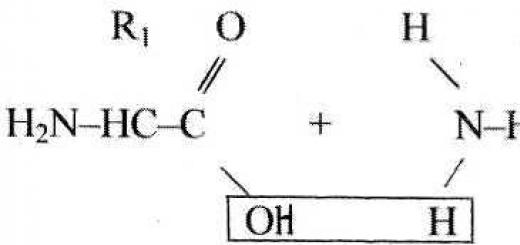
When studying a particular science, it is always important to determine what place it occupies in the system scientific knowledge, what benefits it brings to society. Thus there is a need to describe those functions, which performs sociology. The social purpose of a given science is determined through the functions it performs. It is important to note that sociology implements the entire range of functions inherent in social science.
Main functions of sociology in relation to society, as a rule, the following are called:
1. Cognitive. Sociology allows us to form knowledge about individuals, social groups ah, features and patterns of their behavior. This knowledge is built into a coherent and consistent system of sociological knowledge, on the basis of which conclusions are drawn about current state social organism and new research projects are being built.
2. Critical. The study of negative phenomena in the life of society allows us to recognize and stop the development of dangerous trends by solving a number of social problems fundamentally. A critical look at the state of specific areas public life makes it possible to eliminate emerging social dysfunctions and bring social connections and relationships to new stage development.
3. Applied. The results of specific sociological research in practice make it possible to solve complex social and scientific problems. Any applied sociological research produces a report with a detailed set of recommendations for improving a particular mechanism of social interaction.
4. Humanistic Yu. By studying social reality and communicating the practical results of research to specific citizens, sociology serves to improve public relations and relationships, and improves mutual understanding between different social groups.
5. Prognostic The practice of sociological research allows us to build short- and medium-term forecasts of social development, prevent various deviations in development, and model some trends in changes in society. This function expresses the practical orientation of sociology as a science.
6. Manager. The study of social life by sociology makes it possible to form strict practical recommendations on the management of one or another social group. The life planning of regions of the country, cities, individual organizations and groups can be based on the results of applied sociological research.
7. Transformative. Sociology in public life acts not only as a strict scientific knowledge about society, but also as a tool for transforming human life.
Similar documents
Basic mathematical calculus that is used in sociology: integral and differential calculus, as well as the use of functions and limits. Analysis of the problem of measuring social inequality. Study of social structure in dynamics.
article, added 02/24/2019
Characteristics of sociology as a science of society, social institutions and communities of people. Basic levels of knowledge and branches of sociology. Essence key functions sociology. Sociological research is a tool for understanding social reality.
test, added 11/10/2011
The concept of labor, its essence as the main category of sociology, features and content. The purpose and objectives of the sociology of labor, methods of its study and practical use. Working conditions and their components. The concept and types of labor incentives, performance.
abstract, added 01/17/2009
Social and philosophical prerequisites for the emergence of sociology as a science. Consideration of the main methodological approaches to defining the subject of sociology. Study of the main functions performed by sociology in society. Basic elements of sociology.
test, added 05/03/2016
Characteristics of the subject and analysis of key concepts and content of the sociology of labor. Functional and sociological aspects of labor relations. History of the development of the basic concepts of the sociology of labor. Classic and modern theories sociology of labor.
abstract, added 05/22/2014
The place of sociology in the system of social sciences. Object and subject of sociology. Levels of sociological knowledge. Features of macro- and microsociology. Characteristics of the concepts “Social” and “Social fact”. Description of the functions, methods and laws of sociology.
test, added 08/16/2010
Research and analysis of the main approaches and trends in sociology as a science about society, the patterns of its functioning and development. Definition of an object, characteristics of functions and analysis of sociological methods. Grade latest approaches in sociology.
abstract, added 06/22/2011
The main stages of the evolution of rural sociology. Socio-economic and ethnographic studies of the village in the 60s. XX century The concept, composition, role and significance of rural social infrastructure, features of its formation in connection with the transition to market relations.
course work, added 02/20/2011
Consideration of the object, subject and methods of sociology, the structure of sociological knowledge. Disclosure of the theoretical-cognitive, applied, educational, ideological functions of sociology. Determining its place in the system of social sciences and humanities.
If necessary, limits can be calculated on a computer using mathematical packages MathCad, Maple and others. To calculate this in Maple there is a command
limit(expr,x=val,dir) ,
where expr is the expression for which the limit is calculated (of a function or sequence), x=val is the value of the point for which the limit is calculated, and dir is an optional parameter that can take the following values: left (left limit), right (right limit) .
As a reminder, when you download the Maple package, a new worksheet is automatically loaded and prompted for the > command. You can write any algebraic expression on the command line, written according to the rules accepted in Maple. If you put the symbol; at the end of the expression, then when you press the Enter key or the button with an exclamation mark on the toolbar, the expression will be processed by the program, and the result will be displayed on the monitor.
V Example 1. Using Maple, find the limit 1 2ж + 3 I (example 2a, section 5.5).
w->-oo 2x + 3/
Enter the command
>limit(((2*x-l)/(2*x+3))~(4*x+l) ,x=infinity); ,
press the Enter key and get the answer: e-8. A
V Example 2. Find the limit lim -9.
>limit(n*sin(n!)/(n~2+l),n=infinity); . Answer: 0. A
V Example 3. Find one-sided limits lim - ,
zh-^-o i + 5іIх
and lim -g (see p. 75).
>limit(l/(l+5~(l/x)),x=0,left); .
>limit(l/(l+5~(l/x)),x=0,right); .
Answer: 0. A
To calculate the sum of a series, use the command
>sum(expr,var=varl..var2); ,
where expr is an expression depending on the summation variable var, and varl. .var2 - summation limits.
V Example 4. Find the sum of the series ^ -- (see p. 53).
sum(3/(lCTn),n=l..infinity); .
Answer: -. A 3
V Example 5. Find the sum of a geometric series
q< 1 (см. с. 53). Решение.
>sum(q~n),q=0..infinity); .
In mathematics, it is not the formulas that should be remembered, but the processes of thinking.
Main groups of sociological functions
The main groups of sociological functions include:
- Theoretical-cognitive, or epistemological function. Provides the opportunity to obtain new sociological knowledge, clarify and create concepts, theories, social connections of society, and a general view of society.
- Information function. Allows the public and a wide range of people to gain sociological knowledge.
- Management function. The task of sociologists is to explain social processes and phenomena, find the reasons for their occurrence and ways to resolve problematic issues, and provide recommendations for social management.
- Organizational function. Organization of various social groups: in the political sphere, in production, on vacation, in military units etc.
- Prognostic function. Allows you to predict future events in social life.
- Propaganda function. Allows you to form social values, ideals, create certain public relations, to form images of heroes of society.
Specific functions of sociology
In addition to the main functions of sociology, some scientists identify a number of specific functions:
- E. Durkheim believed that sociology should give specific recommendations for the development and improvement of society.
- V.A. Yadov adds practical-transformative, educational and ideological functions to the main functions. The main applied functions of sociology are the objective analysis of social reality.
- A.G. Zdravomyslov distinguishes ideological, theoretical, instrumental and critical functions.
- G.P. Davidyuk, along with the main functions, highlights the educational function of sociology.
Theoretical-cognitive function
The cognitive-theoretical function is to study and analyze social reality. It is focused on creating new sociological knowledge and is the basis for the implementation of other functions.
The cognitive function is carried out at all levels of sociological knowledge:
- general theoretical level - hypotheses are developed, problems of social reality are formulated, tools and methods of sociological research are determined, social forecasts are made;
- intermediate level - translation general concepts to the empirical level, increasing knowledge about the essence, specific situations, contradictory phenomena of human activity;
- empirical level – new facts identified during sociological research increase the amount of substantiated knowledge about social reality.
Prognostic function
The predictive function gives scientifically based predictions further development individual spheres and structures of society, the whole society as a whole, is the theoretical basis for creating long-term plans for their development.
Social forecasts indicate the necessary changes, show the possibilities of its implementation, and make it possible to give practical recommendations for improving the efficiency of managing social processes.
Depending on the group of social factors to which practical recommendations relate, they may be of the following nature:
- objective (political system, social structure society, working conditions, human behavior, etc.);
- subjective (goals, motives, interests, attitudes, values, public opinion etc.).
Critical function
Thanks to the critical function the world assessed from the point of view of the interests of the individual. Having objective knowledge, it is possible to identify deviations in the development of society, leading to negative social consequences.
There is a differentiated approach to reality. It is indicated that in social structure can be preserved, strengthened and developed, and what can be radically changed.