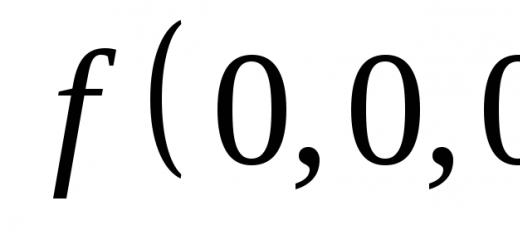Slide 3
A seed is an organ of sexual reproduction and dispersal of plants.
1. Wheat.
2. Buckwheat
5. Timofeevka
Slide 4
Seed structure
Slide 5
Slide 6
Young plant - seedling
1. Embryonic root
2. Embryonic shoot
Slide 7
Safety instructions when performing laboratory work.
- You should work at the table carefully.
- Do not make sudden movements.
- Use caution when using a piercing instrument (needle). Use your fingers to hold the object so as not to prick yourself.
- Keep your work area tidy and do not throw objects around.
- After completing the work, tidy up the work area.
Slide 8
Laboratory work No. 4
Topic: Study of the structure of bean seeds.
Purpose: to study the external and internal structure of the seed of a dicotyledonous plant.
Equipment: magnifying glass, dissecting needle, swollen bean seeds, napkin.
Slide 9
Progress
- Consider the appearance of the bean seed and note its shape.
- Find the hilum and the spermatic opening.
- Using a dissecting needle, remove the skin from the seed (pre-wet the seed so that it swells).
- Find the embryo of the seed. Study its structure. Consider the parts of the embryo: two cotyledons, an embryonic root, a stem, a bud.
- Determine which part of the bean seed contains the reserve nutrients.
- Draw a picture of the seed and label its parts.
- Draw a conclusion.
Slide 10
I believe it or not
Slide 11
bean seed
- Germinal root
- Peel
- Cotyledons
- Germ stalk
Slide 12
Conditions for seed germination
- Water: The seed embryo can only consume nutrients in dissolved form.
- Air oxygen: When seeds germinate, the embryo breathes intensively, requiring a constant flow of oxygen.
- Spare nutrients
- Heat: Different plants need different amounts of heat to germinate. Plants whose seeds require high temperatures to germinate are called heat-loving, while those that germinate at low temperatures are called cold-resistant.

1. Wheat. 2. Chamomile
3. Lupine
4. Clover
5. Peas



Flowering
plants
Monocots
Dicotyledons
corn, tulip
beans, peas

- 1. Embryonic root
- 2. Embryonic shoot

- You should work at the table carefully.
- Do not make sudden movements.
- Use caution when using a piercing instrument (needle). Use your fingers to hold the object so as not to prick yourself.
- Keep your work area tidy and do not throw objects around.
- After completing the work, tidy up the work area.

Laboratory work No. 4
Subject : Study of the structure of the bean seed.
Target : study the external and internal structure of the seed of a dicotyledonous plant.
Equipment : magnifying glass, dissecting needle, swollen bean seeds, napkin.

- Consider the appearance of the bean seed and note its shape.
- Find the hilum and the spermatic opening.
- Using a dissecting needle, remove the skin from the seed (pre-wet the seed so that it swells).
- Find the embryo of the seed. Study its structure. Consider the parts of the embryo: two cotyledons, an embryonic root, a stem, a bud.
- Determine which part of the bean seed contains the reserve nutrients.
- Draw a picture of the seed and label its parts.
- Draw a conclusion.

Germ stalk
Germinal root
Peel
Cotyledons

- Water: The seed embryo can only consume nutrients in dissolved form.
- Air oxygen: When seeds germinate, the embryo breathes intensively and requires a constant supply of oxygen.
- Spare nutrients
- Warm: Different plants need different amounts of heat to germinate. Plants whose seeds require high temperatures to germinate are called heat-loving, while those that germinate at low temperatures are called cold-resistant.

1.5–2 mm 2–4 cm 4–5 cm
Small seeds Medium seeds Large seeds
Poppy Cucumbers Pumpkin
Turnip Carrot Peas
Salad Tomatoes Zucchini
Onions Radishes Beans

The meaning of seeds in nature
The importance of seeds in human life
1. Plant propagation
- Food product
2. Plant dispersal
A. by the wind
B. water
B. Animals
D. Self-spreading
A. Cereals: wheat, rice, corn, buckwheat, etc.
B. Legumes: peas, beans, soybeans, beans, etc.
B. Oilseeds: sunflower, flax, cotton, peanuts, etc.
G. Tonics: coffee, cocoa
D. spices: pepper, cumin, vanilla
2. Material for selection






Thanks for the work.
The presentation was prepared by a biology teacher at MBOU Secondary School
r.p. Sura Kazarinova L.V.
The structure of seeds - here is a presentation in front of you, which we use, of course, as always in sixth grade biology lessons, because in this age group we teach plants in botany lessons. Biology is very educational and interesting, but for teachers it is also work with younger schoolchildren, who are still difficult to keep their attention on studying the subject. And this is not due to a reluctance to learn, but to high mobility at this age. This means that to a biology lesson you need to bring materials that will be able to attract attention. And we know that such materials are presentations on 6th grade biology in the format microsoft powerpoint.
topic Seeds – 6th grade biology” width=”480″ height=”360″ class=”aligncenter size-full wp-image-3810″ />
Biology issues, especially in the lower grades, need to be analyzed in great detail, while, as in any lessons, the teacher sets the task of students consciously understanding the material. This can be achieved if students themselves actively participate in the educational process. And this means that we need to involve them in work. But children get tired of constantly writing in notebooks, so let them work with the Powerpoint presentation tests; you can download it for free, especially since you can easily download it here.
And the World of Biology, our website, tries to help you with this. Fortunately, our colleagues help us very well, sending us their developments, because creating a website, promotion and promotion takes us a lot of time. The World of Biology is a free Internet resource with free materials for biology teachers, where not only a teacher, pupil or student, but anyone can download powerpoint presentations!
Why do teachers use presentations in 6th grade biology lessons?
The point here is not only in the sixth grade, because such developments can be brought and shown in lessons in any grade. It’s just that sixth graders are such an active and restless people that the teacher has to resort to many ways of motivating and attracting attention, and one of these ways is to demonstrate a 6th grade biology presentation on the topic of the lesson.
- Presentation, computer, projector, interactive board - all this is interesting for children, and they perceive such a lesson enthusiastically
- The opportunity to go to the interactive whiteboard and draw some shape on it with a marker - isn’t this happiness for a child?
- The teacher receives a powerful tool for attracting attention, increasing children’s interest and the quality of learning in their lessons.
And for this reason, a biology teacher will always need to download and use additional materials.
Preview:
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Seed, its structure and meaning
Purpose of the lesson: To study the structural features of seeds and their significance. House. task: - learn point 5; - message, or create a crossword puzzle on the topic “Seed” (minimum 10 words)
Variety of seeds Lady's slipper Poppy seeds. 6-11 thousand seeds weigh 3-5 g
Seychelles palm seeds. The weight of one seed is 15-25 kg
Carob fruits and seeds Carob seeds. The weight of one seed is 200 milligrams. Carob fruit
Variety of seeds Cotton seeds
Marigolds Asters Petunia
Laboratory work Topic: Study of the structure of seeds. signs beans wheat Peel Cotyledons (how many) Nutrient reserve (where is it located) Germ (structure)
Structure of a bean seed
Structure of wheat grain
Laboratory work Topic: Study of the structure of seeds. signs beans wheat Peel Cotyledons (how many) 2 1 Nutrient reserve (where is it located) In the cotyledons In the endosperm Embryo (structure) Embryonic root, embryonic stalk, 2 cotyledons Germinal root, embryonic stalk, 1 cotyledon
Seed germination
Believe it or not 1. The cotyledons of a bean seed have the largest mass. 2. All seeds have two cotyledons and an endosperm. 3. The structure of the seeds of all dicotyledonous plants is the same. 4. The root appears first on the seedling. 5. A young plant is called a shoot. 6. The outside of the seeds is covered with bark. 7. Water penetrates into the seed through the seed entrance. 8. Plant seeds that have one cotyledon are called dicotyledonous. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 + - + + - - + -
Fill in the missing words The embryo of a monocot seed consists of ... ..., ... ... and ... ... . The embryo of a monocot seed consists of an embryonic root, an embryonic shoot and one cotyledon. Dicotyledons are plants whose seeds contain... Dicotyledons are plants whose seeds contain two cotyledons.