and provides an examination report, conducts weekly conversations with parents on the student's academic performance, attendance and behavior in any form (by phone , in a face-to-face conversation). Provides characteristics for the student, a summary statement for quarters, and raid reports. If necessary, invites the student and his parents to the prevention council. Involves students in the work of children's and youth organizations, conducts educational activities with difficult students, helps to choose a club or section based on their interests.
Subject teachers : Work individually with students during the lesson and after the lesson. They invite parents to school, speak at parent meetings with information on the student’s progress and behavior in his lesson, and give recommendations on preparing for their subject. In cases of unsatisfactory performance of students, they submit a report on the work carried out with them individual work.
Social teacher: Organizes raids to visit students at home, participates in raids. Conducts individual conversations with students and their parents, takes part in the work of the Prevention Council. Registers children with behavioral or learning disabilities and systematic absences from school for in-school preventive registration. Involving the necessary specialists (medical workers, social workers, lawyers, etc.) to conduct consultations with children and parents and provide them with targeted assistance. Carrying out constant pedagogical observation (control) over the behavior of students in this category, attending classes, mastering educational programs and regulating the situation in favor of the student.
Educational psychologist : Conducting psychological and pedagogical diagnostics of these children to identify the reasons for absences and poor performance. Development of individual routes (plans, programs) for the correction of minors, their further development. Carrying out constant pedagogical observation (control) over the behavior of students in this category, attending classes, mastering educational programs and regulating the situation in favor of the student.
School administration: The school administration organizes the work of the teachers' council on the issue of academic failure and missed lessons. Controls the activities of all units educational process on working with low-achieving, skipping students. Prepares an analytical report on the results of the year on work teaching staff with low-achieving, missing students.
Parents: Parents must come to school at the request of the teacher or class teacher. Parents are required to monitor the student’s performance homework and his visit to the OU. If a child is absent from classes due to illness or other valid reasons, parents help the child catch up on what he missed. educational material through independent study or consultation with a subject teacher. Parents have the right to seek help from the class teacher, psychologist, social teacher, and the administration of the educational institution. In case of parental evasion of their responsibilities, the student and his parents submit materials to the Commission on Minors' Affairs and Protection of Children's Rights for the purpose of taking administrative measures.
Organization of work on registering children in educational institutions:
1. Daily monitoring of attendance at classes is carried out by the class teacher (teacher). In case of missing from 1 to 3 days of classes and/or individual lessons, the total number of which is equal to the specified values, the class teacher finds out the reasons for the absence of the student and his parents (legal representatives). If classes were missed without a good reason and parents did not know about it, they should be warned about the need to strengthen control over the child’s behavior and school attendance.
In addition to the conversation with the class teacher, it is recommended to conduct an individual consultation with an educational psychologist and take all appropriate measures to eliminate the cause of absenteeism. In this case, it is necessary to interact with parents for joint efforts to eliminate the identified causes.
2. If the parents did not properly respond to information about truancy, and the student continues to skip classes, it is necessary to visit such a student at home together with representatives of the KDN and ZP of the district. The visit will help to find out the living conditions of his family, the attitude of his parents (legal representatives) towards him and the reason for his absence from school, as well as determine whether the child (his family) is in a socially dangerous situation and what measures should be taken. A home visit should be documented with a housing inspection report.
If it is known that parents abuse alcoholic beverages, drugs, or are prone to antisocial behavior, you should invite a KDN and ZP employee or an inspector from the Department of Internal Affairs of the Internal Affairs Directorate to visit such a family.
If it was not possible to establish contact with the parents, and the housemates (schoolmates) do not know anything about the location of the family, you should contact the juvenile affairs unit (ODN ATC at the student’s place of residence) to establish the location of the student and his parents .
3. If parents do not take appropriate measures to return the child to school, they should be warned in writing about administrative liability for evading their main responsibilities for raising and obtaining basic general education for their children (Part 2 of Article 63 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, Part. 2 Article 52 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education").
4. In the event that work with the child and parents did not produce the desired results, and the minor continues to not attend classes without good reason, the teacher should be registered with the school in order to carry out individual preventive work with him and implement stricter control.
5. In relation to parents (legal representatives) who do not pay due attention to the upbringing and education of such a student, the KDN and ZP should be informed in detail in writing.
If parents (legal representatives) do not fulfill their responsibilities for the upbringing, education and (or) maintenance of minors and (or) negatively influence their behavior or abuse them, it is necessary to inform the Juvenile Affairs Division of the internal affairs bodies in writing (Clause 1, Article 21 of the Federal Law “On the Basics of Prevention of Neglect and Juvenile Delinquency”).
6. In order to ensure the realization of the right of citizens to receive secondary (complete) general education, increase the responsibility of state educational institutions in Moscow for the full coverage of children and adolescents with general education and maintain the student population, the State educational institution is obliged to maintain documentation on the registration and movement of students (Articles 16, 17 of the Moscow Law “On General Education in Moscow”).
It is very important that the child does not get “lost” between two schools, leaving one and never getting to the other. When transferring a child from one school to another, the receiving school must confirm in writing its consent to his enrollment. In this case, control over the continuation of the minor’s education rests with the administration of the receiving educational institution.
Organization of work to identify and record minors who do not attend or systematically miss classes for unexcused reasons:
1. Technology of educational institutions’ work to identify non-educational children:
Collection and processing of information on the attendance of students at the educational institution;
Preventive work with children “at risk” at all levels: class teacher => psychologist => social teacher => school administration => then out-of-school prevention organizations;
Keeping attendance diaries by class;
Monthly report from class teachers on the attendance and progress of children at risk;
Working with the data bank of children 6–18 years old attending educational institutions: data correction.
2. Directions and forms of preventive work with identified children and children at risk:
Class teacher (daily attendance monitoring, class hours, individual conversations with students and parents)
Social teacher, educational psychologist (individual conversations with students and parents, conducting diagnostic examinations, preventive measures);
Administration (in case the situation worsens);
Prevention Council (development of a pedagogical strategy to eliminate the causes of non-learning);
Individual counseling of parents by various specialists from the educational institution (as necessary);
Identified families are sent to the Center for Support of Children and Adolescents, and are also placed under patronage in the family department.
3. Technology of the educational institution for prevention:
Identification of reasons for non-training;
Organizing joint work with the ODN to provide assistance to the identified family;
Drawing up and implementation of individual training programs;
Organizing free time for “at-risk” students, involving all school children in active school life and extracurricular activities.
The main thing is the organization of comprehensive psychological, social and pedagogical support for students prone to vagrancy and absenteeism without good reason, establishing close interaction with parents or their legal representatives.
Measures to prevent unexcused absences from classes
1. Timely response to school truancy is a necessary condition For successful work on the implementation of legislation on the compulsory receipt of secondary (complete) general education by minors.
Not a single case of missing individual subjects or one day of class without a good reason should be ignored. Students who engage in truancy should be treated with increased attention, not limited to just monitoring progress, it is necessary for everyone possible ways eliminate the conditions and causes of disruptions in their behavior and stop absenteeism.
It must be taken into account that a student who has skipped at least one day of classes, if timely measures are not taken against him, will develop a feeling of impunity, which will push him to repeat absenteeism and ultimately turn him into a malicious truant. He will spend time in game libraries, markets, and train stations. In pursuit of easy money, he may become involved in vagrancy and begging and become prey to crime.
2. Closing gaps in student knowledge is an important component in the system of early prevention of truancy. If for some reason a student has not mastered part of the curriculum, he experiences psychological discomfort because he does not master the program of further material and feels unnecessary in the lesson.
3. Organization of leisure time for students, wide involvement of students in sports, artistic creativity, circle work, are the most important areas educational activities, promote interest in attending school and the formation of law-abiding behavior.
4. When identifying conflicts between parents and children, problems in family education, it is recommended to carry out the work simultaneously with parents and children. A school psychologist and social protection specialist should be involved in such work, and the experience of psychological and pedagogical centers should be used to normalize relationships in conflict families.
5. Work with families in a socially dangerous situation must be carried out in close contact with specialists from the Department of Children's Affairs and Labor Protection, inspectors of the Department of Internal Affairs of the Internal Affairs Directorate, guardianship and trusteeship authorities, psychologists from the Central Children's Social Security Center, the parent community, etc.
However, even the most conscientious work in advanced cases is not always successful. This is why a timely response to unexcused absences and other preventative measures for absenteeism will be much more effective.
Individual preventive work is carried out with all students in the school data bank aimed at preventing or reducing the overall likelihood of missing lessons:
constant, daily monitoring and recording of student attendance;
organization by the school’s psychological and social service of individual and group work with students and their parents to overcome the reasons for absenteeism;
organization of individual work with students who have difficulties in learning curricula; eliminating gaps in students’ knowledge;
timely and immediate notification of institutions and bodies of the prevention system about minors who are maliciously evading education, not attending classes, as well as parents who are interfering with education or evading the upbringing and education of their children (Article 9 of the Federal Law "On the Basics of Prevention of Neglect and Crimes" minors").
Material prepared
teacher-psychologistMKOU
for children in need of psychological and pedagogical
and medical and social assistance -
TsDiK
M.V. Malkova
2012-2013 academic year
on involvement in associationsby interestchildren,
consisting of various types of accounting
The institution pays attention to education great attention working with children enrolled in various types of registration. For many institutions, this is the most pressing and painful problem, which requires a lot of effort and work, but more often it turns out to be unproductive.
Children who are on various types of registration often experience poor academic performance, reluctance to attend interest groups, lack of control and helplessness on the part of their parents, unwanted and sometimes criminogenic company, delinquency and crime.
Parents, busy looking for additional income and overloaded with everyday problems, cannot pay enough attention to their children. Children are left to their own devices. Consequently, child neglect is increasing. Currently, there is a tendency towards a reduction in teenage clubs; many children do not even know about their existence, thus they do not know what to do in free time. Thus, among minors, aggression, contempt for creative work, and disrespect for the law and older people are growing.
Interest associations are among the few that deal with:
Inducing the internal need for self-improvement in children and adolescents,
Increasing the social competence of children, adolescents, youth,
Formation of civic position;
Development of social skills of behavior and attitudes towards independent solution of problem situations,
Formation of a value attitude towards oneself, others, nature, humanity,
Formation of positive self-perception,
Helps you understand yourself as a person,
Formation of moral and legal ideas,
Instilling in children a sense of patriotism and love for the Motherland, and many others.
This is where the important role that interest associations can play for students enrolled in various types of accounting follows. The participation of such children in the work of circles and clubs is a condition for socialization in different areas life activity.
Children and teenagers attend associations when they see a future interesting life, an opportunity to solve your problems.
And the task of teachers is to inform students about the existence of such associations, the content of their activities, the goals and objectives of these associations, as well as motivating students to join them.
Ways to involve children and adolescents in associations can be very diverse. For example:
- Informing.
Design of an information stand where the following will be placed: propaganda leaflets, booklets, posters; work plan of the association; photos; copies of certificates, diplomas, thanks to the children who are part of the association; congratulatory posters, etc.
- Organization of events that motivate “difficult” children for creative activities, personal achievements (for example, the “Kruzhkovets of the Year” competition, creativity festivals, hiking trips, cleanup days for landscaping, drawing competitions, etc.).
- Involving “difficult” children in organizing and participating in various events offered by interest groups on the sixth school day (projects, promotions, holidays, competitions, etc.).
- Involving registered students in solving social problems.
- Involvement in socially beneficial activities.
Thus, the most important stage in the work of a teacher additional education Involving children on various types of registration into interest groups begins with developing their interest in the proposed activities. After which you can talk to your children about joining an association of interests, where they can learn a lot and apply it in the future in their lives.
Added to the site:
1. General Provisions
1.1. This provision has been developed in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, Federal Law dated December 29, 2012 N 273-FZ “On Education in the Russian Federation”, Federal Law dated June 24, 1999 N 120-FZ “On the fundamentals of the system for preventing neglect and juvenile delinquency ", Federal Law of July 24, 1998 N 124-FZ "On Basic Guarantees of the Rights of the Child in the Russian Federation", the Family Code, as well as the Charter of [name of educational organization] and regulates the procedure for internal registration of students of an educational organization who are in a socially dangerous situation and those in need of individual preventive work (hereinafter referred to as accounting).
2. Goals and objectives of recording students and their families
2.1. Educational organization for the purpose of preventing neglect and juvenile delinquency:
Identifies and keeps records of minors who are in a socially dangerous situation, as well as those who do not attend or systematically miss classes for unexcused reasons, takes measures for their upbringing and their receipt of secondary (complete) general education;
Identifies and keeps records of families in a socially dangerous situation and provides them with assistance in training and raising children.
2.2. The main objectives of activities to prevent neglect and juvenile delinquency are:
Prevention of neglect, homelessness, delinquency and antisocial actions of minors, identification and elimination of the causes and conditions conducive to this;
Ensuring the protection of the rights and legitimate interests of minors;
Social and pedagogical rehabilitation of minors in a socially dangerous situation;
Identification and suppression of cases of involvement of minors in the commission of crimes and antisocial actions.
3. Organization of work on registering children in an educational organization
3.1. Educational organization:
Identifies minors who do not attend or systematically miss classes for unexcused reasons, takes measures for their upbringing and their receipt of secondary (complete) general education;
Keeps records of children who do not attend or systematically miss classes for unjustified reasons;
Identifies the reasons and conditions that contribute to absenteeism for unexcused reasons;
Maintains documentation on the registration and movement of students and promptly informs [name local authority authorities in the field of education] and the Commission on Minors' Affairs and the Protection of Their Rights about children who have stopped or are evading education.
3.2. Daily monitoring of class attendance is carried out by the class teacher. In case of missing 1 day of classes, and/or individual lessons, the total number of which is equal to the specified values, the class teacher finds out the reasons for the absence of the student, his parents (legal representatives). If classes were missed without a good reason and the parents did not know about it, they should be warned in writing (notification, diary entry) about the need to strengthen control over the child’s behavior and school attendance.
3.3. In addition to the conversation with the class teacher, an individual consultation is held with an educational psychologist, and together with parents, all appropriate measures are taken to eliminate the identified causes of absenteeism.
3.4. If parents (legal representatives) have not properly responded to information about a child’s absence from school for unexcused reasons, and the student continues to miss school, it is necessary to visit such a student at home together with representatives of the public commission for minors and the protection of their rights (hereinafter - CDN and ZP), an employee - a local police commissioner. A home visit should be documented with a housing inspection report.
If it is established that parents are abusing alcoholic beverages, drugs, or have a tendency to engage in antisocial behavior, an employee of the Department of Traffic Safety and Internal Affairs or an inspector of the Police Department of the Internal Affairs Directorate should be invited to visit such a family.
If it was not possible to establish contact with the parents, and the housemates (schoolmates) do not know anything about the location of the family, you should contact the juvenile affairs unit (PDN of the Internal Affairs Directorate at the student’s place of residence) to establish the location of the student and his parents.
3.5. If parents do not take appropriate measures to return the child to school, they should be warned in writing about administrative liability for evading their main responsibilities for raising and obtaining basic general education for their children.
3.6. In the event that work with the child and parents did not produce the desired results, and the minor continues to not attend classes without good reason, the student should be registered with the school in order to carry out individual preventive work with him and implement stricter control.
3.7. In relation to parents (legal representatives) who do not pay due attention to the upbringing of children and their education, it is necessary to inform in detail, in writing, the KDN and ZP and the PDN of the Internal Affairs Directorate in order to bring parents to administrative responsibility for failure to fulfill or improper fulfillment of their responsibilities for maintenance and upbringing , education, protection of the rights and interests of minors (Article 5.35 of the Administrative Code).
If parents (legal representatives) do not fulfill their responsibilities for the upbringing, education and (or) maintenance of minors and (or) negatively influence their behavior or abuse them, it is necessary to inform the police department of the Internal Affairs Directorate in writing.
3.8. In order to ensure the realization of the right of citizens to receive general education, the educational organization maintains documentation on the registration and movement of students.
4. Grounds for in-school registration
4.1. Students are subject to internal school registration for repeated, systematic absences from school, as well as for long-term absence from school without a good reason at the request of the class teacher.
4.2. For each minor who systematically misses or does not attend classes at an educational institution for a long time, the class teacher (social teacher) creates a Non-Attendance Card.
4.3. The registration card contains information about the minor and his living conditions, about individual preventive work with the minor, and about the measures taken by the educational institution.
4.4. The record card is submitted monthly to [name of local education authority].
From the moment of submitting this form, information about the minor is entered into the data bank of [name of the local authority in the field of education], which indicates that the student is registered with [name of the local authority in the field of education].
4.5. Information on the registration of children, information about which is included in the data bank, is subject to storage and use in a manner that ensures its confidentiality.
5. Procedure for deregistration
5.1. If a student does not miss school without a good reason for six months, the class teacher provides the following documents to the school Prevention Council:
Petition to remove a student from registration;
Characteristics of the student;
An extract from the class register containing information about attendance at classes and current academic performance (certified by the deputy director for educational work);
Certificates on individual work with a student and his parents (legal representatives), etc.
5.2. Based on these documents and oral explanations from the class teacher, at a meeting of the Prevention Council, a decision is made to remove the minor from the school register.
5.3. An extract from the minutes of the decision of the Prevention Council “On deregistration” is sent to [name of the local authority in the field of education].
5.4. In addition, students who have completed their studies or changed educational organizations are removed from the register.
6. Functional responsibilities of employees of educational organizations for the prevention of neglect and juvenile delinquency
6.1. Deputy Director for Educational Work:
Provides organizational and methodological assistance to social educators and class teachers in maintaining internal school records;
Analyzes the conditions and causes of negative manifestations among students and determines measures to eliminate them;
Consults students and their parents on current issues of education, takes part in resolving conflict situations;
Prepares relevant information on the activities of the educational organization to prevent neglect and delinquency among minors;
Provides information on the state of work in an educational organization with students and families who find themselves in a socially dangerous situation, in the event of consideration of materials at a meeting of the Committee for Educational Supervision and the ZP;
Responsible for organizing the maintenance and execution of documentation of internal school records, for interaction with other bodies and institutions of the system for the prevention of neglect and juvenile delinquency.
6.2. Social teacher:
Forms a social and pedagogical database of an educational organization;
Takes part in the preparation of information on the activities of educational organizations to prevent neglect and delinquency among minors;
Takes part in the development individual program social and pedagogical assistance and support, psychological support for a student in a socially dangerous situation;
Consults class teachers on issues of social and pedagogical assistance and support for students and families who find themselves in socially dangerous situations;
Consults students and their parents on issues of education, social and pedagogical assistance and support, as well as issues within his competence;
Informs about services provided by bodies and institutions of social protection of the population, bodies and health care institutions;
Takes part in resolving situations and disputes regarding the protection and protection of the rights of minors;
Analyzes the conditions and causes of negative manifestations among students and determines measures for social and pedagogical assistance and support for children and families in a socially dangerous situation;
Analyzes the conditions and reasons for the emergence of social dangerous situation families and determines measures for social and pedagogical assistance and support for families in this category;
Provides information on the state of work of the educational organization with students and families who find themselves in a socially dangerous situation, in the event of consideration of materials at a meeting of the Committee for Educational Supervision and ZP;
6.3. Classroom teacher:
Provides communication between the educational organization and the student’s family;
Establishes contacts with parents (other legal representatives) of students;
Consults parents (other legal representatives) on issues of raising and educating children, both personally and through specialists from an educational organization;
Organizes an educational and upbringing space in the classroom that is optimal for the development of the positive potential of each student;
Studying individual characteristics students and the dynamics of their development;
Studies and analyzes the degree of satisfaction of participants in the educational process with the life activities of the class team and educational organization;
Monitors the attendance of classes and the progress of each student;
Analyzes the conditions and causes of negative manifestations among class students and determines measures for pedagogical assistance and support for children;
Analyzes the conditions and causes of the socially dangerous situation of families and determines measures for pedagogical assistance and support for families in this category;
Responsible for maintaining internal school records.
6.4. Educational psychologist:
Conducts diagnostics of students at the request of parents (other legal representatives), the administration of the educational organization, and students who have reached the age of fourteen - upon personal request;
Conducts individual and group consultations with children, parents (other legal representatives), teachers on issues within the scope of his professional competence;
Conducts individual and group correctional work with children, parents (other legal representatives), teachers;
Provides psychological support to students, parents (other legal representatives), teachers;
Takes part in the development and preparation of an individual program of social and pedagogical assistance and support, psychological support for a student in a socially dangerous situation;
Develops psychological and pedagogical recommendations for the interaction of teaching staff with minors and families in a socially dangerous situation.
7. Responsibility for maintaining school records of students
7.1. Responsibility for organizing the maintenance of internal school records, preparation of relevant documentation, individual preventive activities in relation to each student placed on internal school records, as well as for interaction with other bodies and institutions of the system for the prevention of neglect and juvenile delinquency is assigned by order of the head of the educational organization to the deputy director for educational work. , social teacher, educational psychologist and class teacher.
7.2. Control over the quality of work on registering students who are in a socially dangerous situation and in need of individual preventive work is assigned to the deputy director of the school for educational work.