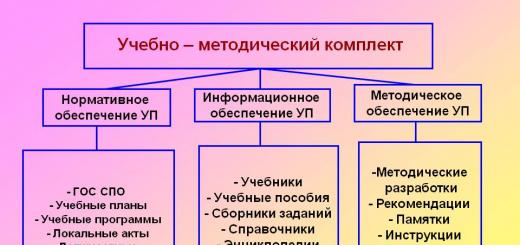
Informatization of society places special demands on the training of specialists. Modern science, business and social science to a greater extent need not just those who can understand the technical intricacies of information technology. There is a need in society for professionals who have received versatile training, have broad erudition and are ready to apply their knowledge and skills in applied fields.
Computer science today is increasingly becoming an applied science. This means that its principles are increasingly used in a variety of areas of production and science: linguistics, geoinformatics, the chemical industry, genetic engineering, and so on. For this reason, specialists in the field of applied computer science need knowledge that goes far beyond information technology.
An applied specialist must be a generalist, that is, master the methods of information technology, statistics, mathematics, and economics. This set of skills makes it possible to be an expert in your chosen field of activity. The range of tasks solved by a professional can be quite wide and is usually determined by the specifics of specific areas of activity of a research institution or commercial enterprise.
Where is applied computer science used?
Applied solves problems on the competent use of computer technology in scientific research. Very often, the success of a particular research work depends on the ability to correctly set the task of developing software or compiling a package of computer programs already on the market. It can be very difficult for ordinary programmers who have no idea about applied computer science to do this, because they lack erudition and special knowledge in a specific narrow field of activity.
The widest opportunities for applied computer science exist in the field of economics and entrepreneurship. It is easier for a professional to provide an enterprise with suitable business tools. For this purpose, it uses the most modern developments in the field of Internet technologies. He has to work with databases, develop a marketing strategy for the company, and keep computer records of technological operations.
An economist specializing in the field of applied computer science deals with solving problems of managing not only information, but also material and financial flows, using specialized information systems. Without such a specialist today it is impossible to imagine the work of a large bank, stock exchange or other institution working in the field of finance.
The most common entrance exams:
- Russian language
- Mathematics (profile) - specialized subject, at the choice of the university
- Physics - optional at university
- Computer science and information and communication technologies (ICT) - at the university's choice
Almost all areas of human activity today are associated with information technology, computing systems and computer systems. It is difficult to imagine modern business, manufacturing, medicine or education without computerization. And in every industry there is a demand for specialists who would install, configure, and maintain information and communication systems.
Specialty 03/09/03 “Applied Informatics” is a response to new challenges of society. It was created at the intersection of different disciplines, so graduates of the course usually have no problems finding a job. You can choose completely different areas of activity that will be related to computer science, economics, and IT. Currently, Russia is experiencing a shortage of such specialists, so the industry has great prospects ahead.
Admission conditions
The profession requires knowledge of the exact sciences. Subjects that school graduates take for admission:
- mathematics (profile),
- Russian language,
- computer science and ICT or physics.
Future profession
A graduate with a bachelor's degree can solve many problems relevant to different fields. He masters the methodologies that are subsequently necessary to implement enterprise automation. Also within his competence is the design, implementation and maintenance of information systems (IS). The profession requires knowledge of numerous tools and systems. As a result, a specialist can work as both a performer and a manager of a service or system, as well as the head of an IT company.
Where to apply
There is a wide choice of places to study. You can master the direction in the capital's universities:
- Moscow State Engineering University (MAMI);
- National Research University "MIET";
- Moscow Technical University of Communications and Informatics (MTUSI);
- Russian New University;
- Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation.
Training period
After completing 11 grades, a school graduate can enter the full-time department, and then he will have to study for 4 years. When choosing a part-time, evening or mixed form of study, the course of study will be 5 years.
Disciplines included in the course of study
The bachelor's program includes many basic subjects that are subsequently necessary for work in various fields. These are the following disciplines:

Acquired skills
During the learning process, the future bachelor will be able to master the following types of activities:
- Modeling and improvement of applied and information processes.
- IC design.
- Processes associated with the use of information systems: their implementation, configuration, operation.
- Training and consultation.
- Assessment of operating environments, information technologies and communications, as well as financial costs of projects related to automation and informatization.
- Preparation of annotations, abstracts, scientific reports, publications in the relevant field.
Job prospects by profession
The graduate of the course has broad prospects for professional fulfillment. Such a specialist is needed in financial and credit institutions, authorities and local governments. You can also get a job in the social sector, in investment and insurance companies.
A bachelor's degree holder can work:
The income of a young specialist starts from 25 thousand in domestic currency. The maximum is difficult to establish: it depends on the level of professionalism, position held and area of activity. After 3 years of work, the salary can be 80-100 thousand rubles. It is very promising to create your own company to work in the IT field.
Advantages of Master's Degree Studies
In the case of further training, the young specialist significantly expands his prospects in terms of professional fulfillment. The master's program involves gaining practical experience and familiarity with modern processes occurring in applied industries.
A master's degree means the ability to use various research methods in the field of design and management of information systems. In the future, you can realize yourself in scientific research in the IT industry and engage in teaching activities.
A comprehensive specialty that includes not only knowledge in the immediate field of computer science, but also knowledge and skills in management, design, law, and economics. Knowledge must be deep, supported by practical skills. An applied computer science specialist is distinguished by “multifunctionality” and versatility.
To date profession "applied computer science" is popular and in demand. High-level specialists are valued and have the opportunity to receive high wages and career growth. It is worth noting that the popularity and demand for representatives of this profession are characteristic not only of our country. Around the world, demand only increases every year.
The specialist understands:
In the intricacies of the development and functioning of the economy; 
Analysis of enterprise activities;
Financial forecasting;
The functioning of the securities market and exchanges;
Features of development at the micro and macroeconomic levels;
At the same time, he owns computer equipment, special programs, and is always aware of the innovations of technical progress that allow a specialist to be an effective and efficient worker.
The specialty combines training in the intricacies of high technology and the functioning of the economy - such “two-in-one” specialists are a real boon for:
Large transnational companies;
Banking institutions;
Running your own business;
Government agencies;
Commercial organizations;
Consulting firms;
Investment companies;
Information services;
Insurance companies.
Representatives of this profession can hold positions programmer, system administrator, logistician, manager, information analyst and many others.
The main qualities of a specialist in the field of applied computer science:
Flexibility of mind;
Ability to quickly navigate the information space;
Analytical mindset, ability to analyze and systematize information;
Extensive knowledge of computer technology and programming.
Training is possible part-time or full-time. After completing your studies at college, you can continue it at a higher educational institution - specialists in the field of applied computer science and can earn a master's degree and teach.
Training in the specialty “Applied Informatics” takes place at the theoretical and practical levels. Practice is a prerequisite for training professional personnel.
What knowledge do students gain during their studies?
Use computer technologies and information systems effectively;
Analyze information in order to solve applied problems;
Development of various options that will help solve applied problems automatically;
Knowledge in the field of improving information systems;
Skills and knowledge required for consultation;
Ability to analyze the activities of organizations;
Knowledge necessary to estimate economic costs;
Ability to present your projects;
Evaluate the costs of developing and automating solutions to applied problems;
Knowledge to continue a scientific career - compiling scientific articles and publications, abstracts, annotations;
Solve applied problems using technical skills.
Training will allow you to become a sought-after specialist in the labor market and gain the opportunity for career growth. Teaching is conducted by experienced teachers who will help you gain theoretical knowledge and consolidate it in practice.
|
Institute |
Institute of Applied Informatics |
|
Direction |
230700.62 - “Applied computer science” |
|
Profile |
Applied informatics in economics |
|
Form and duration of training |
Full-time (budget/commercial) - 4 years (bachelor) |
|
Disciplines |
Database Computing systems, networks and telecommunications Discrete Math Computer Science and Programming Information Security Information systems and technologies OS Information systems design Systems theory and systems analysis |
|
Profile competencies |
survey, description and analysis of economic objects, architecture and IT infrastructure management of information systems creation projects feasibility study of design solutions, preparation of technical specifications for automation of solving applied problems, design of information systems formulation of requirements for created software systems development of software applications, their testing and documentation taking into account standards implementation of business applications, adaptation, configuration and integration of design solutions for the creation of information systems for economic objects coordination of various activities for the creation, maintenance and operation of information systems training and consulting users in the process of operating information systems |
|
Software productsand languages |
|
|
Future professions |
information systems specialist database administrator systems analyst, business analyst Head of automation departments for industrial enterprises, banks, insurance companies director of IT companies, head of enterprise IT services |
|
Graduate department |
Department of Economic Informatics |
According to the founder of Microsoft, Bill Gates, in the “age of electronic technology” the most important condition for the success of any enterprise is the high potential of corporate intelligence (IQ). Corporate IQ is a measure of how freely information is disseminated within a company and accumulated and current knowledge is exchanged.
Ensuring a high level of IQ for enterprises through the creation of information systems is the task of computer scientists.
Computer scientists must not only develop and implement information systems, but also reorganize the activities of enterprises themselves on the basis of new, more efficient technologies. Consequently, they must have combined knowledge both in the field of computer science and in the applied field (economics, management, law, etc.).
Bachelor's degree
This is the first level of a two-level system of higher professional education, which involves obtaining basic professional knowledge and skills for applying them in practical activities, as well as providing the opportunity to move to the second level of higher professional education for more in-depth and specialized training in a specific master’s program. Our department prepares masters in the following areas 230700.68 - “Business engineering” and 230700.68 - “Applied computer science in the delivery of high-tech solutions.”
Relevance
Employers' demand for applied computer scientists is determined by the need for specialists involved in the development of applied information systems for commercial and non-profit organizations, government bodies and management.
A Bachelor of Applied Informatics with a major in Economics is an analyst, developer, economist, organizer, and manager in the field of information technology.
He is able to analyze the business processes of an enterprise, build mathematical and structural models of business processes, competently formulate and set the task of informatization of business processes, prepare technical specifications for the design of an information system, carry out and implement its project, operate, maintain and modernize information systems on various enterprise levels.
A Bachelor of Applied Informatics with a major in Economics is a specialist who understands economics, knows the underwater reefs of economic laws, the market, and is able to model business processes, analyze the activities of enterprises, and predict the state of financial and commodity markets.
Training of specialists involves both mastering various disciplines related to the theoretical and practical foundations of computer science and information technology (about 20 disciplines), and mastering disciplines related to economics, management, and law (about 15 disciplines).
Future work
Having completed a bachelor's degree in Applied Computer Science, you will be able to create information systems, develop IT infrastructure, and this means managing an organization using modern computer technologies.
The profession of “computer scientist” will be in demand in the coming decades, and you are sure to find interesting, creative and promising work in any field of human activity.
Be sure that a future awaits you with interesting and promising work in companies developing and implementing information products, in news agencies and think tanks.
You will be able to work:
information systems specialist, database administrator, systems analyst, business analyst;
head of the automation department of industrial enterprises, banks, insurance companies;
director of an IT company, head of enterprise IT services.
student life
Participation in sporting events of various levels and scales.
Participation in cultural events organized by the Student Club.
Participation in the work of the Case Club.
Participation in student conferences, seminars, competitions.
Participation in creative projects within the student design bureau.
Participation in Russian and international educational programs of the university: from language internships to obtaining diplomas from foreign universities.
Studying foreign languages at the highest level, obtaining an additional specialty and a diploma “Translator in the field of professional communications.”
Studying information technology under international programs at the APTECH center.
Participation in the All-Russian Olympiads in Applied Informatics.
Participation in All-Russian competitions of scientific works in the field of business process reengineering.
Internship at a basic university department, organized at an IT enterprise. The availability of internship places is 100%.
Postgraduate education in the postgraduate specialty 05.25.05 “Information systems and processes” (technical sciences) or in the postgraduate specialty in the field of economic sciences operating at our university.
Benefits of training
high level of training in economic disciplines;
Teaching Staff- highly qualified specialists with experience in practical and teaching activities;
availability of technical base and specialized professional software;
basic departments for practical training for bachelors and masters;
partnerships with MESI and UMO;
training opportunity international program Arena Multimedia(program for training specialists in the field of computer graphics and multimedia technologies);
opportunity to study for master's programs in the field of information technology. Our department prepares masters in the following areas: 230700.68 - “Business engineering” and 230700.68 - “Applied computer science in the delivery of high-tech solutions.”
Our achievements
Participation in diploma project competitions in the direction of “Applied Informatics”:
first place in the competition of diploma projects in the field of higher professional education “Applied Informatics” in 2008 (Tsynkov D.V., group 3093, scientific advisor Pashkov P.M.);
first place in the category “Informatization of the financial environment” of the competition of diploma projects in the field of higher professional education “Applied Informatics” in 2009 (Ignatova A.M., group 4091, scientific adviser Bobrov L.K.).
Participation in competitions in the field of “Applied Informatics”:
first team place final stage of the All-Russian Olympiad in Applied Informatics in 2013. (Heine I., group 9099, Buzulutskova Yu., 9091, Korotchenko E., 9091, scientific supervisor Rodionova Z.V.);
first team place at the regional stage of the All-Russian Olympiad in Applied Informatics in 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2013. (region - Ural and Western Siberia);
first team place at the regional stage of the international 1C programming Olympiad in 2010;
prizes in the international 1C programming Olympiad in 2010.
second team place at the final stage of the All-Russian Olympiad in Applied Informatics in 2007. (Shugurov P.V. gr. 3091, Bardakov V.B. gr. 2091, Minaev M.V. gr. 3091, scientific supervisor Moshegova A.T.);
second team place at the regional stage of the All-Russian Olympiad in Applied Informatics in 2012. (region - Ural and Western Siberia);
third team place at the final stage of the All-Russian Olympiad in Applied Informatics in 2009. (Grishmanovskaya E.A., group 5092, Osipova E.A., group 5091, Slesarenko N.S., group 5091, scientific supervisor Rodionova Z.V.).
Participation in student research competitions:
first place in an open competition of scientific papers within the framework of the XIV scientific and practical conference “Reengineering of business processes based on modern information technologies, knowledge management systems” in 2011, MESI, Moscow;
first place at the All-Russian Conference of Students, Postgraduate Students and Young Scientists “Innovation - 2012” (Tomsk State University);
Student publications:
publication of graduate essays in the almanac “I am a specialist 2010”, “I am a specialist 2011”, “I am a correspondence student 2011”, “I am a specialist 2012”, “I am a specialist 2013”;
publications in the collection of conference proceedings “Master’s Forum – 2012”.
What is applied computer science. Where did this specialty come from and what will you have to do at work later?
Demand
Payability
Competition
Entry barrier
Prospects
What does it mean to be a graduate of the specialty "Applied Informatics"? This means being one hundred percent sure that with the help of information technology, automation of routine processes, technologies for collecting and processing information, the life of a modern person can be made easier and more convenient.
Who is the profession suitable for?
You don't have to be able to assemble a computer blindfolded and reinstall software with just a glance at the mouse. Of course, it will be significantly easier to learn for someone who is already interested in computers. However, something else is important: do you believe with all your heart that the development of technology is right, that you need to look for moments that require improvement, and automate various processes so that millions of operations can take place without human intervention. (For example, in the field of exchange trading of securities, even about 1.3 billion transactions are carried out on accounts every day on an average day: 99.9% are automatic, and only 0.1% of the remaining require human participation.)
Those who want to master a highly regulated specialty will be mistaken if they choose applied computer science. This is an innovative specialty, where you are always pioneers. Even if there is someone else doing the same thing, your job is to figure out how to do it differently.
And for the attention of overly creative people: in this area, especially if we are talking about a complex application, it is easier not to automate the work from scratch, but to improve something. There is something to build on, there is already a general vision of the system by the customer. In a “from scratch” project, six months may pass before the client begins to understand what he needs.
The essence of the matter and the wide possibilities
It is difficult to evaluate the work of an innovative specialist correctly. Often there is no right and wrong, because after a while it turns out that another way of solving a problem is optimal in relation to the once generally accepted one. And this time must be waited.
Applied computer science studies information technologies used elsewhere. A specialist employed in the field combines the skills and abilities to build an information environment that is convenient and easy to use, as well as optimally suited to the task, and knowledge in any subject area of his choice.
 Let's take a look at a professional... a library, for example. What processes require innovation here? Perhaps this is the accumulation of information about various authors and topics, the construction of a library catalog according to a selected characteristic... Or the process of accepting and issuing books - by the way, why not speed it up by using a barcode scanner? This way, reading debt will be determined more accurately, and librarians will become happier!
Let's take a look at a professional... a library, for example. What processes require innovation here? Perhaps this is the accumulation of information about various authors and topics, the construction of a library catalog according to a selected characteristic... Or the process of accepting and issuing books - by the way, why not speed it up by using a barcode scanner? This way, reading debt will be determined more accurately, and librarians will become happier!
Now imagine that this is not a library, but a bank. The scope has changed, but nothing has changed globally. There is a need for cataloging, accumulation of information and, possibly, the use of a barcode scanner (for a faster and more convenient way for clients to deposit money into an account or move this money from a client's account).
So any area requires professional attention from an applied scientist. There is a certain process logic that needs to be studied before making improvements. And the specialist’s goal is to understand how technical knowledge can be adapted to solve problems in the subject area.
Automation is needed everywhere. Cashiers in a store punch receipts using a barcode scanner configured for the store’s product range and its accounting documents. At the factory, information about each part also enters the accounting program directly from the machine. At the dental clinic, your record is maintained electronically; In many Western and some of our medical laboratories, analysis is processed automatically, without human intervention. Accountants work with R-keeper, 1C, SAP-R3 systems, which automate their work.
At the same time, automation tools are still far from perfect - and are constantly evolving. Let’s say, if you are interested in foreign languages and want to study applied computer science, please, there are systems like Lingvo or Promt and electronic dictionaries, and you, as a specialist interested in languages, will understand the requirements for such systems better than others and will be able to improve existing programs with pleasure or develop a new one that will successfully compete with them.
A wide choice of areas of application of knowledge is certainly an advantage for a graduate. Knowledge about how to look for problems to improve processes for working with information and how to solve them is completely unified. After graduation, you can equally well go to work either in a laboratory or in a trading company; both to school and to government agencies. The choice is determined by what your soul is about.
Job responsibilities
The analyst mainly communicates with the development team and with the customer (the project can be either external or internal). He collects information from both customers and intended users of the product and describes it to the development team in terms that they can understand. Answers the question: what needs to be done? It is the analyst who is engaged in the activities most relevant to his specialty.
 A programmer is a member of the development team. Answers the question: how should it be done? Receives information either directly from the customer and users (if the project is very small and does not involve analysts), or from the analyst and from the documents that he prepared. After that, he creates the program.
A programmer is a member of the development team. Answers the question: how should it be done? Receives information either directly from the customer and users (if the project is very small and does not involve analysts), or from the analyst and from the documents that he prepared. After that, he creates the program.
Tester - testing engineer. Unfortunately, the role of this specialist in the project is underestimated. However, it is the tester, or tester, who is responsible for the quality of the product: he writes test scripts for the program to cover the maximum possible use cases and identify the maximum possible number of failures in its operation, as well as the maximum possible number of programmer errors.
A project manager often combines the role of project analyst and project management responsibilities.- distribution of tasks, control over their implementation, assistance to the team in difficult situations and provision of friendly infrastructure (comfortable conditions and the availability of all necessary programs).
Additional requirements
- From the very beginning, a specialist will have to get used to evaluating his work in terms of labor costs. It will be necessary to predict how much time a particular task will take, so that the project manager or client can then estimate these labor costs at the rates established for them.
- This job also requires well-developed communication skills. One of the main skills is the ability to prove and show that everything is well thought out. It is very difficult to prove to a client that he is wrong. And it’s even more difficult to admit later that it was the client who was right, because the “ideal” scenario does not work.
But there is an even more important skill - the ability to recognize the client as the main carrier of knowledge in his subject area. Alas, very often the specialist thinks out for the client what he supposedly needs, and then the client is surprised: even what was not asked for was done. However, it happens that the client himself does not know what he wants. Or he formulates his wishes inaccurately and inattentively, because he simply does not understand what else needs to be explained: for him everything is obvious.
Working at the intersection of areas of knowledge, you will often be an intermediary between narrow specialists in the chosen subject area and technical specialists. And it depends on you whether they will find a common language, whether they will gain a common vision of the situation and a common point of view on the problem being solved. If you are creating a system for a commercial company, then for more than six months you will be explaining to other application specialists “what debit and credit are”, “how can I calculate this coefficient that is indicated in the document.” And explain it as simply as possible. And then you will repeatedly explain to users “when to click on this button,” and object to attacks like “is it difficult to add a new report? It’s almost the same as the other report.”
Your social circle will expand. You will be able to navigate the realities of subject areas. However, conflicts are also possible - so your choice depends on how comfortable you feel in conflict situations and with an abundance of communication.
Basic knowledge
 You must have a good understanding of algebra and the school computer science course - this is not discussed. What about physics and geometry? They are also needed to develop abstract thinking.
You must have a good understanding of algebra and the school computer science course - this is not discussed. What about physics and geometry? They are also needed to develop abstract thinking.
It is very important to know English! Precisely English: otherwise it will be difficult to work even with Russian-speaking clients. The specialty is full of Englishisms and untranslatable terms; new technologies are accompanied by documentation only in English. If the main foreign language is not English, then you need to think carefully before choosing applied computer science.
And it would be nice to be able to play chess - this will develop logical thinking.
Choosing a university and studying
A very good selection criterion is practical teachers! If teaching is the main and only occupation of university teachers, then this is bad: there is a risk that very soon they will teach outdated information.
Look for a university where they give you a lot of tasks, where you need to think a lot abstractly, learn to think in an unusual way, and also constantly look for analogies: after all, the more complex the subject area and the further it is from what the programmer is already familiar with, the more difficult and interesting it will be work.
How can you become a sought-after expert if you are more interested in the applied aspect rather than the technical details? Take a look at universities that specialize in the subject area you want to choose. One person will be more interested in applied computer science in economics, another - in medicine or tourism. And look for training in the specialty “Applied Informatics” in the relevant higher educational institutions.
Need to constantly learn new things
An applied scientist is always learning. And you need to learn the processes of producing programs and technologies, study the new technologies themselves used in a specific project, master new areas of application of knowledge, and comprehend business processes set up differently. The result in training must be achieved very quickly - and just as quickly switch between different knowledge that you already have. During the time you are students, new algorithms for designing processes, new methods of automation, new programs for documentation will be invented - everything will become new.
In the field of information technology, changes are unregulated and often undocumented.
There are so many different technologies today that a specialist will most likely have to work on a project where some of the technologies used will be practically unfamiliar to him. When you get into a project, you may encounter a situation where not only do you not have the slightest idea how to work with the new technology, but seasoned specialists are also not up to date. And that's okay. However, will you have time to complete your studies? But won't the new knowledge turn out to be too complicated? However, having just graduated from university, you will already be on the same level as many colleagues in your industry. Do you want to learn a new profession?