Target: To introduce students to the concept of “chemical organization of a cell.”
Tasks:
educational: show the unity of living and inanimate matter, the different contents of some elements, the complexity of the organic world;
educational: continue the formation of a materialistic worldview on the unity of living and inanimate nature. Instilling interest in studying this topic;
developing: create conditions for reproducing a system of basic knowledge and skills in students’ memory, stimulate search activity; create conditions for systematizing knowledge about the cell; create meaningful and organizational conditions for the development of students’ skills in establishing cause-and-effect relationships, comparing and generalizing the objects being studied; develop communication skills through work in small groups, showing that the relationship between the activities of the student, classmates, teacher, their interests and knowledge is the most important condition for successful work.
Lesson type: combined lesson (lesson-lecture, lesson-conversation, learning new material).
Methods: conversation, story, demonstration of the presentation “Cell theory. Features of cell structure", oral survey.
Visual aids: textbook Yu.I. Polyansky pp. 145-162, poster with a diagram of an animal and plant cell.
During the classes
I. Organizational moment
Greeting, message of the lesson topic and work plan, marking absentees.
II. Check of knowledge
Individual survey of students on the following questions:
Test questions for reviewing material on the topic “The Origin of Life on Earth”
1. Tell us about the formation of planet Earth.
2. List the conditions necessary for the emergence of life.
3. Describe modern ideas about the origin of life.
4. Give the concept of chemical evolution.
5. Describe prebiological systems.
6. Tell us about the beginning of biological evolution.
7. Explain the emergence of eukaryotes.
8. Explain the origin of multicellular organisms.
III. Learning new material Terminology
1. Bioelements are chemical elements that are the basis of organic molecules.
2. Macroelements are chemical elements that are part of organic molecules in quantities exceeding 1%.
3. Microelements - chemical elements included in the composition of organic molecules in quantities not exceeding 0.001%.
4. Homeostasis is a state of dynamic equilibrium of a natural system, supported by the activity of regulatory systems.
5. Buffer solutions - a solution of organic or inorganic substances, the pH value of which does not change when small amounts of alkali or acid are added.
The simplest microorganisms are individual cells. The body of all multicellular organisms consists of a greater or lesser number of cells, which are blocks that form a living organism. Regardless of whether a cell is an integral system or part of it, it has a set of characteristics common to all cells.
Chemical organization of cells(lecture)
Cells contain about 70 elements of the periodic table, which are also found in inanimate nature. This is one of the proofs of the commonality of living and inanimate nature. However, the ratio of elements, their contribution to the formation of the elements that make up the organism and non-living things, differ sharply.
Depending on the ratio of elements in the composition of the body, they are distinguished:
macroelements (98% of cell mass) H 2, O 2, C, N.
trace elements (1.5%) S, P, K, Na, Ca, Mg, Mn, Fe, Cl. Each of them performs very important functions in the cell.
other (0.5%) B, Zn, Cu, I 2, F 2 CO, Se.
All these elements participate in the construction of the body either in the form of ions or as part of certain compounds - molecules of organic and inorganic compounds.
Inorganic substances in the cell
These include water and mineral salts.
Water is the most common inorganic compound in living organisms. Its amount ranges from 10% in tooth enamel to 90% in germ cells. It depends on age, time of day, time of year.
Water molecules are represented by dipoles: depending on the temperature, the molecules can be free or combined into groups with the presence of hydrogen bonds. The dipole nature determines the high chemical activity of water. Water plays the role of a medium in the cell; it brings and carries away nutrients. Water undergoes numerous hydrolysis reactions. Having good thermal conductivity, water regulates the temperature in the cell.
Mineral salts - this is most of the inorganic compounds. They are in the form of ions or undissociated molecules. K + , Na + , Ca +2 are of great importance. They provide a constant water content, solution environment. The buffering environment ensures the constancy of all internal processes in the cell.
Organic substances in a cell
They make up 20-30% of the cell mass. These include biopolymers - proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, fats, ATP, etc.
Different types of cells contain different amounts of organic compounds. Complex carbohydrates predominate in plant cells, while proteins and fats predominate in animal cells. Nevertheless, each group of organic substances in any type of cell performs functions: providing energy, being a building material, carrying information, etc.
Squirrels. Among organic substances, cells and proteins occupy first place in quantity and importance. In animals they account for 50% of the dry mass of the cell.
The human body contains many types of protein molecules that differ from each other and from proteins in other organisms.
Despite the enormous diversity and complexity of structure, proteins are built from 20 amino acids:
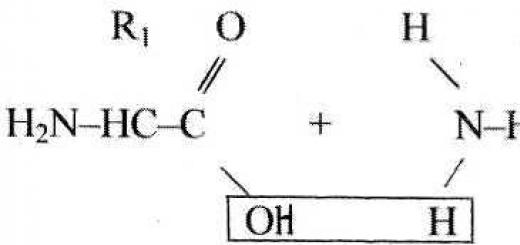
Amino acids have amphoteric properties, so they interact with each other:
Peptide bond: 


When combined, the molecules form: a dipeptide, tripeptide or polypeptide. This is a compound of 20 or more amino acids. The order of transformation of amino acids in a molecule is very diverse. This allows the existence of variants that differ in the requirements and properties of the protein molecules.
The sequence of amino acids in a molecule is called structure.
Primary – linear.
Secondary – spiral.
Tertiary - globules.
Quaternary - association of globules (hemoglobin).
The loss of structural organization by a molecule is called denaturation. It is caused by changes in temperature, pH, and radiation. With minor exposure, the molecule can restore its properties. It is used in medicine (antibiotics).
The functions of proteins in a cell are diverse. The most important is construction. Proteins are involved in the formation of all cell membranes in organelles. The catalytic function is extremely important - all enzymes are proteins. Motor function is provided by contractile proteins. Transport - consists of attaching chemical elements and transferring them to tissues. The protective function is provided by special proteins - antibodies formed in leukocytes. Proteins serve as a source of energy - with the complete breakdown of 1g of protein, 11.6 kJ is released.
Carbohydrates. These are compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Represented by sugars. The cell contains up to 5%. The richest are plant cells - up to 90% of the mass (potatoes, rice). They are divided into simple and complex. Simple - monosaccharides (glucose) C 6 H 12 O 6, grape sugar, fructose. Disaccharide – (sucrose) C ]2 H 22 O 11 beet and cane sugar. Polysugars (cellulose, starch) (C 6 H 10 O 5)n.
Carbohydrates perform mainly construction and energy functions. When 1g of carbohydrate is oxidized, 17.6 kJ is released. Starch and glycogen serve as the cell's energy reserves.
Lipids. These are fats and fat-like substances in the cell. They are esters of glycerol and high molecular weight saturated and unsaturated acids. They can be solid or liquid – oils. In plants they are contained in seeds, from 5-15% of dry matter.
The main function is energy - when 1g of fat is broken down, 38.9 kJ is released. Fats are nutrient reserves. Fats perform a construction function and are a good heat insulator.
Nucleic acids. These are complex organic compounds. They consist of C, H 2, O 2, N 2, P. Contained in the nuclei and cytoplasm.
a) DNA is a biological polynucleotide consisting of two chains of nucleotides. Nucleotides - consist of 4 nitrogenous bases: 2 purines - Adenine and Valine, 2 pyrimedines Cytosine and Guanine, as well as sugar - deoxyribose and a phosphoric acid residue. 
In each chain, nucleotides are connected by covalent bonds. Chains of nucleotides form helices. A DNA helix packed with proteins forms a structure - a chromosome.
b) RNA is a polymer whose monomers are nucleotides similar to DNA, nitrogenous bases - A, G, C. Instead of thymine there is uracin. The carbohydrate in RNA is ribose and there is a phosphoric acid residue.

Double-stranded RNAs are carriers of genetic information. Single-chain - carry information about the sequence of amino acids in a protein. There are several single-stranded RNAs:
Ribosomal – 3-5 thousand nucleotides;
Informational – 300-30000 nucleotides;
Transport - 76-85 nucleotides.
Protein synthesis is carried out on ribosomes with the participation of all types of RNA.
OPTION 1
Water molecule
2) dipole;
3) oxygen has a small positive charge, hydrogen has a negative charge;
proteins, fats, carbohydrates, water;
water, carbon, salts.
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, sulfur;
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, potassium;
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen;
oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, iodine.
biochemical elements;
nutrients;
biochemical substances.
weaker than ionic;
weaker than hydrogen;
moststrengthny type of communication.
Organic substances in cells include
The main chemical elements of a cell include
Those chemical elements that take part in the metabolic process in the cell and have biological activity are called
Covalent bond
Complete the statement:
Hydrophilic substances are substances _________ soluble in water.
Each amino acid is made up of three parts: a _____________ group, a _____________ group, and a free radical.R.
Complete the statement:
polypeptide chain;
twisted spiral;
a spiral twisted into a ball;
globule.
The quaternary structure of a protein is
Define the concept: The loss of a protein molecule's structural organization or protein folding is called __________________.
Match:
1. Monosaccharides A. sucrose, maltose, lactose;
2. Disaccharides B. glycogen, starch, cellulose;
3. Polysaccharides B. Glucose, lactose, sucrose;
G. glucose, fructose, galactose.
With complete combustion of 1 g of the substance, 38.9 kJ of energy was released. This substance was
carbohydrates;
fats;
both carbohydrates and lipids;
not carbohydrates or lipids.
Complete the statement:
The monomers of _ NA, which include the carbohydrate ribose, are ____________,.
Complete the statement:
The DNA molecule contains residues of the nitrogenous bases of four nucleotides: A (adenine),
GCGAATGAACGC
_____________,
Test work on the topic “Chemical organization of the cell”
OPTION 2
1. Water molecule
1) has no charged areas;
2) oxygen has a small positive charge, hydrogen has a negative charge;
3) dipole;
4) oxygen has a small negative charge, hydrogen has a positive charge.
2. Inorganic substances of cells include
water, salts and nucleic acids;
proteins, fats, carbohydrates, water;
proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids;
water, carbon, salts.
Cell macroelements include
1) copper, fluorine, chromium, iodine;
2) iodine, fluorine, chlorine, iron;
3) sulfur, potassium, copper, zinc;
4) oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, sulfur.
Those chemical elements that take part in the metabolic process in the cell and have biological activity are called
1) biologically active substances;
2) biochemical elements;
3) biogenic elements;
4) biochemical substances.
Hydrogen bond
1) the weakest type of connection;
2) stronger than covalent;
3) the most strength ny type of communication.
Complete the statement:
Hydrophobic substances are substances __________ soluble in water.
Fill in the missing concepts in the sentence:
When a protein macromolecule is formed, a strong covalent bond is formed - ______________, and
protein molecules are called ____________.
Complete the statement: Protein is a biopolymer whose monomers are ____________.
The primary structure of a protein is
1) polypeptide chain;
2) twisted spiral;
3) a spiral twisted into a ball;
4) globule.
Define the concept:
Restoring the protein structure and its functional activity is called __________________.
Match:
1. Monosaccharides A.. glycogen, starch, cellulose;
2. Disaccharides B. glucose, fructose, galactose;
3. Polysaccharides B. sucrose, maltose, lactose;
G. glucose, lactose, sucrose.
With complete combustion of 1 g of the substance, 17.6 kJ of energy was released. This substance was
1) proteins;
both carbohydrates and lipids;
carbohydrates;
both carbohydrates and proteins.
Complete the statement:
Monomers _ NA, which include the carbohydrate deoxyribose, are ____________,.
Complete the statement:
The RNA molecule contains residues of the nitrogenous bases of four nucleotides: A (adenine),
G (guanine), C (cytosine) and ___ (________).
Carry out template DNA synthesis:
TsAGTAGTCAAT
_____________
it is carried out according to the principle _________________.
Answers to the test on the topic
"Chemical Organization of the Cell"
| Option I | II Option |
| 7-carboxyl, amino- 8- amino acids 10- denaturation 11: 1-G, 2-A, 3-B 13- RNA, nucleotides 14-T (thymine) 15- TsGCTATCTTGTG, complementarity | 6- practically not 7- peptide, polypeptides 8- amino acids 10- renaturation 11: 1-B, 2-B, 3-A 13- DNA, nucleotides 14-U (uracil) 15 – GTSATSAGTTA, complementarity |
Timofeeva G.V.
Place of work, position:
Municipal educational institution secondary school No. 1, Sobinka, teacher
Vladimir region
Resource characteristics
Education levels:
Secondary (complete) general education
Class(es):
Item(s):
Biology
The target audience:
Teacher (teacher)
Resource type:
Test (test) work
Test.
№ 1. Similarity of elemental composition cells and bodies of inanimate nature testifies...
A-about the material unity of living and inanimate nature
B-about the dependence of living nature on inanimate
B-changes in living nature under the influence of environmental factors
G-about their complex chemistry. composition
No. 2. At what level of organization of life are there similarities between the organic world and inanimate nature?
A-on fabric
B-on molecular
B-on the cellular
In-at atomic
No. 3. A substance in the cell necessary for all chemical reactions, which plays the role of a solvent for most substances, is...
A-polynucleotide
B - polypeptide
B - water
G-polysaccharide
No. 4. Water makes up a significant part of the cell, it...
A - regulates life processes
B - provides the cell with energy
B - gives the cell elasticity
G - promotes cell division
No. 5. What is the average proportion of water in a cell?
A-80%B-1%
B-20%
No. 6. Substances that are highly soluble in water are called:
A - hydrophilicB - amphiphilic
B - hydrophobic
No. 7. What ions ensure the permeability of cell membranes?
A- Ca 2+ B- Zn 2+
B- Na + K + Cl - G- Mg 2+
No. 8. What vital compound does iron contain?
A-chlorophyllB-DNA
B - hemoglobinG-RNA
No. 9. Which chemical compound plays a major role in maintaining osmotic pressure in the cell?
A-protein B- NaCl
B-ATPG-Fat
No. 1 0.What is the name of an organic substance whose molecules contain atoms C, O, H, which performs an energy and construction function?
A - nucleic acid B-protein
B - Carbohydrate G-ATP
No. 11. What carbohydrates are polymers?
A-monosaccharides
B-disaccharides
B-polysaccharides
No. 12. The group of monosaccharides includes:
A-glucose
B - sucrose
B-cellulose
No. 13. Which carbohydrates are insoluble in water?
A-glucose, fructose B-starch
B - ribose, deoxyribose
No. 14. What polysaccharides are characteristic of a living cell?
A-celluloseB-glycogen, chitin
B- Starch
No. 15. Fat molecules are formed:
A-from glycerol, higher carboxylic acidsB-from glucose
B-from amino acids, water D-from ethyl alcohol, higher carboxylic acids
No. 16. Fats perform the following functions in the cell:
A - transport. B - energy
B - catalytic D - informational
No. 17. What compounds do lipids belong to in relation to water?
A - hydrophilic. B - hydrophobic
No. 18.What is the importance of fats in animals?
A-membrane structure B-thermoregulation
B- source of energy D- source of water D- all of the above
No. 19. In what solvents are fats soluble?
A-waterB-alcohol, ether, gasoline
No. 20. Protein monomers are:
A-nucleotidesB-amino acids
B - glucose G-fats
No. 21. The most important organic substance that is part of the cells of all kingdoms of living nature, having a primary linear configuration, is:
A - to polysaccharides. B - to lipids
B - to ATPG - to polypeptides
No. 22. How many of the known amino acids are involved in protein synthesis ?
A-20B-100
B-23
No. 23.What function do proteins not perform in a cell?
A - informational. B - catalytic
B - solvent D - storage
No. 24. Protein molecules that bind and neutralize substances foreign to a given cell perform the function...
A - protective. B - energetic
B - catalytic G - transport
No. 25. What part of the amino acid molecules distinguishes them from each other?
A-radical. B-carboxyl group
B - amino group
No. 26. Through what chemical bond are amino acids connected to each other in a protein molecule of the primary structure?
A - disulfide. B - hydrogen
B - peptide G - ionic
No. 27. What is the name of the reversible process of disruption of the structure of one of the most important organic compounds of the cell, which occurs under the influence of physical and chemical factors?
A-polymerization of glucose B-denaturation of protein
B- doubling of DNAG-oxidation of fats
No. 28. What compounds are part of ATP?
A- nitrogenous base adenine, carbohydrate ribose, 3 molecules of phosphoric acid
B- nitrogenous base guanine, sugar fructose, phosphoric acid residue.
B- ribose, glycerol and any amino acid
No. 29. What is the role of ATP molecules in the cell?
A - provide a transport function. B - transmit hereditary information
B - provide vital processes with energy D - accelerate biochemical reactions
No. 30. Monomers of nucleic acids are:
A-amino acids B-fats
B - nucleotides G-glucose
No. 31. What substances are included in the nucleotide?
- amino acid, glucose B - glycerol, phosphoric acid residue, carbohydrate
B - nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, phosphoric acid residue. D - pectose carbohydrate, 3 phosphoric acid residues, amino acid.
No. 32.What class of chemical substances does ribose belong to?
A-protein B-carbohydrate
B-lipid
No. 33. Which nucleotide is not part of the DNA molecule TO?
A - adenyl. B - uridyl
B - guanyl G - thymidyl
No. 34. Which nucleic acid has the greatest length and molecular weight?
A-DNKB-RNA
No. 35.RNA is:
A - nucleotide containing two energy-rich bonds
B - a molecule in the shape of a double helix, the chains of which are connected by hydrogen bonds
B-single helix
G - long polypeptide chain.
No. 36. Nucleic acids perform the following functions in the cell:
A - catalytic B - construction
B-energyG-information
No. 37. What does the information in one DNA triplet correspond to?
A-amino acidB-gene
B - squirrel
No. 38. Individual differences in the body are caused by:
A-DNA, RNAB fats and carbohydrates
B- nucleic acids and proteins
No. 39. The nucleotide complementary to guanyl nucleotide is:
A - thymidyl B -ts itidyl
B - adenyl G-uridyl
No. 40. The process of doubling DNA molecules is called:
Test.
№1. The similarity of the elementary composition of cells and bodies of inanimate nature indicates...
A-about the material unity of living and inanimate nature
B-about the dependence of living nature on inanimate
B-changes in living nature under the influence of environmental factors
G-about their complex chemistry. composition
№2. At what level of organization of life is there a similarity between the organic world and inanimate nature?
A-on fabric
B-on molecular
B-on the cellular
In-at atomic
№3. A substance in the cell necessary for all chemical reactions, which plays the role of a solvent for most substances, is...
A - polynucleotide
B - polypeptide
B - water
G-polysaccharide
№4.Water makes up a significant part of the cell, it...
A - regulates life processes
B - provides the cell with energy
B - gives the cell elasticity
G - promotes cell division
№5. What is the average proportion of water in a cell?
A-80% B-1%
B-20%
№ 6. Substances that are highly soluble in water are called:
A - hydrophilic B - amphiphilic
B - hydrophobic
№7.What ions ensure the permeability of cell membranes?
A- Ca 2+ B-Zn 2+
B- Na + K + Cl - G-Mg 2+
№8.Which vital compound contains iron?
A-chlorophyll B-DNA
B - hemoglobin G-RNA
№9. Which chemical compound plays a major role in maintaining osmotic pressure in the cell?
A-protein B- NaCl
B-ATP G-Fat
№1 0.What is the name of an organic substance whose molecules contain atoms C, O, H, which performs an energy and construction function?
A - nucleic acid B-protein
B - Carbohydrate G-ATP
№11. What carbohydrates are polymers?
A-monosaccharides
B-disaccharides
B-polysaccharides
№12. The group of monosaccharides includes:
A-glucose
B - sucrose
B-cellulose
№13.Which carbohydrates are insoluble in water?
A-glucose, fructose B-starch
B - ribose, deoxyribose
№14.What polysaccharides are characteristic of a living cell?
A-cellulose B-glycogen, chitin
B- Starch
№15.Fat molecules are formed:
A-from glycerol, higher carboxylic acids B-from glucose
B-from amino acids, water D-from ethyl alcohol, higher carboxylic acids
№16.Fats perform the following functions in the cell:
A - transport. B - energy
B - catalytic G - informational
№17.What compounds do lipids belong to in relation to water?
A - hydrophilic. B - hydrophobic
№18.What is the importance of fats in animals?
A-membrane structure B-thermoregulation
B- source of energy D- source of water D- all of the above
№19. In which solvents are fats soluble?
A-water B-alcohol, ether, gasoline
№20. Protein monomers are:
A-nucleotides B-amino acids
B - glucose G-fats
№21. The most important organic substance that is part of the cells of all kingdoms of living nature, which has a primary linear configuration, is:
A - to polysaccharides. B - to lipids
B - to ATP G - to polypeptides
№22. How many of the known amino acids are involved in protein synthesis ?
A-20 B-100
B-23
№23.What function do proteins not perform in a cell?
A - informational. B - catalytic
B - solvent D - storage
№24.Protein molecules that bind and neutralize substances foreign to a given cell perform the function...
A - protective. B – energy
B - catalytic G - transport
№25. What part of the amino acid molecules distinguishes them from each other?
A-radical. B - carboxyl group
B - amino group
№26. Through what chemical bond are amino acids connected to each other in a protein molecule of the primary structure?
A - disulfide. B - hydrogen
B - peptide G - ionic
№27.What is the name of the reversible process of disruption of the structure of one of the most important organic compounds of the cell, which occurs under the influence of physical and chemical factors?
A-polymerization of glucose B-denaturation of protein
B- DNA doubling D- fat oxidation
№28.What compounds make up ATP?
A- nitrogenous base adenine, carbohydrate ribose, 3 molecules of phosphoric acid
B- nitrogenous base guanine, sugar fructose, phosphoric acid residue.
B- ribose, glycerol and any amino acid
№29. What is the role of ATP molecules in the cell?
A - provide a transport function. B - transmit hereditary information
B - provide vital processes with energy D - accelerate biochemical reactions
№30. Monomers of nucleic acids are:
A-amino acids B-fats
B - nucleotides G-glucose
№31.What substances are included in the nucleotide?
- amino acid, glucose B - glycerol, phosphoric acid residue, carbohydrate
B - nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, phosphoric acid residue. D - pectose carbohydrate, 3 phosphoric acid residues, amino acid.
№32.What class of chemical substances does ribose belong to?
A-protein B-carbohydrate
B-lipid
№33.Which nucleotide is not part of the DNA molecule TO?
A - adenyl. B - uridyl
B - guanyl G - thymidyl
№34.Which nucleic acid has the greatest length and molecular weight?
A-DNA B-RNA
№35.RNA is:
A - nucleotide containing two energy-rich bonds
B - a molecule in the shape of a double helix, the chains of which are connected by hydrogen bonds
B - single helix
G - long polypeptide chain.
№36. Nucleic acids perform the following functions in a cell:
A - catalytic B - construction
B-energy G-information
№37. What does the information of one DNA triplet correspond to?
A-amino acid B-gene
B - squirrel
№38.Individual differences in organisms are due to:
A-DNA, RNA B-fats and carbohydrates
Test Chemical organization of a cell Option 1 Choose one correct answer. 1. Bodies of living and inanimate nature are similar in the set of 1) proteins 3) nucleic acids 2) chemical elements 4) enzymes 2. Magnesium is an essential component of the molecules 1) DNA 3) hemoglobin 2) chlorophyll 4) RNA 3. Name the organic compounds that are contained in the cell in the greatest quantity (in% of wet weight) 1) carbohydrates 3) proteins 2) lipids 4) nucleic acids 4. A significant part of the cell is water, which 1) forms the spindle 3) dissolves fats 2) forms protein globules 4) gives the cell elasticity 5. Water is a good solvent, since 1) its molecules have mutual attraction 3) it heats up and cools slowly 2) its molecules are polar 4) it is a catalyst 6. Water in the cell performs the function 1) catalytic 3) structural 2 ) solvent 4) informational 7. Proteins belong to the group of biopolymers, since they: 1) are highly diverse 3) consist of repeating units 2) play an important role in the cell 4) have a large molecular weight 8. Monomers of protein molecules are 1) nucleotides 3) monosaccharides 2) amino acids 4) lipids 9. Polypeptides are formed as a result of the interaction of 1) nitrogenous bases 3) carbohydrates 2) lipids 4) amino acids 10. The type of number and order of amino acids determines 1) the sequence of RNA triplets 3) the hydrophobicity of fat molecules 2) primary structure of proteins 11. Organic substances that accelerate metabolic processes 1) amino acids 3) enzymes 2) monosaccharides 4) lipids 12. Fiber molecule, unlike a lipid molecule 1) organic substance 3) monomer 2) biopolymer 4) inorganic substance 13. The universal source of energy in the cell is the molecules of 1) fatty acids 3) ATP 2) DNA 4) glucose 14. Storage carbohydrates in an animal cell are 1) chitin 3) starch 2) cellulose 4) glycogen 15. Lipids in the plasma membrane perform the function 1) structural 3) energetic 2) storage 4) catalytic 16. The DNA double helix is formed due to bonds between 1) complementary nitrogenous bases 3) amino acids 2) phosphoric acid residues 4) carbohydrates 17. Fragments of one DNA chain have the following sequence HCAATGGG. Determine the corresponding fragment of its second chain 1) GCAATGGG 3) CGTTTACC 2) ATGGCAAA 4) CGUUACC 18. In a DNA molecule, three adjacent nucleotides are called 1) triplet 3) genome 2) gene 4) genotype 19. In a DNA molecule, there are 31% of nucleotides with adenine. How many nucleotides with cytosine are in this molecule? 1) 45% 3) 25% 2) 43% 4) 19% 20. The principle of complementarity (complementarity) underlies the interaction of 1) amino acids and the formation of primary 3) glucose and the formation of a polysaccharide molecule of the fiber protein structure 2) nucleotides and the formation of a double-stranded 4 ) glycerol and fatty acids and the formation of a DNA molecule fat molecule