Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon that even today attracts the attention of scientists not only due to their lack of knowledge, but also due to their unpredictability, which can harm humanity.
What is an earthquake?
An earthquake is an underground tremors that can be felt by a person largely depending on the power of vibration of the earth's surface. Earthquakes are not uncommon and occur every day in different parts of the planet. Often, most earthquakes occur at the bottom of the oceans, which avoids catastrophic destruction within densely populated cities.
The principle of earthquakes
What causes earthquakes? Earthquakes can be caused by both natural causes and man-made ones.
Most often, earthquakes occur due to faults in tectonic plates and their rapid displacement. For a person, a fault is not noticeable until the moment when the energy generated from the rupture of rocks begins to break out to the surface.
How do earthquakes occur due to unnatural causes? Quite often, a person, through his carelessness, provokes the appearance of artificial tremors, which in their power are not at all inferior to natural ones. Among these reasons are the following:
- - explosions;
- - overfilling of reservoirs;
- - above-ground (underground) nuclear explosion;
- - collapses in mines.
The location where a tectonic plate breaks is the source of an earthquake. Not only the strength of the potential push, but also its duration will depend on the depth of its location. If the source is located 100 kilometers from the surface, then its strength will be more than noticeable. Most likely, this earthquake will lead to the destruction of houses and buildings. Occurring in the sea, such earthquakes cause tsunamis. However, the source can be located much deeper - 700 and 800 kilometers. Such phenomena are not dangerous and can only be recorded using special instruments - seismographs.
The place where the earthquake is most powerful is called the epicenter. It is this piece of land that is considered the most dangerous for the existence of all living things.
Studying earthquakes
A detailed study of the nature of earthquakes makes it possible to prevent many of them and make the life of the population living in dangerous places more peaceful. To determine the power and measure the strength of an earthquake, two basic concepts are used:
- - magnitude;
- - intensity;
The magnitude of an earthquake is a measure that measures the energy released during release from the source in the form of seismic waves. The magnitude scale allows you to accurately determine the origins of vibrations.
Intensity is measured in points and allows you to determine the ratio of the magnitude of tremors and their seismic activity from 0 to 12 points on the Richter scale.
Features and signs of earthquakes
Regardless of what causes an earthquake and in what area it is localized, its duration will be approximately the same. One push lasts on average 20-30 seconds. But history has recorded cases when a single shock without repetitions could last up to three minutes.
Signs of an approaching earthquake are the anxiety of animals, which, sensing the slightest vibrations on the surface of the earth, try to get away from the ill-fated place. Other signs of an imminent earthquake include:
- - the appearance of characteristic clouds in the form of oblong ribbons;
- - change in water level in wells;
- - malfunctions of electrical equipment and mobile phones.
How to behave during earthquakes?
How to behave during an earthquake to save your life?
- - Maintain reasonableness and calm;
- - When indoors, never hide under fragile furniture, such as a bed. Lie down next to them in the fetal position and cover your head with your hands (or protect your head with something extra). If the roof collapses, it will fall on the furniture and a layer may form, in which you will find yourself. It is important to choose strong furniture whose widest part is on the floor, i.e. this furniture cannot fall;
- - When outside, move away from tall buildings and structures, power lines that may collapse.
- - Cover your mouth and nose with a wet cloth to prevent dust and fumes from entering if any object catches fire.

If you notice an injured person in a building, wait until the tremors are over and only then get into the room. Otherwise, both people may be trapped.
Where do earthquakes not occur and why?
Earthquakes occur where tectonic plates break. Therefore, countries and cities located on a solid tectonic plate without faults do not have to worry about their safety.
Australia is the only continent in the world that is not at the junction of lithospheric plates. There are no active volcanoes and high mountains on it and, accordingly, there are no earthquakes. There are also no earthquakes in Antarctica and Greenland. The presence of the enormous weight of the ice shell prevents the spread of tremors across the surface of the earth.
The probability of earthquakes occurring on the territory of the Russian Federation is quite high in rocky areas, where the displacement and movement of rocks is most actively observed. Thus, high seismicity is observed in the North Caucasus, Altai, Siberia and the Far East.
An earthquake is a physical vibration of the lithosphere - the solid shell of the earth's crust, which is in constant motion. Often such phenomena occur in mountainous areas. It is there that underground rocks continue to form, causing the Earth's crust to be especially mobile.
Causes of the disaster
The causes of earthquakes can be different. One of them is the displacement and collision of oceanic or continental plates. During such phenomena, the surface of the Earth vibrates noticeably and often leads to the destruction of buildings. Such earthquakes are called tectonic. They may form new depressions or mountains.
Volcanic earthquakes occur due to the constant pressure of hot lava and all kinds of gases on the earth's crust. Such earthquakes can last for weeks, but, as a rule, they do not cause massive destruction. In addition, such a phenomenon often serves as a prerequisite for a volcanic eruption, the consequences of which can be much more dangerous for people than the disaster itself.

There is another type of earthquake - landslide, which occurs for a completely different reason. Groundwater sometimes forms underground voids. Under the pressure of the earth's surface, huge sections of the Earth fall down with a roar, causing small vibrations that can be felt many kilometers from the epicenter.
Earthquake scores
To determine the strength of an earthquake, they generally resort to either a ten- or twelve-point scale. The 10-point Richter scale determines the amount of energy released. The 12-point Medvedev-Sponheuer-Karnik system describes the impact of vibrations on the Earth's surface.
The Richter scale and the 12-point scale are not comparable. For example: scientists detonate a bomb underground twice. One at a depth of 100 m, the other at a depth of 200 m. The energy expended is the same, which leads to the same Richter rating. But the consequence of the explosion - displacement of the crust - has varying degrees of severity and has different effects on the infrastructure.
Degree of destruction

What is an earthquake from the point of view of seismic instruments? A one-point phenomenon is determined only by the equipment. 2 points can be sensitive animals, and also, in rare cases, especially sensitive people located on the upper floors. A score of 3 feels like the vibration of a building caused by a passing truck. A magnitude 4 earthquake causes slight rattling of glass. With a score of five, the phenomenon is felt by everyone, and it does not matter where the person is, on the street or in a building. An earthquake of magnitude 6 is called strong. It terrifies many: people run out into the street, and mother-in-laws form on some walls of houses. A score of 7 leads to cracks in almost all houses. 8 points: architectural monuments, factory chimneys, towers are knocked over, and cracks appear in the soil. 9 points lead to severe damage to houses. Wooden buildings either topple over or sag heavily. Magnitude 10 earthquakes lead to cracks in the ground up to 1 meter thick. 11 points is a disaster. Stone houses and bridges are collapsing. Landslides occur. No building can withstand 12 points. With such a catastrophe, the topography of the Earth changes, the flow of rivers is diverted and waterfalls appear.
Japanese earthquake
A destructive earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, 373 km from the capital of Japan, Tokyo. This happened on March 11, 2011 at 14:46 local time.

A magnitude 9 earthquake in Japan led to massive destruction. The tsunami that hit the country's east coast flooded large parts of the coastline, destroying houses, yachts and cars. The height of the waves reached 30-40 m. The immediate reaction of people prepared for such tests saved their lives. Only those who left home in time and found themselves in a safe place were able to avoid death.
Japan earthquake victims
Unfortunately, there were no casualties. The Great East Japan Earthquake, as the event became officially known, claimed 16,000 lives. 350,000 people in Japan were left homeless, leading to internal migration. Many settlements were wiped off the face of the Earth, and there was no electricity even in large cities.
The earthquake in Japan radically changed the habitual way of life of the population and greatly undermined the economy of the state. The authorities estimated the losses caused by this disaster at $300 billion.
What is an earthquake from the point of view of a Japanese resident? It is a natural disaster that keeps the country in constant turmoil. The looming threat forces scientists to invent more accurate instruments for detecting earthquakes and more durable materials for building buildings.
Affected Nepal
On April 25, 2015, at 12:35 p.m., an almost 8-magnitude earthquake that lasted 20 seconds occurred in central Nepal. The following happened at 13:00. Aftershocks lasted until May 12. The reason was a geological fault on the line where the Hindustan plate meets the Eurasian plate. As a result of these tremors, the capital of Nepal, Kathmandu, moved to the south by three meters.

Soon the whole earth learned about the destruction caused by the earthquake in Nepal. Cameras installed directly on the street recorded the moment of the tremors and their consequences.
26 districts of the country, as well as Bangladesh and India, felt what an earthquake was like. Authorities are still receiving reports of missing people and collapsed buildings. 8.5 thousand Nepalese lost their lives, 17.5 thousand were injured, and about 500 thousand were left homeless.
The earthquake in Nepal caused real panic among the population. And it is not surprising, because people lost their relatives and saw how quickly what was dear to their hearts collapsed. But problems, as we know, unite, as was proven by the people of Nepal, who worked side by side to restore the former appearance of city streets.

Recent earthquake
On June 8, 2015, an earthquake of magnitude 5.2 occurred in Kyrgyzstan. This is the last earthquake to exceed magnitude 5.
Speaking about a terrible natural disaster, one cannot fail to mention the earthquake on the island of Haiti, which occurred on January 12, 2010. A series of tremors ranging from magnitude 5 to 7 claimed 300,000 lives. The world will remember this and other similar tragedies for a long time.
In March, the shores of Panama experienced a magnitude 5.6 earthquake. In March 2014, Romania and southwestern Ukraine learned the hard way what an earthquake is. Fortunately, there were no casualties, but many experienced anxiety before the disaster. In recent years, earthquake scores have not crossed the brink of catastrophe.
Earthquake Frequency
So, the movement of the earth's crust has various natural causes. Earthquakes, according to seismologists, occur up to 500,000 annually in different parts of the Earth. Of these, approximately 100,000 are felt by people, and 1,000 cause serious damage: they destroy buildings, highways and railways, break power lines, and sometimes carry entire cities underground.
In times of high technology and established rhythms of life, people often forget that they do not control everything until the end. And the manifestations of global events such as earthquakes are only in a few cases truly noticeable. But if this cataclysm does reach civilized corners, this event may remain a scar on people's memories for a long time.
How does an earthquake happen?
Vibrations of the earth's surface, as well as tremors, are the process of an earthquake. Scientists believe that the earth's crust consists of 20 huge plates. They move at a very low speed of about a few centimeters per year through the upper layer of the mantle. The boundaries between plates are often mountains or deep-sea trenches. Where the slabs slide over each other, the edges become folded. And in the crust itself, cracks form - tectonic faults, through which mantle material seeps to the surface. Natural disasters such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions often occur in these places. The area of shock wave divergence sometimes extends for hundreds of kilometers.
Causes of the earthquake
- Collapses of large masses of rock caused by groundwater often cause earth tremors over a short distance.
- In places of active volcanoes, under the pressure of lava and gases on the upper part of the crust, nearby areas are exposed to weak but prolonged tremors, often on the eve of an eruption.
- Man-made activities of people - the construction of dams, mining activity, nuclear weapons testing, accompanied by powerful underground explosions or redistribution of internal water masses.


How an earthquake occurs - earthquake foci
But not only the cause itself directly affects the power of the earthquake, but also the depth of the source of occurrence. The source or hypocenter itself can be located at any depth, from several kilometers to hundreds of kilometers. And it is a sharp displacement of large massifs of rocks. Even with a slight shift, vibrations of the earth's surface will occur, and the range of their movement will depend only on their strength and sharpness. But the further the surface, the less destructive the consequences of the cataclysm will be. The point above the source in the ground layer will be the epicenter. And it is often subject to the greatest deformation and destruction during the movement of seismic waves. 

How an earthquake occurs - zones of seismic activity
Due to the fact that our planet has not yet stopped its geological formation, there are 2 zones - the Mediterranean and the Pacific. The Mediterranean stretches from the Sunda Islands to the Isthmus of Panama. The Pacific covers Japan, Kamchatka, Alaska, moves further to the California mountains, Peru, Antarctica and many other places. There is constant seismic activity due to the formation of young mountains and volcanic activity.


How does an earthquake occur - the strength of the earthquake
The consequences of such earthly activity can be dangerous. There is a whole science for studying and recording it - seismology. It uses several types of measurements of magnitude - a measure of the energy of seismic waves. The most popular Richter scale with a 10-point system.
- Less than 3 points are recorded only by seismographs due to their weakness.
- From 3 to 4 points a person already feels slight swaying of the surface. The environment begins to react - the movement of dishes, the swaying of chandeliers.
- At 5 points, the effect is enhanced; in old buildings, interior decoration may crumble.
- 6 points can significantly damage old buildings, causing rattling or cracking of glass in new houses, but they are already damaged at 7 points;
- Points 8 and 9 cause significant destruction over large areas and bridge collapses.
- The strongest magnitude 10 earthquakes are also the rarest and cause catastrophic destruction.


- When living in high-rise buildings, you should understand that the lower a person is, the better, but during evacuation you cannot use elevators.
- It is worth leaving buildings and moving away from them to a safe distance (turning off electricity and gas), avoiding large trees and power lines.
- If it is not possible to leave the premises, you need to move away from window openings and tall furniture or hide under a strong table or bed.
- While driving, it is better to stop and avoid high points or bridges.


Humanity cannot yet prevent earthquakes, or even predict in detail the reaction of the earth's crust to seismic shocks. Due to the huge number of variables involved, these are incredibly complex forecasts. A person successfully passively defends himself in the form of strengthening buildings and improving the layout of infrastructure. This allows countries located on the line of constant seismic activity to develop successfully.
Lesson summary "Earthquake". Objectives of the lesson: To give children an understanding of such a natural phenomenon as an earthquake. To introduce the rules of safe behavior. Provide children with psychological support in overcoming fear.
Download:
Preview:
LESSON SUMMARY “EARTHQUAKE”
Educational field "Security"
Tasks:
Educational:
Give children an idea of such a natural phenomenon as an earthquake;
Introduce the rules of safe behavior in an emergency;
To form in children an idea of the inextricable connection between man and natural phenomena;
Introduce new concepts into the children's vocabulary: extreme situations, seismic waves, seismologists, seismograph, earth's crust.
Educational:
Develop analytical thinking in the process of research activities.
Educational:
Provide children with psychological support in overcoming fear.
Materials and equipment:
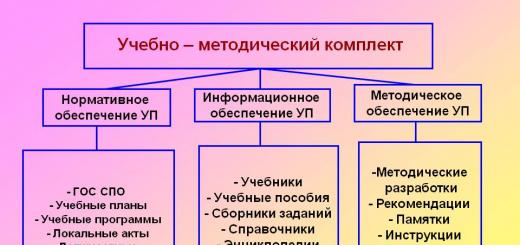
Drawing – a diagram of the “Earth in cross-section”, napkins, a basin of water, a pebble, a device – a seismograph, schematic drawings about safety rules during an earthquake, illustrations with a schematic representation of a room for each child, figures of men, red circles.
PROGRESS OF THE CLASS:
Guys, today I want to talk to you about dangerous situations that we may encounter in life. What dangerous situations do you know?
(fire, flood, accident, explosion, attack by criminals)
Right. These are all dangerous situations, they are also called extreme. Extreme situations always threaten the health and lives of people and harm nature. Listen to a short story.
The earth shook: its first convulsion lasted almost ten seconds. The cracking and creaking of window frames, the clinking of glass, the roar of falling stairs awakened the sleeping people. The ceiling was torn like paper. In the darkness everything swayed and fell. The earth hummed dully.
Guys, you listened to my story. What natural phenomenon do you think it talks about?
That's right, about the earthquake. Do you know what an earthquake is?
Let's figure out together what an earthquake is and why it happens. Look at this drawing. Our planet consists of a core, mantle and crust. The Earth's crust is the outermost layer of the Earth. Below the earth's crust is the mantle. It contains a lot of solutions, gases, and melts. The earth's crust is not a solid crust, like an eggshell, but consists of huge plates. The temperature in the mantle is very high, so sometimes an explosion occurs and the plates of the earth's crust begin to move. These strong tremors and blows inside cause the shaking of the earth - an earthquake. The place where an earthquake originates is called the earthquake focus. The tremors in this place are the strongest. From the source of the earthquake, like from a stone thrown into water, waves run in all directions. These waves are called seismic.
Experience with water.
To make it clear to you how seismic waves occur, we will do an experiment with water. Imagine that a pebble is an explosion inside the Earth; waves emanate from the place where we threw the pebble. Closer to the pebble, the waves are small, but very strong; further on they weaken.
Experience with napkins.
When waves occur, what do you think happens to the Earth's crust?
Let's do one more experiment. There are napkins in front of you. Imagine that this is the earth’s crust and it is affected by earthquake forces from both sides. Place your hands along the edges of the napkin. Move your palms together with the napkin towards the middle. What's happening?
Folds are visible on the surface. This is how the earth's crust changes its shape. Imagine that houses, cars, and power lines would stand on this napkin. What would happen to them?
Unfortunately, people have not yet learned to deal with this natural phenomenon and cannot prevent it. But they can predict and warn about impending danger. For this purpose, our planet is monitored day and night. Such scientists are called seismologists. And scientists - seismologists - are helped by special devices - seismographs. They receive and record all vibrations in the earth's crust. I have prepared such a device for you - a seismograph - to show you how it works.
Demonstration of a device - a seismograph.
When the Earth is at rest, the device draws a straight line. But as soon as tremors and vibrations occur in the earth’s crust, the device immediately begins to record them.
But it is not always possible to predict the time and strength of a future earthquake, and then, if the earthquake is strong, many people die. But this can be avoided if you know how to behave correctly during an earthquake.
Can you tell us about the rules of safe behavior on the street?
Working with illustrations. Modeling the rules of behavior on the street during an earthquake.
Do not panic and move to an open place.
Move in open space, away from buildings, trees, and downed wires.
Protect yourself from falling debris, glass, and heavy objects.
You cannot enter houses or continue moving in public transport.
But during an earthquake you can be not only outside, but also indoors. We will now find out what to do in such cases.
Working at tables.
You each have a drawing of an apartment on your table. It is necessary to place the little people in safe places, and use red circles to mark the places in the apartment where you consider it dangerous to be during an earthquake.
Independent activity of children. Job analysis.
Carlson flies into the group.
Hello guys. What I experienced recently. Just awful.
Educator: - Carlson, what scared you so much?
Carlson: - I survived the earthquake. I was so scared. At first I hid in the closet, but he was shaking so much.
Educator: - Guys, can I hide in the closet or next to it? Why?
What did you do then?
Carlson: - I sat by the window.
Educator: Did Carlson do the right thing? Explain why?
Carlson: - I sat under the bookshelf so that the ceiling wouldn’t fall on me.
Educator: - Carlson, you don’t know at all how to behave correctly during an earthquake. But our guys know and are not afraid of anything. They know earthquake safety very well and can teach you.
Carlson: - Teach me, guys, please.
Educator: - Let's read poems to Carlson about safety rules during an earthquake.
1 child: Natural phenomena can be destructive
And the earthquake is considered the most destructive.
There are not enough words to describe everything, the whole city is distorted,
There are collapsed houses and crippled vehicles.
2nd child: A shock caught you inside, and the path is cut off,
Hurry to stand in the doorway, don’t panic, and don’t be timid,
As soon as the tremors subside, run from the house as soon as possible.
3rd child: A barn, a stable would be opened, the animals could be released into the wild.
And he himself went there, into the open space and breadth, into the square, street, wasteland.
Where there is a field and a plain, only there will you find salvation.
Carlson: - Now I know how to behave correctly during an earthquake and I will no longer be afraid. Thank you guys for teaching me about safety. And now it's time for me to return. Goodbye.
Educator: - Today you learned a lot of new and useful things. It was very interesting for me to communicate with you.
"COGNITION"
Activating children's thinking through solving problem situations, training, viewing and discussing educational books, illustrations on this topic, modeling rules and situations of safe behavior during an earthquake indoors, outdoors, in nature, spatial orientation exercises (creating and reading diagrams, routes).
"READING FICTION"
Listening and discussing works of art, memorizing poems, guessing riddles, games and exercises based on the texts of poems, theatrical activities on topics read.
"COMMUNICATION"
Development of free communication, coherent speech, evidence-based speech in the process of mastering the basics of safe behavior during an earthquake through situational communication, conversations, storytelling, reasoning, guessing riddles.
"SOCIALIZATION"
Encouraging children to self-esteem and evaluate the actions and behavior of others, developing moral and volitional qualities through the creation of game situations, situations of moral choice, and role-playing games.
"HEALTH"
Formation of primary value ideas about health and a healthy lifestyle through the organization of routine processes, observations, conversations, explanations, games, reading.
Integration of educational areas in the process of forming the foundations of safe behavior in emergency situations in preschoolers
"SAFETY"
Formation of ideas about emergency situations and methods of behavior in them.
sss
"PHYSICAL CULTURE"
Maintaining physical activity through children’s participation in outdoor games, relay races, and games-competitions that promote the development of psychophysical qualities, coordination of movements, the ability to navigate in space, and the consolidation of safe behavior skills in emergency situations.
"MUSIC"
To promote a deeper emotional perception of the material through musical accompaniment of all types of children's activities, conversations on the content of the song, musical and rhythmic movements, and the development of artistic abilities.
"ARTISTIC CREATIVITY"
Development of figurative representation, observation, the ability to notice the characteristic features of objects or objects and convey them through various types of productive activities (drawing, appliqué, design).
Target:
- give children an idea of such a formidable natural phenomenon as an earthquake;
- talk about the reasons for its occurrence, signs of an approaching earthquake and ways to survive this natural phenomenon.
Tasks:
- Educational: introduce children to new concepts: earthquake source, epicenter, seismogram, seismic areas; talk about the operation of the seismograph device.
- Educating: fostering a caring attitude towards your life and the lives of other people.
- Developmental: development of thinking, memory, spatial imagination, logical thinking.
Equipment: Computer, screen, “World Map”, atlases.
During the classes
1. Organizational momentTeacher: Hello guys! Let's check if everything is ready for the lesson. I will name the items, and you check their availability: Textbook, notebook, atlas, diary, pencil case. You are ready!
2. Checking homework (frontal survey)– In the last lesson you talked about the structure of the Earth. A few questions on this topic:
1) What is in the center of our planet?
2) What is the name of the upper solid shell of the Earth?
3) What shell comes after the earth’s crust? Where did this name come from?
4) Is the thickness of the earth’s crust the same everywhere? Where is it most powerful? And the thinnest? So what is the earth's crust like?
The earth's crust experiences movements: horizontal and vertical.
What examples of slow movements can you give? ( Dam slide. Cm. Annex 1)
5) Working with slides.
What do we see on the slide? Where is the horst and where is the graben?
What will happen if rapid movements of the earth's crust occur?
The topic of our lesson: “Earthquakes.”
3. Study a new topic– What natural phenomenon is this poem about?
Children. About the earthquake.
An earthquake is a rapid movement of the earth's crust.
Few of the formidable natural phenomena can compare in destructive power and danger with an earthquake. The history of mankind counts millions of victims, hundreds of cities and towns, buildings, damaged and destroyed by this natural disaster.
The source of the earthquake They call the place in the depths of the earth where an earthquake originates, where a rupture or displacement of rocks occurs.
Epicenter of the earthquake called the place on the surface of the earth closest to the hearth.
(Children draw the source and epicenter of the earthquake in their notebooks. Children write down the concepts: source, epicenter, earthquake.)
In Russia, earthquakes most often occur in the Pacific Ocean region, on the Kuril-Kamchatka arc. Many people believe that earthquakes occur in areas where there are mountains. But that's not true. There is no place in our country where a strong earthquake has not occurred at some point. For example, in 1230, 1446 and 1556 the inhabitants of Vladimir felt the underground element, in 1446, 1802 and 1977 - in Moscow, in 1230 and 1556 - in Nizhny Novgorod.
Earthquake strength – degree of earthquake manifestation on the earth’s surface; is assessed in points. Most countries have adopted the international 12-point scale, while Japan has adopted a 7-point scale.
A 12-point international seismic scale has been created based on the intensity and depth of the source. (Richter scale) . (named after the American seismologist C. F. Richter (1900–1985), who proposed it in 1935).
Conventionally, earthquakes are divided into:
- Weak – 1–3 points
- Moderate – 4 points
- Quite strong – 5 points
- Strong – 6 points
- Destructive – 8 points
- Devastating – 9 points
- Destructive – 10 points
- Catastrophic – 11–12 points.
Science studies earthquakesSeismology.
Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. Constant observations of earthquakes are carried out by the seismic service. The modern global network includes over 2000 stationary seismic stations, the data of which is systematically published in seismological bulletins and catalogues.
A special device called seismograph.(Description of the device).
It records an earthquake, noting the time, strength and direction of each individual shock. The course of an earthquake is called seismogram . It is written on paper inserted into a seismograph.
Good seismographs record not only the earthquake that occurred in the area where the instrument is installed, i.e. where the seismic station is located or in the immediate vicinity, but also the most distant earthquakes and make it possible to determine at what distance from the station they occurred, as well as their strength.
The question of at what depth the earthquake source is located is decided by calculations based on the seismogram. An earthquake can last several hours or a whole day. Sometimes a known area of the Earth experiences shaking of varying strength over a period of days, weeks or months. It is estimated that about 20 catastrophic earthquakes occur on our planet per year, 150 destructive, 7,000 strong and more than 150,000 weak. And the territory where earthquakes have already occurred or are expected to occur is called a seismic region.
Almost every earthquake is accompanied by sound phenomena, which make a strong impression and inspire horror in a person. The underground roar is sometimes like the dull rumble of thunder, sometimes the bubbling of boiling water, sometimes the roar of a heavy train or a landslide, sometimes the whistle of the wind, sometimes the squeal of a projectile flying, or an explosion. Sounds sometimes lead the earthquake wave, sometimes lag behind it. Observations have shown that most earthquakes originates at a depth of 50 km from the earth’s surface, a small part – at a depth of 50 to 100 km and only isolated earthquakes emanate from depths up to 300-700 km.
The consequences of earthquakes are very dangerous. They cause landslides, tsunamis, fires and even volcanic eruptions. In seconds, cities are destroyed and thousands of people die. According to some estimates, earthquakes have killed 150 million people since the beginning of civilization.
The largest earthquake of the 20th century occurred on December 7, 1986. at 11:41 am in Armenia. It covered an area with a population of over 700 thousand people. The strength of the tremors at the epicenter of the natural disaster reached more than 10 points. The cities of Kirovokan, Stepanakert, Leninakan were especially affected, and Spitak was practically wiped off the face of the earth. Tens of thousands of people died under the ruins.
Subsidences of larger areas or their failures occur during very strong earthquakes, reaching even 60 m in depth and are accompanied by the eruption of water and mud. In Lisbon, during the earthquake of 1755, an embankment with a mass of people gathered on it sank, and during the earthquake of 1861, a failure occurred in the delta of the Selenga River on Lake Baikal - the subsidence of an area of about 260 km2, which, together with the dwellings and herds located on it, sank below the level of the lake on average by 2.9 m.
If an earthquake occurs at the bottom of the ocean (sea), a tsunami is formed. This occurred in December 2004, claiming more than 200,000 lives.
How to predict an impending disaster? There are a number of signs that can be used to predict a natural disaster in advance.
Signs of a near earthquake:
- sudden changes in water level in reservoirs or its turbidity;
- the smell of gas in areas where there was none before;
- disturbance of birds and domestic animals;
- weak tremors of the earth's surface;
- disturbance in the operation of radio, telegraph, electromagnetic devices.
- TVs take programs from other countries
Earthquakes occur very often in Japan. The Japanese keep special types of fish in their home aquariums, by whose behavior they learn about an upcoming earthquake. A few hours before the shock, the fish begin to behave restlessly, rushing about, throwing themselves out of the water.
The royal primrose grows in Indonesia; it is noticed that it blooms before a volcanic eruption, and as is known, this is often preceded by an earthquake, which is why this flower is called the flower of death.
- It is very important for anyone to know the rules of safe behavior during an earthquake.
- At the first shock, try to immediately leave the building within a few minutes.
- Go down the stairs only, notifying neighbors of the need to leave the building.
- If you stay in the apartment, you need to stand in the doorway or in the corner of the room, away from windows, lamps, cabinets and mirrors. Why?
- Avoid panic.
- If an earthquake catches you in a car, you need to stop immediately and not get out of the car until the shaking is over.
Knowing about the danger of earthquakes, people began to develop new methods of construction. This is how in Japan they build houses on shock absorbers that dampen seismic waves.
4. Consolidation of what has been learned- What natural phenomenon were we talking about today?
- What is the strength of an earthquake?
- What is the focus of an earthquake? Epicenter?
- One scientist in an interview said that our planet is shaking as if in a fever... Do you agree with him?
- Are there living seismographs?
- Where does the “Flower of Death” grow?
- Are there man-made earthquakes? (i.e. caused by human activity)
- What did we talk about today?
- What new did you learn?