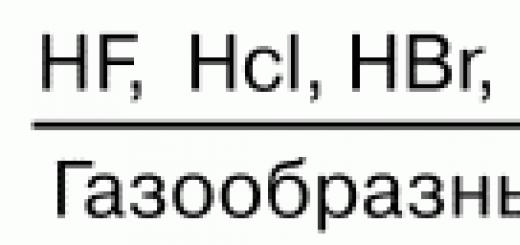Unified state exam in CHEMISTRY
prepared by the Federal State Scientific Institution"FEDERAL INSTITUTE OF PEDAGOGICAL MEASUREMENTS"

Chemistry Content Element Codifier
for compiling control measuring materials
unified state exam 2007
The codifier is compiled on the basis of the mandatory minimum content of the basic general and secondary (complete) education in chemistry (appendices to the Orders of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. Russia dated March 5, 2004 No. 000).
Bold italics indicate large blocks of content. Separate elements of the content, on the basis of which the verification tasks are made, are indicated in the blocks by the code of the controlled element.
Section code |
controlled element | Content elements verified by CMM tasks |
1 | Chemical element |
|
Forms of existence of chemical elements. Modern ideas about the structure of atoms. Isotopes. |
||
The structure of the electron shells of atoms of the elements of the first four periods. Atomic orbitals, s - and p-elements. The electronic configuration of the atom. Ground and excited states of atoms . |
||
Periodic law and the periodic system of chemical elements. Radii of atoms, their periodic changes in the system of chemical elements. Patterns of changes in the chemical properties of elements and their compounds by periods and groups. |
||
2 | Substance |
|
Chemical bond: covalent (polar and non-polar), ionic, metallic, hydrogen. |
||
Methods for the formation of a covalent bond. Characteristics of a covalent bond: bond length and energy . Formation of an ionic bond. |
||
Electronegativity. The degree of oxidation and valence of chemical elements. |
||
Substances of molecular and non-molecular structure. The dependence of the properties of substances on the features of their crystal lattice. |
||
Variety of inorganic substances. Classification of inorganic substances. |
||
General characteristics of metals of the main subgroups of groups I-III in connection with their position in the periodic system of chemical elements and structural features of their atoms. |
||
Characteristics of transition elements - copper, zinc, chromium, iron according to their position in the periodic system of chemical elements and structural features of their atoms. |
||
General characteristics of non-metals of the main subgroups of groups IV-VII in connection with their position in the periodic system of chemical elements and structural features of their atoms. |
||
Characteristic chemical properties of inorganic substances of various classes: simple substances (metals and non-metals); oxides (basic, amphoteric, acid); bases, amphoteric hydroxides, acids; medium and acid salts. |
||
Theory of the structure of organic compounds. Isomerism, homology. |
||
Variety of organic substances. Classification of organic substances. Systematic nomenclature. |
||
Homologous series of hydrocarbons. Isomers of hydrocarbons. Structural and spatial isomerism. |
||
Features of the chemical and electronic structure of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, their properties. |
||
aromatic hydrocarbons. Benzene, its electronic structure, properties. Homologues of benzene (toluene). |
||
Electronic structure of functional groups of oxygen-containing organic compounds. |
||
Characteristic chemical properties of oxygen-containing organic compounds: limiting monohydric and polyhydric alcohols, phenol; aldehydes and saturated carboxylic acids. |
||
Complex ethers. Fats. Soap. |
||
Carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides . |
||
Amino acids as amphoteric organic compounds. Squirrels. |
||
Interrelation of different classes: inorganic substances; organic substances. |
||
3 | Chemical reaction |
|
Classification of chemical reactions in inorganic and organic chemistry. |
||
The reaction rate, its dependence on various factors. |
||
Thermal effect of a chemical reaction. Thermochemical equations. |
||
Reversible and irreversible chemical reactions. chemical balance. Equilibrium shift under the influence of various factors. |
||
Dissociation of electrolytes in aqueous solutions. Weak and strong electrolytes. |
||
Ion exchange reactions. |
||
Redox reactions. Corrosion of metals and methods of protection against it. |
||
Salt hydrolysis. Environment of aqueous solutions: acidic, neutral, alkaline. |
||
Electrolysis of melts and solutions (salts, alkalis). |
||
Reactions characterizing the main properties and methods of obtaining: hydrocarbons; |
||
Natural sources of hydrocarbons, their processing. |
||
Basic methods for the synthesis of macromolecular compounds (plastics, synthetic rubbers, fibers). |
||
Calculation of the mass of a solute contained in a certain mass of a solution with a known mass fraction. |
||
Calculations: volume ratios of gases in chemical reactions. |
||
Calculations: the mass of a substance or the volume of gases according to a known amount of a substance from those participating in the reaction. |
||
Calculations: thermal effect of the reaction. |
||
Calculations: mass (volume, amount of substance) of the reaction products, if one of the substances is given in excess (has impurities). |
||
Calculations: mass (volume, amount of substance) of the reaction product, if one of the substances is given as a solution with a certain mass fraction of the solute. |
||
Finding the molecular formula of a substance. |
Chemistry codifier includes:
- Section 1. The list of content elements to be tested at the unified state exam in chemistry;
- Section 2 List of requirements for the level of training, checked at the unified state exam in chemistry.
Content elements verified by CMM tasks
1. THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF CHEMISTRY
1.1 Modern ideas about the structure of the atom
1.1.1 The structure of the electron shells of atoms of the elements of the first four periods: s-, p- and d-elements. Electronic configuration of atoms and ions. Ground and excited states of atoms
1.2.2 General characteristics of metals of IA–IIIA groups in connection with their position in the Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev and structural features of their atoms
1.2.3 Characterization of transition elements (copper, zinc, chromium, iron) according to their position in the periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev and structural features of their atoms
1.2.4 General characteristics of non-metals of groups IVА–VIIA in connection with their position in the Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev and structural features of their atoms
1.3 Chemical bond and structure of matter
1.3.1 Covalent chemical bond, its varieties and formation mechanisms. Characteristics of a covalent bond (polarity and bond energy). Ionic bond. Metal connection. hydrogen bond
1.3.2 Electronegativity. and
1.3.3 Substances of molecular and non-molecular structure. Type of crystal lattice. The dependence of the properties of substances on their composition and structure
1.4 Chemical reaction
1.4.1 Classification of chemical reactions in inorganic and organic chemistry
1.4.2 Thermal effect of a chemical reaction. Thermochemical equations
1.4.3 The rate of a chemical reaction, its dependence on various factors
1.4.4 Reversible and irreversible chemical reactions. chemical balance. Shift in chemical equilibrium under the influence of various factors
1.4.5 Electrolytic dissociation of electrolytes in aqueous solutions.
1.4.6 Ion exchange reactions
1.4.7 Hydrolysis of salts. Environment of aqueous solutions: acidic, neutral, alkaline
1.4.8 Redox reactions. Corrosion of metals and methods of protection against it
1.4.9 Electrolysis of melts and solutions (salts, alkalis, acids)
1.4.10 Ionic (V.V. Markovnikov's rule) and radical mechanisms of reactions in organic chemistry
2. INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
2.1 Classification of inorganic substances. (trivial and international)
4.1.6 The main methods for obtaining (in the laboratory) specific substances belonging to the studied classes of inorganic compounds
4.1.7 Basic methods for obtaining hydrocarbons (in the laboratory)
4.1.8 Basic methods for the production of organic oxygen-containing compounds (in the laboratory)
4.2 General ideas about industrial methods for obtaining essential substances
4.2.1 The concept of metallurgy: general methods for obtaining metals
4.2.2 General scientific principles of chemical production (on the example of industrial production of ammonia, sulfuric acid, methanol). Chemical pollution of the environment and its consequences
4.2.3 Natural sources of hydrocarbons, their processing
4.2.4 Macromolecular compounds. Reactions of polymerization and polycondensation. Polymers. Plastics, fibers, rubbers
4.2.5 Use of studied inorganic and organic substances
4.3.1 Calculations using the concept of "mass fraction of a substance in solution"
4.3.2 Calculations of volume ratios of gases in chemical reactions
4.3.3 Calculations of the mass of a substance or volume of gases from a known amount of a substance, mass or volume of one of the substances participating in the reaction
4.3.4 Heat of reaction calculations
4.3.5 Calculations of the mass (volume, amount of substance) of the reaction products, if one of the substances is given in excess (has impurities)
4.3.6 Calculations of the mass (volume, amount of substance) of the reaction product, if one of the substances is given as a solution with a certain mass fraction of the dissolved substance
4.3.7 Establishing the molecular and structural formula of a substance
4.3.8 Calculations of the mass or volume fraction of the yield of the reaction product from the theoretically possible
4.3.9 Calculations of the mass fraction (mass) of a chemical compound in a mixture
Skills and activities tested by KIM tasks
Know/Understand:
1. The most important chemical concepts
- Understand the meaning of the most important concepts (highlight their characteristic features): substance, chemical element, atom, molecule, relative atomic and molecular masses, ion, isotopes, chemical bond, electronegativity, valency, oxidation state, mole, molar mass, molar volume, molecular substances and non-molecular structure, solutions, electrolytes and non-electrolytes, electrolytic dissociation, hydrolysis, oxidizing agent and reducing agent, oxidation and reduction, electrolysis, chemical reaction rate, chemical equilibrium, reaction heat, carbon skeleton, functional group, isomerism and homology, structural and spatial isomerism , the main types of reactions in inorganic and organic chemistry.
- Reveal relationships between concepts.
- Use the most important chemical concepts to explain individual facts and phenomena.
2. Basic laws and theories of chemistry
- Apply the basic principles of chemical theories (the structure of the atom, chemical bonding, electrolytic dissociation, acids and bases, the structure of organic compounds, chemical kinetics) to analyze the structure and properties of substances
- Understand the limits of applicability of the studied chemical theories
- Understand the meaning of the Periodic Law D.I. Mendeleev and use it for qualitative analysis and substantiation of the basic laws of the structure of atoms, the properties of chemical elements and their compounds
3. The most important substances and materials
- Classify inorganic and organic substances according to all known classification criteria
- Understand that the practical use of substances is due to their composition, structure and properties
- Be aware of the role and significance of the substance in practice
- Explain the general methods and principles for obtaining the most important substances
Be able to:
1. name
- studied substances according to trivial or international nomenclature
2. Define / classify:
- valency, oxidation state of chemical elements, ion charges;
- in compounds and type of crystal lattice;
- spatial structure of molecules;
- the nature of the environment of aqueous solutions of substances;
- oxidizing agent and reducing agent;
- belonging of substances to different classes of inorganic and organic compounds;
- homologues and isomers;
- chemical reactions in inorganic and organic chemistry (according to all known classification criteria)
3. Characterize:
- s-, p- and d-elements according to their position in the Periodic system of D.I. Mendeleev;
- general chemical properties of simple substances - metals and non-metals;
- general chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic compounds, properties of individual representatives of these classes;
- structure and chemical properties of the studied organic compounds
4. Explain:
- dependence of the properties of chemical elements and their compounds on the position of the element in the Periodic system D.I. Mendeleev;
- the nature of the chemical bond (ionic, covalent, metallic, hydrogen);
- the dependence of the properties of inorganic and organic substances on their composition and structure;
- the essence of the studied types of chemical reactions: electrolytic dissociation, ion exchange, redox (and compose their equations);
- the influence of various factors on the rate of a chemical reaction and on the shift in chemical equilibrium
5. Plan/Perform:
- an experiment on obtaining and recognizing the most important inorganic and organic compounds, taking into account the acquired knowledge about the rules for safe work with substances in the laboratory and at home;
- calculations by chemical formulas and equations
Test work Grade 8
CMM specification for carrying out control work No. 1 on the topic "Atoms of chemical elements"
The purpose of the test: to assess the level of mastery of the content of the topic "Atoms of chemical elements" by each student
“The content of the control tasks is determined by the content of the work program on the topic “Atoms of chemical elements” of the subject “chemistry”: simple and complex substance, chemical element, periodic system of chemical elements, chemical formula, relative atomic and molecular masses, atomic structure, structure of electron shells, chemical bond.
Difficulty level
Code by specifier
Job type
Subject
Score in points
1
B
C-1.6.
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
Simple and complex matter
2 minutes.
1b
2
B
C-4.5.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
2 minutes.
1b
3
B
C-1.2.
UP-2.5.1
Qualitative task
Periodic system
2 minutes.
1b
4
B
C-1.1.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
isotopes
2 minutes.
1b
5
B
C-1.1.
UP-2.2.1.
Qualitative task
The structure of the atom
2 minutes.
1b
6
B
C-1.1.
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
2 minutes.
1b
7
B
C-1.1.
UP-2.5.1.
Qualitative task
The structure of the electron shell
2 minutes.
1b
8
B
C-1.3.
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
Electronegativity
2 minutes.
1b
9
B
C-1.2.
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Periodic system
2 minutes.
1b
10
B
C-1.2.1.
UP-2.2.1.
Design problem
The structure of the atom
2 minutes.
1b
11
P
C-1.6.
UP-1.1.
Matching
Signs of chemical elements
4 min.
2b
12
P
C-4.5.
UP-1.2.
Relative molecular weight
4min
2b
13
AT
C-1.1.
UP-2.5.1
The electronic structure of the atom
8min
3b
14
AT
C-1.3.
UP-1.2.
Types of chemical bond
8 min.
3b
Codifier
control work No. 1on the topic "Atoms of chemical elements"
THE CODE
1
Substance
Periodic law and Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev 1
1.2.1
Groups and periods of the Periodic system. The physical meaning of the serial number of a chemical element
1.2.2
Patterns of changes in the properties of elements and their compounds in connection with the position in the Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev
Atoms and molecules. Chemical element. Simple and complex substances
4
Carrying out calculations based on formulas and equations of reactions
THE CODE
1
Know/Understand:
1.2.
the most important chemical concepts: substance, chemical element, atom, molecule, relative atomic and molecular masses, chemical bond.
2.
be able to name
2.1.1
chemical elements;
2.2
be able to explain
2.2.1
the physical meaning of the atomic (serial) number of a chemical element, group and period numbers in the Periodic system of D.I. Mendeleev, to which the element belongs;
2.4
be able to identify
2.4.1
2.5
Compose:
2.5.1.
schemes of the structure of atoms of the first 20 elements of the Periodic system D.I. Mendeleev;
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
13
score
Maximum score
14.
score
The correct answer to the question is presented and sufficient justification is given, which does not contain errors.
The correct answer to the question is presented, but its rationale is not complete enough
Only correct answer is given
Maximum score
Number of points
Less than 7
7-10
11-15
16-20
Grade
Achievement level
Short
Base
elevated
Test work Grade 8
KIM specification for monitoring control work for the first half of the year.
Type of control: internal monitoring
The purpose of the test: to assess the level of mastering by each student of the content of the topics "Atoms of chemical elements", "Types of chemical bonds", "Simple substances. Quantitative ratios”, “Compounds of chemical elements”
The content of control tasks is determined by the content of the work program on the topics: "Atoms of chemical elements", "Types of chemical bond", "Simple substances. Quantitative ratios”, “Compounds of chemical elements”
You have 45 minutes to complete the test. The work consists of 2 parts and includes 15 tasks.
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 4 advanced tasks. For the performance of each task - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing the task -3 points.
The maximum number of points is 24 points
When developing tasks, time standards were taken into account, enshrined in the GIA Specification for tasks of various levels of complexity and for the performance of the entire work.
The distribution of tasks by difficulty levels, checked elements of subject content, level of training, types of tasks and execution time is presented in Table 1
Difficulty level
Code by specifier
Job type
Subject
Score in points
1
B
C-1.2.1. UP-1.1.1.
Qualitative task
Periodic system
1b
2
B
C-1.2.1. UP-1.1.1.
Qualitative task
isotopes
1b
3
B
C-1.1.1. UP-1.1.1.
Qualitative task
The structure of the atom
1b
4
B
C-1.2.1. UP-1.1.1.
Qualitative task
The structure of the atom
1b
5
B
C-1.2.1. UP-1.2.1.
Qualitative task
1b
6
B
C-1.2.1. UP-1.2.1.
Qualitative task
Periodic system
1b
7
B
C-1.2.1. UP- 1.2.1.
Qualitative task
Allotropy
1b
8
B
C-1.2.1. UP-1.1.1.
Qualitative task
The structure of electron shells
1b
9
B
C-4.3.1. UP- 2.5.2.
Design problem
mole
1b
10
B
C-1.2.1. UP- 1.1.3.
Qualitative task
Simple substances
1b
11
P
C-1.2.1. UP-1.2.1.
Matching
The structure of the atom
2b
12
P
C-1.3.1. UP-2.4.2.
Matching
Types of chemical bond
2b
13
P
C-4.3.1. UP-2.5.2.
Design problem
Molecular mass
2b
14
P
C-1.2.1. UP-1.1.3.
Matching
Aggregate state of substances
2b
15
P
C-4.3.3. UP-.
Calculation problem with an open answer
3b
16
P
C-4.3.3. UP-.
Calculation problem with an open answer
3b
Test work Grade 8
CMM specification for carrying out control work No. 2 on the topic "Compounds of chemical elements"
Type of control: internal monitoring
The purpose of the test: to assess the level of development by each student of the content of the topic "Compounds of chemical elements"
You have 45 minutes to complete the test. The work consists of 2 parts and includes 14 tasks.
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing 13.14 tasks -3 points.
The maximum number of points is 20 points.
When developing tasks, time standards were taken into account, enshrined in the GIA Specification for tasks of various levels of complexity and for the performance of the entire work.
The distribution of tasks by difficulty levels, checked elements of subject content, level of training, types of tasks and execution time is presented in Table 1
Difficulty level
Code by specifier
Job type
Subject
Estimated time to complete the task.
Score in points
1
B
C-1.6.
UP-1.1
Qualitative task
General formulas of the main classes of inorganic substances.
2 minutes.
1b
2
B
C-4.5.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
Oxidation state
2 minutes.
1b
3
B
C-1.6.
UP-2.4.4
Qualitative task
2 minutes.
1b
4
B
C-1.6
UP-2.4.4
Qualitative task
Classes of inorganic compounds
2 minutes.
1b
5
B
C-1.6
UP-2.4.4
Qualitative task
Classes of inorganic compounds
2 minutes.
1b
6
B
C-1.6
UP-2.2.1
Qualitative task
Nomenclature of inorganic compounds
2 minutes.
1b
7
B
C-4.5.2
UP-2.8.1.
Design problem
Mass fraction
2 minutes.
1b
8
B
C-1.3.
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
Ion charge
2 minutes.
1b
9
B
C-1.2.
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
Crystal cell
2 minutes.
1b
10
B
C-1.2.1.
UP-2.2.1.
Qualitative task
Pure substances and mixtures
2 minutes.
1b
11
P
C-1.4.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
Oxidation state
4 min.
2b
12
P
C-1.6
UP-2.4.4
Matching
Classes of inorganic compounds
4min
2b
13
AT
C-4.5.2.
UP-2.8.1
Design problem
Volume fraction
8min
3b
14
AT
C-5.3, 4.5.1.
UP-2.8.1
Qualitative task with an open answer
Mass fraction, man in the world of substances.
8 min.
3b
Codifier
Elements of the content and requirements for the level of training of students for conducting monitoring tests in chemistry for the first half of the year.
Section 1. Codifier. Content elements
THE CODE
Content elements verified by CMM tasks
1.1.1.
The structure of the electron shells of atoms of the elements of the first four periods
1.2.1.
Periodic law and Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev Patterns of changes in the properties of elements and their compounds by periods and groups
4.3.1.
Calculation of the mass of a substance.
4.3.3.
Calculations of the mass of a substance or volume of gases.
Section 2. Codifier. Requirements for the level of training.
THE CODE
Skills and activities tested by KIM tasks
1.1.1.
Understand the meaning of the most important concepts (highlight their characteristic features): substance, chemical element, atom, molecule, relative atomic and molecular masses, ion, isotopes, chemical bond, electronegativity.
1.2.1.
Apply the basic provisions of chemical theories (structure of the atom, chemical bond,) to analyze the structure and properties of substances
1.1.3.
Use the most important chemical concepts to explain individual facts and phenomena
2.4.2.
Explain the nature of the chemical bond (ionic, covalent, metallic, hydrogen);
2.5.2.
calculations by chemical formulas and equations
Test in chemistry, grade 8
Codifier
Elements of content and requirements for the level of training of students, for conductingcontrol work No. 2on the topic "Compounds of chemical elements"
Section 1. Codifier. Content elements
THE CODE
Content elements verified by CMM tasks
1
Substance
Valency of chemical elements. The degree of oxidation of chemical elements
Pure substances and mixtures
The structure of substances. Chemical bond: covalent (polar and non-polar), ionic, metallic
5
Chemistry and life
Man in the world of substances, materials and chemical reactions
4
Methods of knowledge of substances and chemical phenomena. Experimental Foundations of Chemistry
4.5.2.
Calculating the mass fraction of a solute in a solution
4.5.1
Calculation of the mass fraction of a chemical element in a substance
Section 2. Codifier. Requirements for the level of training.
THE CODE
Skills and activities tested by KIM tasks
1
know
chemical symbols: signs of chemical elements, formulas of chemicals, equations of chemical reactions;
1.2.
the most important chemical concepts: substance, chemical element, atom, molecule, relative atomic and molecular masses, ion, cation, anion, chemical bond, electronegativity, valence, degree of oxidation, mole, molar mass, molar volume, solutions, electrolytes and non-electrolytes, electrolytic dissociation, oxidizing agent and reducing agent, oxidation and reduction, reaction heat, main types of reactions in inorganic chemistry;
2.
Know how to name:
2.1.2
compounds of the studied classes of inorganic substances
2.2
Define:
2.4.1
the composition of substances according to their formulas;
2.4,2
valency and oxidation state of an element in a compound
2.4.4
belonging of substances to a certain class of compounds
2.5
Compose:
2.5.2.
formulas of inorganic compounds of the studied classes;
Calculate:
2.8.1
mass fraction of a chemical element according to the formula
Assessment system for tests in chemistry
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing the task -3 points.
Part 2. Solving a task with a detailed answer.
13
score
The correct answer is given to the question
The correct answer to the question was presented, but a mathematical error was made
Only correct answer is given
Maximum score
14.
score
The formula of the substance is written down, the chemical name is given, the mass fraction is calculated
The formula of the substance is written down, the chemical name is given
The formula of the substance is written
Maximum score
Translation of the test score into marks on a five-point system.
Number of points
Less than 7
7-10
11-15
16-20
Grade
Achievement level
Short
Base
elevated
Test work Grade 8
Specification of KIM for conducting control work No. 3 on the topic "Changes that occur with substances"
Type of control: internal monitoring
The purpose of the test: to assess the level of mastery of the content of the topic "Changes that occur with substances" by each student
“The content of control tasks is determined by the content of the work program on the topic “Changes that occur with substances” of the subject “chemistry”: physical, chemical phenomena, signs of chemical reactions, types of chemical reactions, exothermic and endothermic reactions, catalyst, pure substances, mixtures, methods separation of mixtures, chemical equations, coefficients.
You have 45 minutes to complete the test. The work consists of 2 parts and includes 14 tasks.
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing 13.14 tasks -3 points.
The maximum number of points is 20 points.
When developing tasks, time standards were taken into account, enshrined in the GIA Specification for tasks of various levels of complexity and for the performance of the entire work.
The distribution of tasks by difficulty levels, checked elements of subject content, level of training, types of tasks and execution time is presented in Table 1
Difficulty level
Code by specifier
Job type
Subject
Estimated time to complete the task.
Score in points
1
B
C-2.1
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
Phenomena that occur with substances.
2 minutes.
1b
2
B
C-2.1
UP-1.2.1
Qualitative task
Signs of chemical reactions.
2 minutes.
1b
3
B
C-2.1
UP-2.5.3
Qualitative task
Arrangement of coefficients
2 minutes.
1b
4
B
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Types of chemical reactions
2 minutes.
1b
5
B
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Types of chemical reactions
2 minutes.
1b
6
B
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Types of chemical reactions
2 minutes.
1b
7
B
C-2.1
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
Conditions for the occurrence of chemical reactions.
2 minutes.
1b
8
B
C-2.2
UP-1.2
Qualitative task
A range of stress metals
2 minutes.
1b
9
B
C-2.1
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Types of chemical reactions
2 minutes.
1b
10
B
C-4.5.3
UP-2.8.3
Design problem
Calculations on chemical equations.
2 minutes.
1b
11
P
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Matching
Types of chemical reactions
4 min.
2b
12
P
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Matching
Types of chemical reactions
4min
2b
13
AT
C-2.1
UP-2.5.3
Qualitative task with an open answer.
Chemical equations. Types of chemical reactions.
8min
3b
14
AT
C-4.5.3
UP-2.9.2
Calculation problem with an open answer
Calculation problem with an open answer.
8 min.
3b
Test in chemistry, grade 8
Codifier
Elements of content and requirements for the level of training of students, for conductingcontrol work No. 3on the topic "Changes occurring with substances"
Section 1. Codifier. Content elements
THE CODE
Content elements verified by CMM tasks
Pure substances and mixtures
Chemical reaction. Conditions and signs of chemical reactions. Chemical equations. Conservation of the mass of substances in chemical reactions
Classification of chemical reactions according to various criteria: the number and composition of the starting and obtained substances, changes in the oxidation states of chemical elements, absorption and release of energy
4.5.3
Section 2. Codifier. Requirements for the level of training.
THE CODE
Skills and activities tested by KIM tasks
1
Know/Understand:
the most important chemical concepts: substance, chemical element, atom, molecule, relative atomic and molecular masses, ion, cation, anion, chemical bond, electronegativity, valency, oxidation state, mole, molar mass, molar volume, solutions, electrolytes and non-electrolytes, electrolytic dissociation, oxidizing agent and reducing agent, oxidation and reduction, reaction heat, main types of reactions in inorganic chemistry;
1.2.1
characteristic features of the most important chemical concepts;
2.
Be able to define / classify, compose, calculate:
2.4.5
types of chemical reactions;
2.5.3
equations of chemical reactions
2.8.3
use the acquired knowledge and skills in practical activities and everyday life for:
2.9.2
explanations of individual facts and natural phenomena;
Assessment system for tests in chemistry
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing the task -3 points.
Part 2. Solving a task with a detailed answer.
13
score
The equation of a chemical reaction is written
Arranged odds
Reaction type indicated
Maximum score
14.
score
The correct answer to the question is presented and sufficient justification is given, which does not contain errors.
The correct answer to the question is presented, but its rationale is not complete enough
Only correct answer is given
Maximum score
Translation of the test score into marks on a five-point system.
Number of points
Less than 7
7-10
11-15
16-20
Grade
Achievement level
Short
Base
elevated
Test work Grade 8
Specification of KIM for conducting control work No. 4 on the topic “Solutions. Properties of electrolyte solutions »
Type of control: internal monitoring
The purpose of the test: to assess the level of mastering by each student of the content of the topic “Solutions. Properties of electrolyte solutions»
You have 45 minutes to complete the test. The work consists of 2 parts and includes 14 tasks.
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing 13.14 tasks -3 points.
The maximum number of points is 20 points.
When developing tasks, time standards were taken into account, enshrined in the GIA Specification for tasks of various levels of complexity and for the performance of the entire work.
The distribution of tasks by difficulty levels, checked elements of subject content, level of training, types of tasks and execution time is presented in Table 1
Difficulty level
Code by specifier
Job type
Subject
Estimated time to complete the task.
Score in points
1
B
C-2.4
UP-1.2.2
Qualitative task
Electrolytic dissociation
2 minutes.
1b
2
B
C-2.3
UP-2.2.3.
Qualitative task
Degree of dissociation
2 minutes.
1b
3
B
C-2.1
UP-2.2.3
Qualitative task
Changing the color of indicators
2 minutes.
1b
4
B
C-2.5
UP-2.4.6
Qualitative task
Ion exchange reactions
2 minutes.
1b
5
B
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Conditions for the occurrence of ion exchange reactions
2 minutes.
1b
6
B
C-2.5
UP-2.4.6
Qualitative task
Ion exchange reactions
2 minutes.
1b
7
B
C-3.2.1.
UP-2.3.3.
Qualitative task
2 minutes.
1b
8
B
C-3.2.2.
UP-2.3.3.
Qualitative task
Chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances
2 minutes.
1b
9
B
C-2.2
UP-2.4.5
Qualitative task
Qualitative reactions
2 minutes.
1b
10
B
C-3.3.
UP-2.3.4.
Qualitative task
genetic connection
2 minutes.
1b
11
P
C-2.5
UP-2.4.6
Matching
Ion exchange reactions
4 min.
2b
12
P
C-2.5
UP-2.4.5
Matching
Ion exchange reactions
4 min.
2b
13
AT
C-3.2.3.,3.2.4.
UP-2.5.3
Qualitative task with an open answer.
Chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances
8 min.
3b
14
AT
C-4.5.3
UP-2.8.3.
Calculation problem with an open answer
Calculations by the chemical equations of the volume of a substance by the mass of the reaction products
8 min.
3b
Test in chemistry, grade 8
Codifier
Elements of content and requirements for the level of training of students, for conductingcontrol work No. 4 on the topic “Solutions. Properties of electrolyte solutions »
Section 1. Codifier. Content elements
THE CODE
Content elements verified by CMM tasks
2
Chemical reaction
Electrolytes and non-electrolytes
Cations and anions. Electrolytic dissociation of acids, alkalis and salts (medium
Ion exchange reactions and conditions for their implementation
3
Elementary Foundations of Inorganic Chemistry
3.2.1.
3.2.2.
3.2.3.
Chemical properties of acids
3.2.4.
Chemical properties of salts
3.3.
4
.
Experimental Foundations of Chemistry
4.5.3.
Calculation of the amount of a substance, mass or volume of a substance from the amount of a substance, mass or volume of one of the reactants or reaction products
Section 2. Codifier. Requirements for the level of training.
THE CODE
Skills and activities tested by KIM tasks
1
Know/Understand:
1.2.2
about the existence of a relationship between the most important chemical concepts
2.
Be able to explain / classify, compose, calculate:
2.2.3.
the essence of the process of electrolytic dissociation and ion exchange reactions
2.3.3
chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances (oxides, acids, bases and salts)
2.8.3
amount of a substance, volume or mass of a substance by the amount of a substance, volume or mass of reactants or reaction products
2.4
determine
2.4.6.
the possibility of ion exchange reactions;
2.5.
make up
2.5.3.
equations of chemical reactions
2.3.4.
Assessment system for tests in chemistry
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing the task -3 points.
Part 2. Solving a task with a detailed answer.
13
score
Three equations of chemical reactions are written in molecular and ionic form
Two reaction equations are written in molecular and ionic form
One reaction equation written in molecular and ionic form
Maximum score
14.
score
2) The amount of substance and the mass of silver nitrate contained in the initial solution were calculated: according to the reaction equation
3) The mass fraction of silver nitrate in the initial solution was calculated
The answer is correct and complete, contains all the elements
3
2
1
0
Maximum score
3
Translation of the test score into marks on a five-point system.
Number of points
Less than 7
7-10
11-15
16-20
Grade
2
3
4
5
Achievement level
Short
Base
elevated
Test work Grade 8
Specification of KIM for carrying out the final monitoring control work.
Type of control: internal monitoring
The purpose of the test: to assess the level of mastery of the content of the topics of the 8th grade chemistry course by each student.
According to the content, the work will allow you to check the success of mastering the topics:
1. Periodic law and the periodic system of chemical elements. The structure of the atom.
2. Chemical bond.
3. Compounds of chemical elements.
4. Chemical reactions. electrolytic dissociation.
5. Methods for obtaining substances, the use of substances and chemical reactions.
The work will reveal the formation of the following subject skills:
1. Describe the structure of the atom, the properties of elements and their compounds by position in the periodic system.
2. Determine the type of chemical bond, the degree of oxidation of chemical elements.
3. Name substances, classify them, describe properties and methods of obtaining.
4. Compose equations of chemical reactions of various types, ED equations.
5. Carry out calculations using chemical formulas and equations.
The work will reveal the assimilation of content at a basic level (B), advanced (P)
high (in)
You have 45 minutes to complete the test. The work consists of 2 parts and includes 14 tasks.
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing 13.14 tasks -3 points.
The maximum number of points is 20 points.
When developing tasks, time standards were taken into account, enshrined in the GIA Specification for tasks of various levels of complexity and for the performance of the entire work.
The distribution of tasks by difficulty levels, checked elements of subject content, level of training, types of tasks and execution time is presented in Table 1
Difficulty level
Code by specifier
Job type
Subject
Estimated time to complete the task.
Score in points
1
B
C-1.6.
UP-1.3.
Qualitative task
Chemical formulas
2 minutes
1b
2
B
C-1.1.
UP-1.1.
Qualitative task
The structure of the atom
2 minutes
1b
3
B
C-1.3.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
chemical bond
2 minutes
1b
4
B
C-1.3.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
Crystal cell
2 minutes
1b
5
B
C-2.2
UP-2.5.3.
Qualitative task
Types of chemical reactions
2 minutes
1b
6
B
C-3.3.
UP-2.3.4.
Qualitative task
genetic connection
2 minutes
1b
7
B
C-3.2.1.
UP-2.3.3.
Qualitative task
Chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances
2 minutes
1b
8
B
C-2.2.
UP-1.1.
Qualitative task
Reaction characteristic
2 minutes
1b
9
B
C-2.6.
UP-1.2.
Qualitative task
Redox reactions
2 minutes
1b
10
B
C-3.2.3.
UP-2.3.3.
Qualitative task
Chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances
2 minutes
1b
11
P
C-3.2.4.
UP-2.3.3.
Matching
Chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances
4 min
2b
12
P
C-1.6.
UP-2.1.2.
Matching
Classification of inorganic substances
4 min
2b
13
AT
C-4.5.3.
UP-2.8.3.
Calculation problem with an open answer
Calculations on the chemical equations of the volume of a substance by the mass of the reaction products
8 min
3b
14
AT
C-3.3.
UP-2.5.3..
Qualitative task with an open answer
Compose equations of reactions of different types
8 min
3b
Test in chemistry, grade 8
Codifier
Elements of the content and requirements for the level of training of students, for the final monitoringcontrol work
Section 1. Codifier. Content elements
THE CODE
Content elements verified by CMM tasks
1
Substance
1.6.
Atoms and molecules. Chemical element. Simple and complex substances. The main classes of inorganic substances. Nomenclature of inorganic compounds
1.1
The structure of the atom. The structure of the electron shells of atoms of the first 20 elements of the Periodic Table D.I. Mendeleev
1.3.
The structure of substances. Chemical bond: covalent (polar and non-polar), ionic, metallic
2
Chemical reactions.
2.2.
Classification of chemical reactions according to various criteria: the number and composition of the starting and obtained substances, changes in the oxidation states of chemical elements, absorption and release of energy.
2.6.
Redox reactions. Oxidizing agent and reducing agent
3
Elementary foundations of inorganic chemistry.
3.2.1.
Chemical properties of oxides: basic, amphoteric, acidic
3.2.2.
Chemical properties of bases
3.2.3.
Chemical properties of acids
3.2.4.
Chemical properties of salts (medium)
3.3.
The relationship of different classes of inorganic substances
4
Methods of knowledge of substances and chemical phenomena. Experimental Foundations of Chemistry
4.2.
Determination of the nature of the medium of a solution of acids and alkalis using indicators. Qualitative reactions to ions in solution (chloride, sulfate, carbonate ions, ammonium ion
4.4.
Obtaining and studying the properties of the studied classes of inorganic substances
4.5.3.
Calculation of the amount of a substance, mass or volume of a substance from the amount of a substance, mass or volume of one of the reactants or reaction products
Section 2. Codifier. Requirements for the level of training.
THE CODE
Skills and activities tested by KIM tasks
1
Know/Understand:
1.1.
chemical symbols: signs of chemical elements, formulas of chemicals, equations of chemical reactions;
1.2.
element, atom, molecule, relative atomic and molecular masses, ion, cation, anion, chemical bond, electronegativity, valency, oxidation state, mole, molar mass, molar volume, solutions, electrolytes and non-electrolytes, electrolytic dissociation, oxidizing agent and reducing agent, oxidation and recovery, thermal effect of the reaction, the main types of reactions in inorganic chemistry;
2
Know how to name:
2.1.2.
compounds of the studied classes of inorganic substances;
2
Be able to describe:
2.3.3.
chemical properties of the main classes of inorganic substances (oxides, acids, bases and salts);
2.3.4.
the relationship between the composition, structure and properties of individual representatives of organic substances
Be able to compose:
2.5.3.
equations of chemical reactions
Be able to calculate:
2.8.3.
amount of a substance, volume or mass of a substance by the amount of a substance, volume or mass of reactants or reaction products
Assessment system for tests in chemistry
Part 1 includes 10 basic level tasks. Each question has 4 possible answers, of which only one is correct. For the completion of each task - 1 point.
Part 2 consists of 2 advanced tasks and 2 high level tasks. For completing tasks 11.12 - 2 points, if one mistake is made, then the answer is estimated at 1 point. If two or more errors are made or there is no answer, then 0 points are given. The last two tasks require a full answer. For completing the task -3 points.
Part 2. Solving a task with a detailed answer.
13
Content of the criterion
score
1) The reaction equation is composed:
2) Molecular weights determined
3) Gas volume calculated
The answer is correct and complete, contains all the elements
3
The first two elements of the answer are written correctly
2
One element of the answer is correctly written
1
All elements of the answer are written incorrectly
0
Maximum score
3
14.
Content of the criterion
score
The correct answer to the question is presented and sufficient justification is given, which does not contain errors.
3
The correct answer to the question is presented, but its rationale is not complete enough
2
Only correct answer is given
1
Maximum score
3
Translation of the test score into marks on a five-point system.
Number of points
Less than 7
7-10
11-15
16-20
Grade
2
3
4
5
Achievement level
Short
Base
elevated
Secondary general education
Demo version of the exam-2019 in chemistry
We bring to your attention an analysis of the demo version of the USE-2019 in chemistry.This material contains explanations and a detailed solution algorithm, as well as recommendations on the use of reference books and manuals that may be needed in preparation for the exam.
On August 24, 2018, a demo version of the USE-2019 in chemistry appeared on the official website of FIPI, as well as a specification and a codifier.
The manual contains training tasks of basic and advanced levels of complexity, grouped by topic and type. The tasks are arranged in the same sequence as proposed in the examination version of the exam. At the beginning of each type of task are the content elements to be checked - topics that should be studied before proceeding with the implementation. The manual will be useful for teachers of chemistry, as it makes it possible to effectively organize the educational process in the classroom, conduct ongoing monitoring of knowledge, and prepare students for the exam.
The structure and content of the KIM USE in chemistry in 2019 is regulated by the following documents:
- Codifier of content elements and requirements for the level of training of graduates of educational organizations for the unified state exam in chemistry in 2019;
- Specification of control measuring materials for the unified state exam in chemistry in 2019;
- Demonstration version of the control measuring materials of the Unified State Exam 2019
Codifier was developed on the basis of the federal component of the state standard for secondary (complete) general education in chemistry of 2004 and adequately determines the total volume of content checked by the USE control measuring materials. The content basis of control measuring materials is specified in the codifier due to the presence in it of operationalized skills and activities of two large blocks “know/understand” and “be able”, which are presented in the requirements of the standard.
The codifier covers a minimum of knowledge, skills, methods of cognitive and practical activities that meets the requirements for the level of training of graduates, and thus ensures the independence of KIM from teaching chemistry at school according to variant programs and textbooks.
AT specifications of control measuring materials in chemistry
- the appointment of KIM USE was determined;
- documents are presented that determine the content of the KIM USE;
- describes approaches to the selection of content, the development of the structure of the KIM USE
- the structure of the KIM USE is presented, the characteristics of tasks of various types are given, it is shown how they are distributed by parts of the work, by content blocks and content lines, by types of skills being tested and methods of action;
- the time for completing the work, additional materials and equipment that can be used during the exam are indicated;
- a system for evaluating individual tasks and the entire work as a whole is presented;
- changes in KIM USE 2019 compared to 2018 are described;
- a generalized plan of the KIM USE variant of 2019 is presented.
Demo version USE in Chemistry 2019 compiled in full accordance with the codifier and specification and makes it possible to get acquainted with the types of tasks that will be presented in the 2019 examination paper, with the level of their complexity, the requirements for the completeness and correctness of writing a detailed answer, with the criteria for assessing tasks.
However, it should be taken into account that:
- tasks included in the demo, do not cover all content elements, which will be tested with CMM variants in 2019;
- a complete list of elements that can be controlled at the unified state exam in 2019 is given in the codifier of content elements and requirements for the level of preparation of graduates of organizations for the unified state exam;
- appointment The demo version is to enable any USE participant and the general public to get an idea of the structure of the KIM options, the types of tasks and their levels of complexity: basic, advanced and high.
The examination paper consists of two parts, including 35 tasks. Part 1 contains 29 tasks of basic and advanced difficulty with a short answer. The answer to the tasks of part 1 is a sequence of numbers or a number. Part 2 contains 6 tasks of a high level of complexity with a detailed answer. The answers to tasks 30-35 include a detailed description of the entire progress of the task.
3.5 hours (210 minutes) are allotted to complete the examination paper in chemistry.
When performing work, the Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev, table of solubility of salts, acids and bases in water, electrochemical series of metal voltages. These accompanying materials are attached to the text of the work. You may also use a non-programmable calculator.
Tasks in the examination paper are divided into four content blocks, which are divided into content lines:
- “Theoretical foundations of chemistry: “The structure of the atom. Periodic law and Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev. Patterns of changes in the properties of chemical elements by periods and groups. “The structure of matter. Chemical bond";
- "Inorganic substances: classification and nomenclature, chemical properties and genetic relationship of substances of various classes";
- "Organic substances: classification and nomenclature, chemical properties and genetic relationship of substances of various classes";
- Methods of knowledge in chemistry. Chemistry and life: Chemical reaction. Methods of knowledge in chemistry. Chemistry and life. Calculations by chemical formulas and reaction equations.
When determining number of tasks KIM USE, focused on checking the assimilation of the educational material of individual blocks, first of all, the occupied by them volume in the content of the chemistry course.
Consider the tasks presented in the examination paper, referring to the demo version of the exam in chemistry 2019.
Block “Structure of the atom. Periodic law and Periodic system of chemical elements D.I. Mendeleev. Patterns of changes in the properties of chemical elements by periods and groups. “The structure of matter. Chemical bond»
This block contains tasks of only a basic level of complexity, which were focused on testing the assimilation of concepts that characterize the structure of atoms of chemical elements and the structure of substances, as well as testing the ability to apply the Periodic Law to compare the properties of elements and their compounds.
Let's take a look at these tasks.
Tasks 1-3 are united by a single context:
Exercise 1
Determine the atoms of which of the elements indicated in the row in the ground state have four electrons at the external energy level.
Task 3
From among the elements listed in the row, select two elements that exhibit the lowest oxidation state, equal to -4.
Write down the numbers of the selected elements in the answer field.
For execution tasks 1 it is necessary to apply knowledge about the structure of the electron shells of atoms of chemical elements of the first four periods, s-, p- and d- elements, about uh electronic configurations of atoms, ground and excited states of atoms. The presented elements are in the main subgroups, therefore the number of external electrons of their atoms is equal to the number of the group to which this element is located. The four outer electrons have silicon and carbon atoms.
Task 1 in 2018 was successfully completed by 61.0% of examinees.
Successful completion tasks 2 involves understanding the meaning of the Periodic Law of D.I. Mendeleev and regularities of changes in the chemical properties of elements and their compounds by periods and groups in connection with the peculiarities of the structure of atoms of elements. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that it is necessary not only to select elements that are in the same period, but be sure to arrange them in a certain sequence. In this task, you should arrange the elements in ascending order of their metallic properties. To do this, we must remember that within one period of increasing the charge of the nucleus of an atom, the metallic properties of the elements decrease. Therefore, in order of increasing metallic properties, the elements of the III period should be arranged in the sequence: Si - Mg - Na.
In 2018, task 2 was successfully completed by 62.0% of examinees.
For execution tasks 3 one should understand the meaning of the concepts of a chemical element, atom, molecule, ion, chemical bond, electronegativity, valence, oxidation state, be able to determine valence, oxidation state of chemical elements, ion charges, using the basic principles of the theory of atomic structure. The lowest oxidation state of non-metal elements is determined by the number of electrons that are not enough to complete the external electronic level, which can contain no more than eight electrons. The lowest oxidation state, equal to -4, will have non-metal elements of the 4th group, in this context - silicon and carbon.
Task 3 was successfully completed by 80.2% of the exam participants.
The results of completing these tasks in 2018 indicate that schoolchildren cope with them quite successfully, in contrast to tasks 4 the same block, aimed at determining the ability to determine the type of chemical bond in compounds, determine the nature of the chemical bond (ionic, covalent, metallic, hydrogen) and the dependence of the properties of inorganic and organic substances on their composition and structure. In 2018, only 52.6% of the participants in the exam were able to complete this task.
Task 4
From the proposed list, select two compounds in which there is an ionic chemical bond.
- Ca(ClO 2) 2
- HClO 3
- NH4Cl
- HClO 4
- Cl2O7
Write down the numbers of the selected connections in the answer field.
When performing this task, it is necessary to analyze the qualitative composition of each substance specified in the task. Schoolchildren often do not take into account that within one substance, different types of chemical bonds can exist between atoms, depending on the value of their electronegativity. So, between the atoms of chlorine and oxygen in calcium chlorate Ca (ClO 2) 2 there is a covalent polar bond, and between the chlorate ion and calcium - ionic. Schoolchildren also forget that inside the ammonium cation, the nitrogen atom is connected to hydrogen atoms by covalent polar bonds, but the ammonium cation itself is connected to the anions of acid residues by ionic bonds. Thus, the correct answer is calcium chlorate (1) and ammonium chloride (3).
Block "Inorganic substances"
The assimilation of the content elements of this block is checked by tasks of basic, advanced and high levels of complexity: a total of 7 tasks, of which 4 tasks of a basic level of complexity, 2 tasks of an increased level of complexity and 1 task of a high level of complexity.
Tasks of the basic level of complexity of this block are presented by tasks with a choice of two correct answers out of five and in the format of establishing a correspondence between the positions of two sets (task 5).
Completing the tasks of the "Inorganic Substances" block involves the use of a wide range of subject skills. Among them are skills: to classify inorganic and organic substances; name substances according to international and trivial nomenclature; characterize the composition and chemical properties of substances of various classes; compose reaction equations confirming the relationship of substances of various classes.
While doing tasks 5 At the basic level of complexity, students need to demonstrate the ability to classify inorganic substances according to all known classification criteria, while demonstrating knowledge of the trivial and international nomenclature of inorganic substances.
Task 5
Establish a correspondence between the formula of a substance and the class / group to which this substance belongs: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Among the presented substances, NH 4 HCO 3 belongs to acid salts, KF - to medium salts, NO is a non-salt-forming oxide. Thus, the correct answer is 431. The results of completing task 5 in 2018 indicate that graduates successfully mastered the ability to classify inorganic substances: the average percentage of completing this task was 76.3.
Schoolchildren cope a little worse with tasks of a basic level of complexity, in which they need to apply knowledge about the characteristic chemical properties of inorganic substances of various classes. These include tasks 6 and 7 .
Task 6
From the proposed list, select two substances, with each of which iron reacts without heating.
- calcium chloride (solution)
- copper(II) sulfate (solution)
- concentrated nitric acid
- dilute hydrochloric acid
- aluminium oxide
When completing this task, it is necessary to carry out the following sequence of mental operations: determine the chemical nature of all the compounds proposed in the task, and then, on the basis of this, determine that iron will not react with a solution of calcium chloride and with aluminum oxide, and concentrated nitric acid at room temperature passivates iron . In accordance with the position in the electrochemical series of voltages, iron reacts without heating with copper (II) sulfate, replacing copper from this salt, and with dilute hydrochloric acid, displacing hydrogen from it. The correct answer is therefore 24.
Task 7 in 2018 was completed by 62.8% of graduates.
Task 7
A strong acid X was added to one of the test tubes with a precipitate of aluminum hydroxide, and a solution of substance Y was added to the other. As a result, the precipitate was observed to dissolve in each of the test tubes. From the proposed list, select substances X and Y that can enter into the described reactions.
- hydrobromic acid
- sodium hydrosulfide
- hydrosulfide acid
- potassium hydroxide
- ammonia hydrate
Task 7 requires a thorough analysis of the conditions, the application of knowledge of the properties of substances and the essence of ion exchange reactions. Task 7 is evaluated with a maximum of 2 points. In 2018, 66.5% of graduates completed task 7.
When performing task 7, proposed in the demo version, it must be taken into account that aluminum hydroxide exhibits amphoteric properties and interacts with both strong acids and alkalis. Thus, substance X is a strong hydrobromic acid, substance Y is an alkali potassium hydroxide. The correct answer is 14.
Tasks 8 and 9 of an increased level of complexity are focused on a comprehensive test of knowledge about the properties of inorganic substances. These tasks are presented in the format of establishing a correspondence between two sets. The performance of each of these tasks is evaluated with a maximum of 2 points.
Task 8
Establish a correspondence between the formula of a substance and the reagents, with each of which this substance can interact: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
SUBSTANCE FORMULA |
REAGENTS |
|
|
D) ZnBr 2 (p–p) |
1) AgNO 3, Na 3 PO 4, Cl 2 2) BaO, H 2 O, KOH 3) H 2, Cl 2, O 2 4) HBr, LiOH, CH 3 COOH (solution) 5) H 3 PO 4 (p–p), BaCl 2, CuO |
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
When completing task 8, it is necessary to apply knowledge both about the characteristic properties of the main classes of inorganic compounds, and about the specific properties of individual representatives of these classes.
So, it should be taken into account that sulfur can react with hydrogen, acting as an oxidizing agent, and oxidize under the action of chlorine and oxygen (3).
Sulfur oxide (VI) is a typical acidic oxide that reacts with basic oxide BaO, water and potassium hydroxide (2).
Zinc hydroxide is amphoteric and can react with both acids and alkalis (4).
Zinc bromide can enter into an exchange reaction with silver nitrate and sodium phosphate to form insoluble salts - AgCl and Zn 3 (PO 4) 2, and also interact with chlorine, which displaces bromine from it (1).
So the correct answer is 3241.
This task turns out to be traditionally difficult for schoolchildren: in 2018, 49.3% of graduates completed it completely.
Task 9 presented in the format of establishing a correspondence between the reacting substances and the reaction products between these substances.
Task 9
Establish a correspondence between the starting substances that enter into the reaction and the products of this reaction: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
STARTING SUBSTANCES |
REACTION PRODUCTS |
|
A) Mg and H 2 SO 4 (conc.) B) MgO and H 2 SO 4 B) S and H 2 SO 4 (conc.) D) H 2 S and O 2 (ex.) |
1) MgSO 4 and H 2 O 2) MgO, SO 2 and H 2 O 3) H 2 S and H 2 O 4) SO 2 and H 2 O 5) MgSO 4 , H 2 S and H 2 O 6) SO 3 and H 2 O |
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
When performing task 9, it is necessary to analyze the properties of the substances that enter into the reaction, the conditions for the processes, predict the products of these reactions, choosing them from the proposed list. The fulfillment of the task provides for the complex application of knowledge of the chemical properties of specific substances, taking into account the specified conditions for the reaction between them. When performing this task, it is desirable to write down the equations of the corresponding reactions, which will facilitate the formulation of the answer.
Consider task 9, presented in the demo version. We take into account that concentrated sulfuric acid in the reaction with magnesium will exhibit oxidizing properties due to sulfur atoms in the +6 oxidation state. The reaction products are magnesium sulfate, hydrogen sulfide and water (5).
Magnesium oxide is a basic oxide, which, when interacting with sulfuric acid, forms a salt - magnesium sulfate and water (1).
Concentrated sulfuric acid oxidizes sulfur to sulfur dioxide (4).
In excess of oxygen, hydrogen sulfide is oxidized to sulfur dioxide (4).
So the correct answer is 5144.
Assimilation of knowledge about the relationship of inorganic substances is checked using tasks of a basic level of complexity with a short answer (task 10) and a task of a high level of complexity with a detailed answer (task 32).
Task 9, like task 8, turned out to be difficult for graduates: in 2018, 47.4% of examinees completed it.
Consider task 10 the basic difficulty level from the demo.
Task 10
- KCl (solution)
- K2O
- HCl (ex.)
- CO 2 (solution)
Write in the table the numbers of the selected substances under the corresponding letters.
Sodium carbonate can be obtained by reacting carbon dioxide with potassium oxide K 2 O (2). When carbon dioxide is passed through a solution of an average salt K 2 CO 3, an acid salt KHCO 3 (5) is formed. Hydrochloric acid is also proposed in the list of substances, but in its excess, carbon dioxide is formed, and not an acid salt. So the correct answer is 25.
Task 10, which is assessed with a maximum of 2 points, was successfully completed by 66.5% of graduates in 2018.
Task 32 a high level of complexity is a description of a "thought experiment". To cope with this task, it is often necessary, in addition to the chemical properties of substances, to also know their physical properties (state of aggregation, color, smell, etc.).
Consider task 32 from the demo.
Task 32
During the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of copper (II) nitrate, a metal was obtained. The metal was treated with concentrated sulfuric acid when heated. The resulting gas reacted with hydrogen sulfide to form a simple substance. This substance was heated with a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide.
Write the equations for the four described reactions.
Possible answer:
- 2Cu (NO 3) 2 + 2H 2 O \u003d 2Cu + 4HNO 3 + O 2 (electrolysis)
- Cu + 2H 2 SO 4 (conc.) = CuSO 4 + SO 2 + 2H 2 O
- SO 2 + 2H 2 S \u003d 3S + 2H 2 O
- 3S + 6KOH = 2K 2 S + K 2 SO 3 + 3H 2 O
(possible formation of K 2 S 2 O 3)
Task 32, which is assessed with a maximum of 4 points (one point for each correctly formulated reaction equation), was successfully completed by 37.6% of graduates in 2018.
Block "Organic substances"
The content of the block "Organic substances" is a system of knowledge about the most important concepts and theories of organic chemistry, the characteristic chemical properties of the studied substances belonging to various classes of organic compounds, the relationship of these substances. This block includes 9 tasks. Assimilation of the content elements of this block is checked by tasks of basic (tasks 11–15 and 18), advanced (tasks 16 and 17) and high (task 33) levels of complexity. These tasks also tested the formation of skills and activities similar to those that were named in relation to the elements of the content of the "Inorganic substances" block.
Consider the tasks of the block "Inorganic substances".
While doing tasks 11 At the basic level of complexity, students need to demonstrate the ability to classify organic substances according to all known classification criteria, while demonstrating knowledge of the trivial and international nomenclature of organic substances.
Task 11
Establish a correspondence between the name of the substance and the class / group,
to which this substance belongs: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
Among the substances presented, methylbenzene refers to hydrocarbons, aniline to aromatic amines, and 3-methylbutanal is an aldehyde. Thus, the correct answer is 421. The results of completing task 11 in 2018 indicate that the ability to classify organic substances, compared with the same skill in relation to inorganic substances, is slightly less developed among graduates: the percentage of completion of this task is 61.7.
While doing tasks 12 of the basic level of complexity, graduates need to apply the basic provisions of the theory of organic compounds to analyze the structure and properties of substances, determine the type of chemical bonds in compounds, the spatial structure of molecules, homologues and isomers.
Task 12
From the proposed list, select two substances that are structural isomers of butene-1.
- butane
- cyclobutane
- butin-2
- butadiene-1,3
- methylpropene
Write down the numbers of the selected substances in the answer field.
The isomers of butene-2 having the molecular formula C 4 H 8 will be cyclobutane and methyl propene. The correct answer is 25.
For graduates, this task turned out to be quite difficult: in 2018, the average percentage of its completion was 56.2.
Task 13 the basic level of complexity is aimed at testing the ability to characterize the chemical properties and the main methods for producing hydrocarbons.
Task 13
From the proposed list, select two substances, when interacting with a solution of potassium permanganate in the presence of sulfuric acid, a change in the color of the solution will be observed.
- hexane
- benzene
- toluene
- propane
- propylene
Write down the numbers of the selected substances in the answer field.
When performing this task, it must be taken into account that a solution of potassium permanganate in the presence of sulfuric acid is capable of oxidizing hydrocarbons containing double and triple bonds, as well as benzene homologues. Of the substances presented in the task, these are toluene (methylbenzene) and propylene. Thus, the correct answer is 35. In 2018, only 57.7% of graduates successfully completed this task.
While doing tasks 14 the basic level of complexity requires the application of knowledge about the characteristic chemical properties of oxygen-containing organic compounds.
Task 14
From the proposed list, select two substances with which formaldehyde reacts.
- Ag 2 O (NH 3 solution)
- CH 3 DOS 3
Write down the numbers of the selected substances in the answer field.
Formaldehyde is capable of both reduction and oxidation reactions: hydrogen (3) will reduce it to methanol, and under the action of an ammonia solution of silver oxide (4) it will be oxidized. The correct answer is 34. The percentage of completion of task 14 is even lower than task 13: in 2018, only 56.9% of graduates successfully completed it.
Task 15 the basic level is aimed at testing the ability to characterize the chemical properties and methods for obtaining nitrogen-containing organic compounds (amines and amino acids), as well as biologically important substances (fats, carbohydrates).
Task 15
From the proposed list, select two substances with which methylamine reacts.
- propane
- chloromethane
- hydrogen
- sodium hydroxide
- hydrochloric acid
Write down the numbers of the selected substances in the answer field.
Methylamine is able to react with chloromethane (2), forming a secondary amine salt - dimethylamine chloride, as well as with hydrochloric acid (5), also forming a salt - methylamine chloride. The correct answer is 25. In 2018, only 47% of exam participants successfully completed task 15. The extremely low results of this task allow us to conclude that graduates have poorly formed knowledge about the chemical properties of nitrogen-containing organic compounds and methods for their preparation. The reason for this may be due to the insufficient attention paid to this element of content in the process of studying organic chemistry at school.
Task 16 is focused on testing knowledge of the characteristic chemical properties of hydrocarbons and methods for their production at an increased level of complexity.
Task 16
Establish a correspondence between the name of the substance and the product that is mainly formed during the interaction of this substance with bromine: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
Ethane enters into a substitution reaction with bromine to form bromoethane (5).
The substitution of the hydrogen atom during the bromination of isobutane occurs predominantly at the tertiary carbon atom, resulting in the formation of 2-bromo,2-methylpropane (2).
Bromination of cyclopropane is accompanied by ring breaking with the formation of 1,3-dimethylpropane (3).
During the bromination of cyclohexane, in contrast to cyclopropane, a hydrogen atom substitution reaction occurs in the cycle and bromocyclohexane (6) is formed.
Thus, the correct answer is 5236. This task was completed by the graduates quite successfully - in 2018, 48.7% of the examinees completed it.
Task 17 is aimed at testing the ability to characterize the chemical properties and methods for obtaining oxygen-containing organic compounds (limiting monohydric and polyhydric alcohols, phenol, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters) at an increased level of complexity.
Task 17
Establish a correspondence between the reacting substances and the carbon-containing product that is formed during the interaction of these substances: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
To successfully complete such tasks, it is necessary not only to apply knowledge of the chemical properties of organic compounds, but also to master chemical terminology. In addition, it is necessary to write down the equations of the reactions indicated in the condition in order to make sure that your answer is correct.
The reaction product of acetic acid and sodium sulfide is sodium acetate (5) and hydrogen sulfide.
Formic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium formate (4) and water.
Formic acid under the action of copper (II) hydroxide, when heated, is oxidized to carbon dioxide (6).
The reaction product of ethanol with sodium is sodium ethoxide (2) and hydrogen.
Thus, the correct answer is 5462. In 2018, 48.6% of examinees successfully completed task 17.
Assimilation of the content element "the relationship of hydrocarbons and oxygen-containing organic compounds" is checked task 18 basic level of difficulty and task 33 high level of complexity.
Task 18
The following scheme of transformations of substances is given:
Determine which of the given substances are substances X and Y.
- Cu(OH)2
- NaOH (H2O)
- NaOH (alcohol)
Write in the table the numbers of the selected substances under the corresponding letters.
Ethanol can be obtained from chloroethane under the action of an aqueous solution of alkali (4). Acetaldehyde is formed by the interaction of ethanol with copper oxide (II) (2) when heated. The correct answer is 52. The performance of this task was evaluated with a maximum of 2 points. In 2018, only 56.4% of examinees successfully completed it.
Consider also task 33 of a high level of complexity, which tests the assimilation of the relationship of organic compounds of various classes.
Task 33
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Possible answer:
At a temperature of 180 °C in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, propanol-1 undergoes dehydration with the formation of propene:
Propene, interacting with hydrogen chloride, forms mainly 2-chloropropane in accordance with Markovnikov's rule:

Under the action of an aqueous solution of alkali, 2-chloropropane is hydrolyzed to form propanol-2:
Further, propene (X 1) must be obtained again from propanol-2, which can be carried out as a result of an intramolecular dehydration reaction at a temperature of 180 ° C under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid:
The product of propene oxidation with an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate in the cold is the dihydric alcohol propanediol-1,2, potassium permanganate is reduced to manganese(IV) oxide, which forms a brown precipitate:

In 2018, 41.1% of examinees were able to complete this task completely correctly.
Block “Chemical reaction. Methods of knowledge in chemistry. Chemistry and life. Calculations by chemical formulas and reaction equations"
Assimilation of the elements of the content of this block is checked by tasks of various levels of complexity, including 4 tasks of a basic level of complexity, 4 tasks of an increased level of complexity and 2 tasks of a high level of complexity.
The fulfillment of the tasks of this block provides for the verification of the formation of the following skills: to use in specific situations knowledge about the application of the studied substances and chemical processes, industrial methods for obtaining certain substances and methods for their processing; plan an experiment to obtain and recognize the most important inorganic and organic substances based on the acquired knowledge about the rules for safe work with substances in everyday life; carry out calculations on chemical formulas and equations.
Some of the elements of the content of this block, such as determining the nature of the environment of aqueous solutions of substances, indicators, calculations of the mass or volume fraction of the yield of the reaction product from the theoretically possible, calculations of the mass fraction (mass) of a chemical compound in a mixture, were checked as part of one task in combination with others content elements.
Consider the tasks of this block from the demo version.
Task 19 aimed at testing the ability to classify chemical reactions in inorganic and organic chemistry according to all known classification criteria.
Task 19
From the proposed list of types of reactions, select two types of reactions, which include the interaction of alkali metals with water.
- catalytic
- homogeneous
- irreversible
- redox
- neutralization reaction
Write down the numbers of the selected types of reactions in the answer field.
The reaction of interaction of alkali metals with water is irreversible (3) and redox (4). The answer is 34.
An analysis of the performance of task 19 in 2018 indicates that schoolchildren experience difficulties in determining the types of reactions in inorganic and organic chemistry: only 54.3% of the examinees successfully completed this task.
Task 20 checks the assimilation of the ability to explain the influence of various factors on the rate of a chemical reaction.
Task 20
From the proposed list of external influences, select two influences that lead to a decrease in the rate of the chemical reaction of ethylene with hydrogen.
- temperature drop
- increase in ethylene concentration
- use of a catalyst
- decrease in hydrogen concentration
- pressure increase in the system
Write in the answer field the numbers of the selected external influences.
The reaction rate decreases with decreasing temperature (1) and with decreasing concentration of reactants, in this case, hydrogen (4). An increase in the concentration of reactants, the use of a catalyst, and an increase in pressure, leading to an increase in the concentration of gaseous substances, on the contrary, increase the rate of the reaction of ethylene with hydrogen. The correct answer is 14. It should be noted that the examinees cope with this task very successfully: the percentage of its completion in 2018 was 78.6.
Tasks on the topic "Oxidation-reduction reactions" are presented in the exam at a basic and high level of complexity. When performing these tasks, schoolchildren need to demonstrate the ability to determine the degree of oxidation of chemical elements in compounds, explain the essence of redox reactions, and compose their equations. At the same time, the task of a high level of complexity is united by a single context with the task on the topic “Electrolytic dissociation. Ion exchange reactions»
Tasks at the basic level of complexity on the topic "Oxidation-reduction reactions" - tasks for "establishing a correspondence between the positions of two sets." Consider the task on this topic from the demo version.
Task 21
Establish a correspondence between the reaction equation and the property of the nitrogen element that it exhibits in this reaction: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
In reaction A, the oxidation state of nitrogen does not change and remains equal to –3, i.e. nitrogen does not exhibit redox properties (3).
In reaction B, nitrogen increases the oxidation state from –3 in NH 3 to 0 in N 2, i.e. is a reducing agent (2).
In reaction B, nitrogen also increases the oxidation state from –3 in NH 3 to +2 in NO, i.e. is a reducing agent (2).
So the correct answer is 322.
Assimilation of knowledge about the processes of electrolysis of melts and solutions is checked assignment 22 an increased level of complexity in the format of establishing a correspondence between the positions of two sets.
Task 22
Establish a correspondence between the salt formula and the electrolysis products of an aqueous solution of this salt, which were released on inert electrodes: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
SALT FORMULA |
ELECTROLYSIS PRODUCTS |
|
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
To complete this task, it is necessary to know and be able to apply the patterns of product release on the electrodes in the process of electrolysis of solutions and melts of salts, alkalis, acids.
Sodium phosphate is a salt formed by an active metal and an oxygen-containing acid. The electrolysis products of this salt will be hydrogen at the cathode and oxygen at the anode (1).
During the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of potassium chloride, hydrogen will be released at the cathode, and chlorine at the anode (4).
Copper (II) bromide is a salt formed by a metal that is in the electrochemical series of voltages after hydrogen, so only copper will be released at the cathode. Bromide anion is an anion of oxygen-free acid, which will be oxidized at the anode with the release of bromine (3).
The composition of copper (II) nitrate includes an oxygen-containing anion, which is not oxidized at the anode. Due to the oxidation of water at the anode, oxygen will be released (2).
Thus, the correct answer is 1432. It should be noted that schoolchildren successfully cope with this task: the percentage of its completion in 2018 is high - 75.0.
Task 23
Establish a correspondence between the name of the salt and the ratio of this salt to hydrolysis: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
When completing this task, examinees must demonstrate knowledge of the processes of hydrolysis of salts of various types, depending on the strength of the acid and base that form them.
Ammonium chloride is a salt formed by a weak base and a strong acid, so it hydrolyzes at the cation (1).
Potassium sulfate is a salt formed from a strong base and a strong acid, so it does not undergo hydrolysis (3).
Potassium carbonate is a salt formed by a strong base and a weak acid, so it undergoes anion hydrolysis (2).
Aluminum sulfide is a salt formed by a weak base and a weak acid, therefore it is hydrolyzed both by the cation and by the anion, and in the aqueous medium there is a complete and irreversible hydrolysis of this salt, as evidenced by a dash in the solubility table (4).
Thus, the correct answer is 1324. The percentage of completion of this task is quite high: in 2018, 62.6% of examinees successfully completed it.
The USE tasks related to the concept of "chemical equilibrium", as well as the concept of "rate of a chemical reaction", do not require quantitative calculations. For their implementation, it is enough to apply knowledge at a qualitative level (“shifts towards a direct reaction”, etc.).
Task 24
Establish a correspondence between the equation of a reversible reaction and the direction of the shift in chemical equilibrium with increasing pressure: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
REACTION EQUATION |
DIRECTION OF SHIFT OF CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM |
|
A) N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) ↔ 2NH 3 (g) B) 2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) ↔ 2H 2 O (g) C) H 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g) ↔ 2НCl (g) D) SO 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g) ↔ SO 2 Cl 2 (g) |
1) shifts towards a direct reaction 2) shifts towards the back reaction 3) practically does not move |
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
The task on the topic “Chemical equilibrium” is aimed at testing the assimilation of the concepts of “reversible and irreversible chemical reactions”, “chemical equilibrium”, “shift of chemical equilibrium under the influence of various factors”. When completing this task, it is necessary to demonstrate the ability to explain the influence of various factors on the shift in chemical equilibrium.
Reactions A, B and D proceed with a decrease in the number of molecules of gaseous substances, therefore, in accordance with the Le Chatelier principle, with an increase in pressure, the equilibrium will shift towards the direct reaction (1).
Reaction B proceeds without changing the number of molecules of gaseous substances; therefore, an increase in pressure will not affect the shift in equilibrium (3). So the correct answer is 1131.
In 2018, 64.0% of examinees successfully completed this task.
The greatest difficulties for USE participants arise when completing tasks of an increased level of complexity in the format of “establishing a correspondence between the positions of two sets”, which test the assimilation of knowledge about the experimental foundations of chemistry and general ideas about industrial methods for obtaining the most important substances. These include tasks 25 and 26.
Task 25 checks the assimilation of knowledge about qualitative reactions to inorganic and organic substances.
Task 25
Establish a correspondence between the formulas of substances and a reagent with which you can distinguish aqueous solutions of these substances: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
SUBSTANCE FORMULA |
||
A) HNO 3 and NaNO 3 B) KCl and NaOH C) NaCl and BaCl 2 D) AlCl 3 and MgCl 2 |
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
This task has a pronounced practice-oriented character. When performing it, it is necessary to apply not only theoretical knowledge of the chemical properties of substances, but also the ability to plan and conduct a chemical experiment. Successful completion of this task requires experience in conducting a real chemical experiment.
Nitric acid can be distinguished from sodium nitrate using copper (1). Nitric acid reacts with copper to form blue copper (II) nitrate and release nitric oxide (IV) or nitric oxide (II), depending on the concentration. Sodium nitrate does not react with copper.
Potassium chloride can be distinguished from sodium hydroxide using copper (II) sulfate (5), with which sodium hydroxide interacts to form a blue precipitate of copper (II) hydroxide. Potassium chloride does not interact with copper (II) sulfate.
Barium chloride, unlike sodium chloride, reacts with copper (II) sulfate (5) to form a white crystalline precipitate of barium sulfate.
Both aluminum chloride and magnesium chloride react with sodium hydroxide solution (2) to form white amorphous precipitates of the respective hydroxides. However, aluminum hydroxide, unlike magnesium hydroxide, dissolves in an excess of alkali solution, tk. has amphoteric properties.
So the correct answer is 1552.
Completing a task to test knowledge about qualitative reactions is traditionally difficult for schoolchildren. In 2018, only 44.8% of examinees successfully completed this task. The results of this assignment indicate that the graduates have not mastered the skills of experimental work on studying the properties of substances and conducting chemical reactions. This may be due to a significant reduction in the time allotted to conduct a real chemical experiment when studying chemistry at school.
Task 26 checks the assimilation of the rules of work in the laboratory, general ideas about industrial methods for obtaining the most important substances and their application.
Task 26
Establish a correspondence between the substance and its main field of application: for each position indicated by a letter, select the corresponding position indicated by a number.
Write in the table the selected numbers under the corresponding letters.
This task, like task 25, has a practice-oriented character. To successfully complete this task, the examinee must have factual knowledge of the methods for obtaining substances, their areas of application, methods for separating mixtures, and the technological principles of some chemical industries.
The substances presented in this task are widely used in technology, industry, and everyday life. Methane is primarily used as a fuel (2). Isoprene is a monomer for rubber production (3), ethylene is a monomer for plastics production (4). It should be noted that the percentage of completion of this task, even after changing its content saturation and reducing the level of complexity from advanced to basic, still remains extremely low: in 2018, only 44.8% of examinees completed it.
Tasks of a high level of complexity on the topics "Redox Reactions" and "Ion Exchange Reactions" are connected by a single context. For execution tasks 30 examinees must independently choose from the proposed list of substances substances between which a redox reaction can occur, and not work with a ready-made reaction scheme, as was the case in previous years. Next, you should draw up an equation for the reaction, bring the electronic balance and indicate the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. For execution tasks 31 it is necessary to choose from the proposed list of substances substances between which an ion exchange reaction is possible, and then write down the equations in molecular, full and abbreviated ionic forms. Both tasks are worth a maximum of 2 points each. When completing this task, students also need the ability to write equations for ion exchange reactions in molecular, full and reduced ionic form.
Consider tasks 30 and 31 with a single context from the demo.
Task 30
From the proposed list of substances, select substances between which a redox reaction is possible, and write down the equation for this reaction. Make an electronic balance, indicate the oxidizing agent and reducing agent.
To complete this task, it is necessary to analyze the redox properties of the proposed substances. Among the proposed substances, potassium permanganate is a viable oxidizing agent, which will exhibit oxidizing properties due to manganese atoms in the highest oxidation state of +7.
Sodium sulfite, due to sulfur atoms in an intermediate oxidation state of +4, is able to exhibit both oxidizing and reducing properties. When interacting with potassium permanganate - a strong oxidizing agent - sodium sulfite will be a reducing agent, oxidizing to sodium sulfate.
The reaction can take place in various media, in the context of this list of substances - in neutral or alkaline. Let's pay attention to the fact that in the answer, only one equation of the redox reaction should be written.
Possible answer:

Sodium sulfite or sulfur in the +4 oxidation state is a reducing agent.
Potassium permanganate or manganese in the +7 oxidation state is an oxidizing agent.
Task 31
From the proposed list of substances, select substances between which an ion exchange reaction is possible. Write down the molecular, full, and abbreviated ionic equations for this reaction.
Among these substances, an ion exchange reaction between potassium bicarbonate and potassium hydroxide is possible, as a result of which the acid salt will turn into an average one.
Possible answer:

Tasks 30 and 31 are able to differentiate graduates by the level of training. It should be noted that the complication of the wording of task 30 led to a decrease in the percentage of its completion: if in 2017 68% of graduates successfully completed it, then in 2018 - only 41.0%.
The percentage of task completion is 31 - 60.1. At the same time, graduates with a high level of training confidently coped with the preparation of a redox reaction and an ion exchange reaction, while poorly trained graduates practically did not complete these tasks.
In the control work of the exam in chemistry, a large role is assigned to calculation problems. This is explained by the fact that when solving them, it is necessary to rely on knowledge of the chemical properties of compounds, to use the ability to draw up equations of chemical reactions, i.e. to use in interconnection the theoretical base and certain operational-logical and computational skills.
The solution of computational problems requires knowledge of the chemical properties of substances and involves the implementation of a certain set of actions that ensure the correct answer is obtained. These actions include:
- drawing up equations of chemical reactions (in accordance with the condition of the problem) necessary to perform stoichiometric calculations;
- performing calculations necessary to find answers to the questions posed in the condition of the problem;
- formulating a logically justified answer to all the questions posed in the task condition (for example, to determine the physical quantity - mass, volume, mass fraction of a substance).
However, it should be borne in mind that not all of these actions must necessarily be present when solving any calculation problem, and in some cases some of them can be used repeatedly.
According to the codifier of content elements and requirements for the level of training of graduates of educational organizations for the unified state exam in chemistry, students should be able to carry out the following calculations using chemical formulas and reaction equations:
- calculations using the concept of "mass fraction of a substance in solution";
- calculations of volume ratios of gases in chemical reactions;
- calculations of the mass of a substance or volume of gases according to a known amount of a substance, mass or volume of one of the substances participating in the reaction;
- calculations of the thermal effect of the reaction;
- calculations of the mass (volume, amount of substance) of the reaction products, if one of the substances is given in excess (has impurities);
- calculations of the mass (volume, amount of substance) of the reaction product, if one of the substances is given as a solution with a certain mass fraction of the dissolved substance;
- establishment of the molecular and structural formula of a substance;
- calculations of the mass or volume fraction of the yield of the reaction product from the theoretically possible;
- calculations of the mass fraction (mass) of a chemical compound in a mixture.
When solving computational problems, students often admit the following typical mistakes:
- do not distinguish between the mass of the solution and the mass of the solute;
- when finding the amount of a gaseous substance, divide its mass by the molar volume or, conversely, divide the volume of the gaseous substance by its molar mass;
- forget to place the coefficients in the reaction equations;
- they do not find which substance is in excess (this error may also be associated with a lack of skill in solving problems on “excess - deficiency”);
- when calculating, they incorrectly transform mathematical formulas, without thinking about the absurdity of the answer received (for example, they produce multiplication, but not division the mass of the solute to its mass fraction when finding the mass of the solution).
Most computational problems it is better to solve in prayers, since this method is more rational. However, the solution method itself and its rationality are not taken into account when evaluating computational problems. The main thing is that the student demonstrates the logic of the solution method proposed by him and, in accordance with it, performs the correct calculations, which should lead him to the correct answer.
An analysis of the results of performing computational tasks in 2018 shows that computational tasks of even a basic level of complexity cause difficulties for schoolchildren. First of all, this concerns tasks 28 and 29 . In problem 28, it is necessary to carry out calculations of the volumetric ratios of gases in chemical reactions or calculations using thermochemical equations. With task 27, in which it is necessary to make calculations using the concept of "mass fraction of a substance in a solution", schoolchildren cope more successfully.
When performing computational tasks of a basic level of complexity, it is necessary to pay attention to the dimension of the desired value (g, kg, l, m 3, etc.) and the degree of accuracy of its rounding (to integers, tenths, hundredths, etc.).
Here are the calculation tasks of the basic level of complexity from the demo version of the USE 2019.
Task 27
Calculate the mass of potassium nitrate (in grams) that should be dissolved in 150.0 g of a solution with a mass fraction of this salt of 10% to obtain a solution with a mass fraction of 12%. (Write down the number to tenths.)
Answer: ___________________
The correct answer is 3.4.
Task 27 in 2018 was successfully completed by 61.2% of examinees.
Task 28
As a result of the reaction, the thermochemical equation of which
2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) \u003d 2H 2 O (g) + 484 kJ,
1452 kJ of heat were released. Calculate the mass of the resulting water (in grams). (Write down the number to the nearest integer.)
Answer: ___________________
In this example, the found mass of the resulting water is 108 g. We write down the answer: 108.
Task 28 in 2018 was successfully completed by only 58.3% of the examinees.
Task 29
Calculate the mass of oxygen (in grams) required for the complete combustion of 6.72 liters (N.O.) of hydrogen sulfide. (Write down the number to tenths.)
Answer: ___________________
The correct answer is 14.4.
In 2018, 60% of graduates completed task 29.
Tasks of a high level of complexity 34 and 35 are not always accessible even to schoolchildren with a good and excellent level of preparation. When solving problem 35, many schoolchildren do not understand the chemistry of the processes described in the problem, and make mistakes when compiling reaction equations. Thus, a lack of understanding of what the phrase “part of the substance has decomposed” means does not allow these students to draw up equations for the corresponding reactions and carry out the necessary calculations on them. Another typical error is associated with determining the mass of the resulting solution, which ultimately leads to an incorrect finding of the desired mass fraction of substances in the solution.
Consider task 34 high level of complexity from the demo version.
Task 34
When a sample of calcium carbonate was heated, part of the substance decomposed. At the same time, 4.48 l (n.o.) of carbon dioxide were released. The mass of the solid residue was 41.2 g. This residue was added to 465.5 g of hydrochloric acid solution taken in excess. Determine the mass fraction of salt in the resulting solution.
In your answer, write down the reaction equations that are indicated in the condition of the problem, and give all the necessary calculations (indicate the units of measurement of the required physical quantities).
Possible answer:
Reaction equations are written:
CaCO 3 \u003d CaO + CO 2
CaCO 3 + 2HCl \u003d CaCl 2 + CO 2 + H 2 O
CaO + 2HCl = CaCl 2 + H2O
The amount of substance compounds in the solid residue was calculated:
n(CO 2) \u003d V / V m \u003d 4.48 / 22.4 \u003d 0.2 mol
n (CaO) \u003d n (CO 2) \u003d 0.2 mol
m(CaO) = n ∙ M = 0.2 ∙ 56 = 11.2 g
m (CaCO 3 residue) \u003d 41.2 - 11.2 \u003d 30 g
n (CaCO 3 residue) \u003d m / M \u003d 30 / 100 \u003d 0.3 mol
The mass of salt in the resulting solution was calculated:
n (CaCl 2) \u003d n (CaO) + n (CaCO 3) \u003d 0.5 mol
m(CaCl 2) \u003d n ∙ M \u003d 0.5 ∙ 111 \u003d 55.5 g
n (CO 2) \u003d n (CaCO 3 residue) \u003d 0.3 mol
m(CO 2) \u003d n ∙ M \u003d 0.3 ∙ 44 \u003d 13.2 g
The mass fraction of calcium chloride in solution is calculated:
m (solution) \u003d 41.2 + 465.5 - 13.2 \u003d 493.5 g
w(CaCl 2) \u003d m (CaCl 2) / m (solution) \u003d 55.5 / 493.5 \u003d 0.112, or 11.2%
In 2018, 21.3% of the exam participants completely completed task 34 and received four maximum points for its completion.
While doing tasks 35 it is required not only to determine the molecular formula of the organic substance, but also, on the basis of the chemical properties described in the condition for setting its chemical properties, to establish its structural formula, and also to draw up an equation for one of the characteristic chemical reactions involving this substance. Consider problem 35 of a high level of complexity.
Task 35
Organic substance A contains 11.97% nitrogen, 9.40% hydrogen and 27.35% oxygen by mass and is formed by the reaction of organic substance B with propanol-2. It is known that substance B is of natural origin and is able to interact with both acids and alkalis.
Based on these conditions of the assignment:
- carry out the necessary calculations (indicate the units of measurement of the required physical quantities) and establish the molecular formula of the original organic substance;
- make a structural formula of this substance, which unambiguously reflects the order of bonding of atoms in its molecule;
- write the reaction equation for obtaining substance A from substance B and propanol-2 (use the structural formulas of organic substances).
Possible answer:
Calculations were carried out and the molecular formula of substance A was found. The general formula of substance A is C x H y O z N m .
w(C) = 100 - 9.40 - 27.35 - 11.97 = 51.28%
x:y:z:m=51.28/12:9.4/1:27.35/16:11.97/14=5:11:2:1.
Molecular formula of substance A - C 5 H 11 O 2 N
The structural formula of substance A has been compiled:

The equation for the reaction of obtaining substance A is written:
Difficulties arise for schoolchildren in compiling the structural formula of the desired organic substance, which unambiguously reflects its properties, as well as in compiling the reaction equation in accordance with the condition of the problem. Only 25.7% of the exam participants in 2018 were able to fully cope with this task and get the maximum 3 points for solving it.
It should be noted that tasks with a detailed answer can be completed by graduates in various ways.
In conclusion, we highlight several basic principles for organizing the preparation of students for the exam.
The main task of preparing for the exam should be purposeful work on repetition, systematization and generalization of the studied material, on bringing the key concepts of the chemistry course into the knowledge system.
It is also impossible to reduce the preparation for the exam only to training in the performance of tasks similar to the tasks of the examination paper of the current year. Tasks of various types in various formats should be widely used, which are aimed not at simply reproducing the acquired knowledge, but at testing the formation of skills to apply theoretical knowledge in new learning situations.
When studying, repeating and consolidating educational material, it is necessary to use various tasks, including those related to the transformation of information from one form to another: the compilation of general tables, graph diagrams, diagrams, graphs, notes, etc.
And, of course, the primary role in preparing for the exam is played by the experience and knowledge acquired by schoolchildren when performing and discussing the results of a real chemical experiment, which should be given special attention in the process of studying a school chemistry course.
The Unified State Examination (USE) is a form of state final certification conducted in order to determine the compliance of the results of mastering the main educational programs of secondary general education by students with the relevant requirements of the federal state educational standard or educational standard. For these purposes, control measuring materials (CMM) are used, which are sets of tasks of a standardized form.
The USE is conducted in accordance with the Federal Law "On Education in the Russian Federation" dated December 29, 2012 No. 273-FZ and the Procedure for Conducting State Final Attestation for Educational Programs of Secondary General Education, approved by Order of the Ministry of Education of Russia and Rosobr-nadzor dated November 7, 2018 No. 190 / 1512.
Approaches to the selection of content, the development of the structure of the KIM USE.
The selection of the content of KIM for the USE in Chemistry in 2020 was generally carried out taking into account the general guidelines on the basis of which the examination models of previous years were formed. Among these installations, the most important from a methodological point of view are the following.
KIM are focused on testing the assimilation of the knowledge system, which is considered as an invariant core of the content of existing programs in chemistry for general education organizations. In the standard, this system of knowledge is presented in the form of requirements for the preparation of graduates. These requirements correspond to the level of presentation in the KIM of the content elements being checked.
The standardized versions of the KIM, which will be used during the exam, contain tasks that differ in the form of presentation of the conditions and the type of the required answer, in the level of complexity, as well as in the ways of assessing their performance. The tasks are based on the material of the main sections of the chemistry course. As in previous years, the object of control within the framework of the USE 2020 is the knowledge system of the basics of inorganic, general and organic chemistry. The main components of this system include: leading concepts of a chemical element, substance and chemical reaction; basic laws and theoretical provisions of chemistry; knowledge about the consistency and causality of chemical phenomena, the genesis of substances, ways of knowing substances. In the standard, this system of knowledge is presented in the form of requirements for the level of training of graduates.
Free download e-book in a convenient format, watch and read:
Download the book Unified State Exam 2020, Chemistry, Grade 11, Specification, Codifier, Project - fileskachat.com, fast and free download.
- USE 2020, Chemistry, Grade 11, Demo, Codifier, Specification, Project
The following tutorials and books:
- In the piggy bank of the pedagogical experience of future teachers of chemistry, preparation for the OGE and the Unified State Examination, Kozhina L.F., Kosyreva I.V., Tyurina I.V., Vasilchikova O.A., 2019
- Unified State Examination 2020, Chemistry, Standard variants of examination tasks from the developers of the Unified State Examination, Medvedev Yu.N., 2020
- USE 2020, Chemistry, 10 training options for examination papers to prepare for the unified state exam, Savinkina E.V., Zhiveinova O.G., 2019