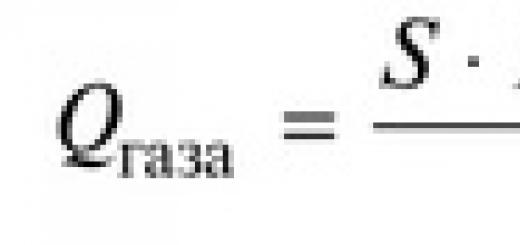The outline of land areas, terrain and local objects are indicated on the map with color and symbols. So, fields and meadows are light green; various reservoirs - blue; sands - yellow; hills, mountains - dark yellow and various tones of brown; trails, dirt roads, buildings in populated areas - gray or brown.
Conventional signs, usually close in design to the actual shapes of objects, are divided into four main groups:
1) Contour or scale signs (Fig. 36), they denote large-sized objects that can be expressed on a map scale - areas of forest, meadows, arable land, lakes, swamps, large rivers, sands, etc. Their boundaries contours are indicated by solid lines or dots in accordance with the actual contours on the ground. The area inside the outline is covered with appropriate paints and filled with additional symbols.

2) Off-scale signs (Fig. 37) are used to designate important, small-sized objects that cannot be expressed on the map scale. These include wintering quarters, wells, some landmarks - various towers, factory chimneys, radio masts, etc. These images on the map are enlarged, and it is impossible to judge from them the actual size of the objects.
3) Roads, trails, streams, power lines and other linear images, the scale of which reflects only the length, occupy an intermediate position between scale and non-scale signs and are called linear (Fig. 38).

4) Explanatory signs - abbreviations, names, numbers that explain the meaning of the symbol. For example, lake - lake, pass - lane, river - river; proper names of objects and inscriptions that provide additional characteristics. For example, in the outline of the forest the inscription “ber. 30/35-5" means: birch, height 30 m, diameter 35 cm, distance between trees 5 m, or at the summit sign the number indicates height, etc.
Terrain image. The most visual and accurate way to depict the terrain is the method of contour lines with digital elevation marks. Horizontal lines are closed curved lines that connect points located at the same height above sea level (Fig. 39). Horizontal lines clearly convey landforms. Using them, you can determine the height of terrain points. Horizontal lines are drawn at intervals of equal height, which are called section heights. The following section heights are accepted on the maps: 10 m for a map of scale 1: 50,000; 20 m - 1: 100,000; 40 m - 1:200,000.

Highlands and lowlands of the terrain - basins - are indicated by the same horizontal lines. Berghatches are used to distinguish between highs and lows. Berghstrich is a short line, located perpendicular to the horizontal in the direction of lower terrain. The steepness of the slope when depicting the relief using the contour line method is indicated by the convergence or stretching in the arrangement of the contour lines. The closer the horizontal lines are to each other, the steeper the slope. However, the maximum steepness of the slope, depicted by horizontal lines, does not exceed 45°. Steeper slopes are represented by conventional signs - ravines, cliffs. They are shown on maps and plans in dark brown. On small-scale maps, for greater clarity, the hillshading method is used along with contour lines. Its essence lies in the thickening of the shadows as the steepness of the slope increases. Shading is done with gray or brown paint. Flat surfaces remain white.
Grid on maps. When determining the location of objects - landmarks, standing points - on a map, coordinate grids are used, which allow you to quickly find or indicate the exact position of a particular terrain point. Coordinates are angular or linear quantities that determine the position of points on any surface (on the earth's surface, on a map) or in space. Geographic coordinates are angular values - geographic latitude and longitude, which determine the position of points on the earth's surface relative to the equator and a plumb line at a given point on the earth's surface. The angle in degrees shows how much a particular point on the globe is north or south of the equator. If a point is located in the northern hemisphere, then its latitude will be called northern, if in the southern hemisphere, then southern latitude.
Geographic longitude is also measured by the angle formed by the plane of the meridian, taken as the initial (zero), and the meridian passing through a given point. For uniformity in determining longitudes, we agreed to consider the prime meridian to be the meridian passing through the astronomical observatory in Greenwich (England, near London), and to call it Greenwich. All points on the globe located east of the Greenwich prime meridian to the 180° meridian will have east longitude, and all points west of the prime meridian will have west longitude. Using a map with meridians and parallels marked on it, you can determine the latitude and longitude of any point or object.
On large-scale topographic maps, a grid of meridians and parallels is shown outside the frame of the map sheet in the form of divisions (segments) equal to the linear value of one minute in longitude and latitude. On maps of scale 1:500,000 and 1:100,000, the grid of meridians and parallels is depicted on the entire sheet and its exits are labeled outside the map frame.
Topic: “Conditional colors of the physical map of the hemispheres.”
Educational: To form an idea of the physical map of the hemispheres, what conventional colors the surface of the Earth is depicted on the map of the hemispheres, to know the location of the equator, south and north poles on the map.
Educational: aesthetic, love for the Earth, Motherland.
Correctional and developmental: development of mental activity, motor skills, attention, memory, logical thinking, speech correction.
Equipment: Physical map of the hemispheres, globe, textbook, atlas.
Vocabulary work: physical map of the hemispheres, map symbols.
Progress of the lesson.
Organizational moment. Hello
Teacher:
What shapes of the earth's surface do you know?
What conventional colors are found on the map?
What do they mean?
Our planet has an uneven surface. Vast spaces are occupied by seas and oceans. Lakes and many rivers flow across the Earth.
On land there are lowlands, hills, and mountains.
Write down the definition. A physical map is a geographical map that depicts the surface of land, seas, and oceans.
Oceans, seas, rivers, lakes on a physical map are indicated in blue in different shades. The deepest parts of the oceans are marked in dark blue.
The land surface is indicated by different conventional colors, depending on the height of the area. The altitude of the area is measured from ocean or sea level.
Green on the maps indicates low places up to 200 meters above sea level - these are plains or lowlands.
The hills are painted in different shades of yellow. They are located at an altitude of 200 to 500 meters above sea level. Mountains shown in brown on the map have a height of 500 meters and above. (The story is accompanied by an analysis of Fig. 76).
On a physical map there is an altitude scale and a depth scale, which can be used to determine the approximate height of the area on land and the depth of the sea or ocean. (The story is accompanied by an analysis of Fig. 77 and a scale of heights and depths in the atlas).
Fastening:
Instructions: “In front of you are cards with a table on them.. Fill in the empty cells of the table, as well as the sentences that you must complete, and a punched card. Don’t rush to fill out the table right away, check yourself again and only then give an answer.”
Task1 Shade the rectangles with the conventional colors of the physical map. Write what the colors mean.
___________________ _______________ ____________ _______
__________________ _______________ ____________ __________
Task 2: Complete the sentences.
Water on physical maps is depicted in ______ color.
The surface of the land is represented by ___________________, ________________ flowers.
Add your conclusion.
A physical map is a geographical map that is shown to us by ________________________________________________
Task 3. Underline the correct word.
Geographical objects on the map only need to be shown with a pen, ruler, finger, or pointer.
Bottom line. Giving ratings with comments.
What does the green color indicate on the plan and on the physical map? and got the best answer
Answer from ЂaisiaKonovalov[guru]
2.) on a physical map, green indicates low areas of the earth’s surface
4) on the plan, forests are indicated in green.
On the site plan, rivers and lakes are shown as blue water, and forests as green - the color of vegetation. Fields, vegetable gardens - - there is no special sign, so such areas are left white on the plan. The symbol of the bows resembles stalks of grass. Sands are represented by brown dots. Small streams, roads, narrow streets are depicted with conventional signs in the form of lines. Such symbols are generally accepted. They are used on all terrain plans.
Answer from Yatyana Dovbyalik[active]
I advise you to read it carefully!! !
Mountains are large, narrow, elongated areas of the lithosphere surface, rising above the adjacent plains by more than 500 m.
Since mountains form part of the relief, let’s agree on what we mean by relief. Relief is a set of irregularities in the surface of the lithosphere.
I show the participants a physical map of Russia in the atlas and ask them to answer the question: “What does it show in color?” . Answer: "Relief". Please remember the answer for later discussion.
To the question: “What color are the mountains shown on the map?” , I hear: “Brown or various shades of brown.” He is accepted as unfaithful. This is how an answer is assessed if it is completely or partially incorrect. Please find the New Siberian Islands on the map and see what is located north of them. It turns out - the Lomonosov Ridge in the Arctic Ocean.
I ask: “Is the ridge a mountain?” , “Are they shown in brown?” . No, light blue. “Which question was answered: the one posed or another?” . It turns out that they answered the question: “What color are mountains shown on land?” .
Correct answer: “On the land of this map, the mountains are marked in various shades of brown, and in the water area (seas and oceans) - from white to light blue.”
To the question - “What color are the plains shown on land maps? - I get the answer: “Green”. The answer is also not accepted.
To reasonably answer this question, you need to know the content of the concept “plain”. Plains are large, oval-shaped areas of the lithospheric surface with minor irregularities up to 500 m. They are distinguished according to the absolute elevations of the terrain.
1) up to 200 m – lowlands, painted dark green;
2) from 200 to 500 m – green plains with elevations up to 500 m;
3) over 500 m to 4-5 km - plateaus, plateaus, highlands.
The highest plain on Earth is the Tibetan Plateau with altitudes of 4-5 km. On the map, the Tibetan Plateau is shown in dark brown, and the Central Siberian Plateau is shown in light brown, because its heights are 800-1000 m. For example, the Ural Mountains are marked with the same color, the maximum height of which is 1895 m - Mount Narodnaya, and average – 1000 m.
I repeat my first question:
“What does the color scheme show on a physical map?” . After a short meeting of the participants, I heard in response: “Absolute marks of the terrain, but not the relief.” For this purpose, the map is accompanied by a scale of depths and heights in meters. If the relief were reflected, the land plains would be depicted as areas of a monochromatic green color, and the mountains as elongated areas of brown without any shades.
Topic: Conventional colors of a physical map.
Goals: - introduce students to the conventional colors of a physical map;
Develop map reading skills using conventional colors;
Reinforce the concepts of “plan”, “map”, “scale”;
Correction and development of visual-figurative thinking when working with
By card;
Developing the ability to respond with complete, detailed statements to the teacher’s questions.
Equipment : physical map of Russia, textbooks, workbooks, cards with individual tasks, presentation for the lesson.
New concepts : conventional colors of the physical map;
Terrain height scale from sea level.
During the classes.
Org moment.
In order for you to remember what topic we studied in the last lesson, you will have to solve the riddles:
There are fields - you can’t plow,
There are roads - you can't drive.
There is no water in the rivers and seas,
What is this and where does it happen, give me the answer.
S K I'm at school on the wall,
There are mountains and rivers on me,
I won’t hide it from you -
I'm also standing at school.
Okay, well done!
Yes, in the last lesson we got acquainted with the plan and map.
Activating students' knowledge: now pay attention to the screen.
1.What images of the earth’s surface exist? (slide 2) answers.
2.What is a site plan? They answer. Checking(slide3) - read
3.What is a card? They answer. Checking(slide4). - read.
4.Globe - what is it? They answer. Checking(slide 5) - read.
5. What is shown on the site plan? They answer. Checking(slide6). -reading.
6.What is shown on the cards? They answer. Checking(slide7).
7. What are the purposes of cards? They answer. Let's check.
(slides 8-12)
7.Is the scale the same on the site plan and the map? They answer.
8. What is scale? They answer. Checking(slide13) read.
Practical task: on the physical map p. 10, use the scale to find the distance between cities that are encrypted. Once you decipher the names of the cities, what will you do next? Measure the distance, then what? Fine. We found the scale on page 11 to be 1 cm 250 km. How do we find out what the distance between cities is? That's right, you need to multiply the received cm by 250 km. Answers: from Magadan to Moscow - from Yakutsk to Magadan - from Yakutsk to Moscow -
Fine.
Learning new material:
While working with a physical map, you probably noticed that the map is painted in different colors. Who knows what the concept of “conditional colors of a physical map” means? Answers.(slide 14). Name what conventional colors are found on the map? Answers.
Our planet has an uneven surface. On land there are lowlands, hills, plains, and mountains.
A physical map is a geographical map that depicts the surface of land, seas, and oceans.
Oceans, seas, rivers, lakes on a physical map indicateblue in different shades.The deepest parts of the oceans markdark blue.
The land surface is indicated by different conventional colors, depending on the height of the area.(slide 15)
The altitude of the area is measured from ocean or sea level.(slide16)
On a physical map there is an altitude scale and a depth scale, which can be used to determine the approximate height of the area on land and the depth of the sea or ocean.
Exercise: first group - you need to take cards with any color and match them with the text on the board. The second group - you need to take cards with a hint and match their colors with the geographical map. Fine.
Working with the textbook p. 83 we read and answer the questions:
1.What is a physical card?
2. How do physical maps indicate different shapes of the Earth’s surface?
3. Why do we need a scale of heights and depths on a physical map? Well done!
Working with the map: - find the mountains on the map. Read what they are called.
Find large plains and lowlands on the map. Read their names;
Find the sea on which the city, Magadan, is located, read its name.
Consolidation.
1. Work in workbooks p. 32 task 1, 2,3, 4.
Lesson summary: How do physical maps indicate the different shapes of the Earth's surface? They answer. Checking(slide 17).
D/Z p.83-85 question No. 5
Lesson grades.
Thanks everyone.
Preview:
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Conditional colors of the physical map
What images of the earth's surface exist?
A plan is a drawing of a small area of land.
A map is a reduced image of the earth's surface, made using conventional colors and symbols.
Globe - a three-dimensional reduced model of the globe.
The plan depicts small areas of the area - a city, a village, a field, a forest, etc.
Large areas of land and bodies of water are marked on the maps.
According to their purpose, cards are different: physical; geological; political; economic; administrative; natural areas.
Administrative map of the region
Physical map of the hemispheres
Economic map
Scale is a number that shows how many times the distances on the ground are reduced when depicted on the plan.
Conventional colors on a physical map show the shape of the Earth's surface. Using the height and depth scale on a physical map, you can determine the approximate height of the area on land and the depth of the sea or ocean.
Conditional colors of the physical map.
Terrain height scale from sea level.
The shapes of the earth's surface on a physical map are shown using color. Green indicates low places - lowlands, yellow - highlands, brown - mountains. Water bodies (oceans, seas, rivers, lakes) are marked in blue and blue.
Looking at geographic maps is quite interesting. Moreover, they are diverse. At school we had large wall maps, atlases and outline maps. I always liked finding all sorts of mountains and seas, rivers and plains on maps.
Shades of blue on a geographical map always indicate one thing - water.
What is blue in our nature? That's right: sky and water. But why is the sky on maps? This means that they represent all sorts of water bodies. What does this mean? That's what:
- oceans and seas;
- straits and bays;
- bays and estuaries;
- lakes and rivers;
- reservoirs and swamps (shown on maps as thin broken lines).
It is very comfortable. You can immediately see where the water is. There is more blue on the maps, since land still occupies a smaller part of our planet. Moreover, if rivers and lakes are painted the same color, then oceans and even large seas have different shades of blue. This is done in order to immediately focus attention on the depth. The bluer the color on the map, the greater the depth of the reservoir in this place. Even just looking at a geographical map, you can imagine which place is deeper.

Even on maps with a large scale (with a large reduction of the Earth), it is simply impossible to reflect on small objects (on rivers, lakes) all their depths, and there is no point in doing so. But on topographic maps of the area (where the scale is small and the size allows) sometimes depths are highlighted with more saturated shades of blue or conditional blue lines.
Shades of blue on old maps
Water was not always drawn blue on maps. In ancient maps, seas and oceans were simply not painted over. And the rivers were drawn in some other color: brown, black, green... .

In ancient times, people simply did not distinguish the color blue. It was as if he didn't exist. Some peoples did not even have such a word for “blue”. And there is not much blue in nature. Therefore, apparently, it appeared as a color much later than other colors. Only after this did they begin to paint water in shades of blue on geographical maps.
It’s so good that this blue color still appeared. After all, it is much more convenient when the water is blue, the earth is brown, and the vegetation is green.