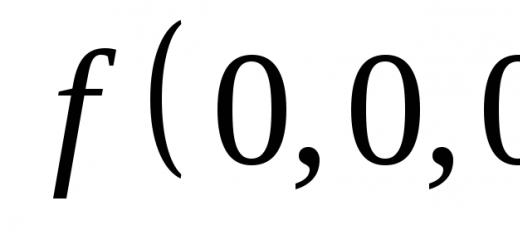to the letter from the Department of Education
dated March 25, 2015 No. DO-1913-04-07
Department of Education of the Vladimir Region Administration
State Autonomous Educational Institution of Additional Professional Education of the Vladimir Region “Vladimir Institute for Educational Development
named after L.I. Novikova"
Basic approaches to psychological and pedagogical support for the introduction of the federal state educational standard for preschool education
Guidelines for
teaching staff of preschool educational organizations
L.N.Prokhorova. Basic approaches to psychological and pedagogical support for the introduction of the federal state educational standard for preschool education. Methodological recommendations for teaching staff of preschool educational organizations / L.N. Prokhorova, head of the department of preschool education VIRO, candidate of pedagogical sciences, associate professor, psychologist of the highest qualification category - M.: Vladimir Institute for Educational Development, 2015.
The proposed methodological recommendations are addressed to various subjects of educational relations: heads of preschool educational organizations, teachers of all categories and temporary creative teams involved in the design and creation of a system of psychological and pedagogical support for the introduction of the federal state educational standard for preschool education
The introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education led to changing the paradigm of teacher education and turning it essentially into psychological and pedagogical education, which means the need to develop a system of psychological and pedagogical support that will allow preschool students to carry out positive socialization, personal development, initiative, and creative abilities in the process of their professional activities.
The system of psychological and pedagogical support for the introduction of the federal state educational standard for preschool education is being developed by the teaching staff of preschool educational institutions in order to ensure equal opportunities for every child in receiving high-quality preschool education, taking into account the characteristics of the teaching staff and the requests of the parent community (based on monitoring results).
Psychological and pedagogical support – This is a holistic, systematically organized activity, during which socio-psychological and pedagogical conditions are created to ensure the full development of the personality of children in all main educational areas, namely: in the areas of social-communicative, cognitive, speech, artistic, aesthetic and physical development of the personality of children against the backdrop of their emotional well-being and positive attitude towards the world, towards themselves and towards other people.
In the Russian language dictionary S.I. Ozhegov interprets accompaniment as follows - “to follow along with someone, being nearby, leading somewhere or following someone” (S.I. Ozhegov, 1990). The use of support is dictated by the need to integrate the processes of provision, support, protection, assistance, as well as to emphasize the independence of the subject in decision-making. Analysis of scientific literature gives reason to assume that the essence of pedagogical support is considered and understood in the following meanings: as a system of pedagogical actions; as a set of measures of a different nature; as a goal-oriented process; as an educational technology.
The following stages of psychological and pedagogical support are distinguished (T.V. Anokhina):
Diagnostic: involves the detection of the problems of the person being accompanied, his awareness of their significance and the desire to resolve them.
Search: joint search for reasons and solutions together with the person being accompanied.
Design: building a contractual relationship between the teacher and the person being accompanied in order to move towards solving the problem.
Activity: complementary activities of the teacher and the accompanied person, where the person being accompanied mainly acts.
Reflexive: analysis of joint activities to solve the problem, discussion of the results obtained, ways to solve the problem.
Tasks psychological and pedagogical support:
Systematic assessment of the level of individual development of children associated with assessing the effectiveness of pedagogical actions.
Creation of socio-psychological conditions for the disclosure of cognitive, creative capabilities of pupils and their successful development in children's activities.
Organization of assistance to children with special educational needs (including problems in psychological development and learning).
Psychological and pedagogical support for preschool teachers and parents of pupils
The development of a system of psychological and pedagogical support, as well as the organization of all work on its implementation, should be based on scientific validity, consistency, age and sociocultural adequacy, information security and practical expediency.
Regulatory framework The development of a system of psychological and pedagogical support are the following documents at the federal and regional levels:
Federal Law No. 273-FZ of December 29, 2012 “On Education in the Russian Federation”;
Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated October 17, 2013 No. 1155 “On approval of the federal state educational standard for preschool education” (registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on November 14, 2013, No. 30384);
Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Education and Science of Russia) dated August 30, 2013 N 1014 Moscow "On approval of the Procedure for organizing and implementing educational activities in basic general education programs - educational programs of preschool education"
Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated April 8, 2014 No. 293 “On approval of the Procedure for admission to training in educational programs of preschool education” (registered with the Ministry of Justice on May 12, 2014, No. 32220, entered into force on May 27, 2014);
Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated October 18, 2013 No. 544n “On approval of the professional standard “Teacher” (pedagogical activities in the field of preschool, primary general, basic general, secondary general education) (educator, teacher)”;
Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 15, 2013 No. 26 “On approval of SanPiN 2.4.1.3049-13 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the design, content and organization of the operating mode of preschool educational organizations”;
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 5, 2013 No. 662 “On monitoring the education system”;
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 15, 2013 No. 706 “On approval of the Rules for the provision of paid educational services”;
Letter of the Department of State Policy in the Sphere of General Education of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated February 28, 2014 No. 08-249 “Comments on the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education”;
Letter of the Department of State Policy in the Sphere of General Education of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated January 10, 2014 No. 08-10 “On the Action Plan to ensure the introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education” (hereinafter referred to as the Action Plan to ensure the introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education (No. 08-10) );
Letter of Rosobrnadzor dated 02/07/2014 No. 01-52-22/05-382 “On the inadmissibility of the requirement from organizations carrying out educational activities under preschool education programs to immediately bring statutory documents and educational programs into compliance with the Federal State Educational Standard for Educational Education”;
Letter of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated January 10, 2014 No. 08-5 “On compliance by organizations carrying out educational activities with the requirements established by the federal state educational standard for preschool education”;
Resolution of the Regional Governor dated December 31, 2013 No. 1567 “On amendments to the Regional Governor’s resolution dated February 28, 2013 No. 220 “On approval of the action plan (“road map”) of the Vladimir region “Changes in sectors of the social sphere aimed at increasing the efficiency of education and science";
Resolution of the Regional Governor dated 02/04/2014 No. 59 “On approval of the State Program of the Vladimir Region “Development of Education” for 2014-2020”;
Action plan for the introduction of Federal State Educational Standards for Preschool Education (road map) / for 2014 – 2016.
The system of psychological and pedagogical support is built taking into account:
1) the individual needs of the child related to his life situation and health condition, which determine the special conditions for his education (hereinafter referred to as special educational needs),
2) individual needs of certain categories of children, including those with disabilities;
3) opportunities for the child to master the Program at different stages of its implementation.
When developing a system of psychological and pedagogical support, one should focus on the main principles, laid down in the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child, the Federal State Educational Standard for Education:
1) support for the diversity of childhood; preserving the uniqueness and intrinsic value of childhood as an important stage in the overall development of a person, the intrinsic value of childhood - understanding (considering) childhood as a period of life that is significant in itself, without any conditions; significant because of what is happening to the child now, and not because this period is a period of preparation for the next period;
2) the personal developmental and humanistic nature of the interaction between adults (parents (legal representatives), teaching and other employees of the Organization) and children;
3) respect for the child’s personality;
4) implementation of the Program in forms specific to children of a given age group, primarily in the form of play, cognitive and research activities, in the form of creative activity that ensures the artistic and aesthetic development of the child;
5) full-fledged experience by the child of all stages of childhood (infancy, early and preschool age), enrichment (amplification) of child development;
6) building educational activities based on the individual characteristics of each child, in which the child himself becomes active in choosing the content of his education, becomes a subject of education (hereinafter referred to as individualization of preschool education);
7) assistance and cooperation of children and adults, recognition of the child as a full participant (subject) of educational relations;
8) supporting children’s initiative in various activities;
9) cooperation of the Organization with the family;
10) age adequacy of preschool education (compliance of conditions, requirements, methods with age and developmental characteristics);
11) taking into account the ethnocultural situation of children’s development.
Developers of a system of psychological and pedagogical support for the introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard need to focus on conceptual ideas and values preschool education laid down in the Federal State Educational Standard, the main of which are:
changing the paradigm of teacher education and transforming it essentially into psychological and pedagogical education means the need for such content that will allow, in the process of their professional activities, training focused on the development of students, taking into account their characteristics and the comprehensive disclosure of their intellectual and personal potential, the realization of developmental potential preschool education;
preserving the uniqueness and intrinsic value of preschool childhood as an important stage in the overall development of a person;
realization of the child’s right to full and free development;
familiarization with cultural values, socialization of the child in society, and not teaching him writing, counting and reading, which occurs through the leading type of children's activity - play;
the priority of goals, values, and developmental needs of the child’s inner world suggests that psychological and pedagogical support should be based on those mental personal achievements that the child actually has and constitute the unique baggage of his personality;
the orientation of educational activities towards creating conditions that allow the child to independently build a system of relationships with the world, people around him and himself, and make personally significant positive life choices.
the most important component of the mechanism for the formation of social experience is activity that corresponds to certain pedagogical conditions, which should: reproduce life situations, rely on children's impressions of everyday life; arouse the child’s personal interest and understanding of the social significance of the results of their activities; offer the child active action related to planning an activity, discussing various options for participating in it, responsibility, self-control and evaluation; imply mutual assistance, create a need for cooperation.
Main subjects psychological and pedagogical support in a preschool organization are:
Pupils;
Teachers;
Parents of pupils (legal representatives).
The introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education has identified a number of problems for all subjects of educational relations: for teachers - this is the design of methodological support for the implementation of standards, the choice of means and ways to achieve goals-results, the assessment of educational results at the preschool level of education; for children it is readiness for development and learning at the next level of education; for parents - the need to understand what standards are and how to help their children socialize successfully.
All the identified problems of subjects of educational relations are interconnected, and it is necessary to understand how teachers and parents are really able to help develop in children such personal qualities as independence, initiative, responsibility, ensuring their positive socialization.
The system of psychological and pedagogical support of the educational process in a preschool educational institution must contain a specification of goals, objectives, content, planned results, as well as methods, techniques and technologies used in its implementation.
Your own teaching staff system should be built taking into account the specifics of a preschool educational organization ( conditions implementation of the educational process), as well as in accordance with individual development trajectory of children as part of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard.
The organization and full functioning of the educational process requires the concerted efforts of many social actors: preschool educational institutions, families, institutions of additional education, culture and sports.
Elena Izmailova
Methodological recommendations for preschool teachers “Organization of project activities in a preschool educational organization”
« Organization of project activities
V preschool educational organization»
Currently, innovative technologies are being actively introduced into preschool educational institutions. One such technology is project activities(project method) .
Project(from lat. projectus - thrown forward, protruding, protruding forward)– this is unique activity, having a beginning and an end in time and aimed at achieving a predetermined result or goal. The result project activities is to create a unique product, the quality of which has certain requirements.
Uniqueness activities when working with pedagogical technology is the free choice of the form of work with children (including non-traditional ones, in the use various methodological and pedagogical techniques aimed not so much at developing certain skills in working with various materials, but at uniting common efforts to achieve a common goal.
Projects in kindergarten are, as a rule, educational in nature. Preschoolers according to their psychophysiological development, they are not yet able to independently create their own from beginning to end project. Therefore, teaching the necessary skills and abilities is the main task educators.
Currently projects classified according to different signs: by composition of participants; by target setting; by topic; according to implementation deadlines.
The most significant is the dominant species activities.
In practice preschool institutions use the following types projects:
Research - a research search is carried out, the results of which are presented in the form of some kind of creative product (newspapers, dramatizations, card indexes of experiments, children's design, etc.).
Role-playing games - project with elements of creative play as children enter image fairy tale characters and solve the problems in their own way;
Information and practical oriented: children collect information about some object, phenomenon from different sources, and then implement it, focusing on social interests: group design, stained glass, etc.;
- creative: as a rule, they do not have a detailed structure of joint activities of participants.
The results are presented in the form of a children's party, exhibition, design and headings of a newspaper, album, almanac, etc., for example "Theater Week".
Since the leading view preschooler's activity is a game, then, starting from a young age, role-playing and creative games are used projects.
In addition, the following types are used projects, How:
Complex, for example "World of Theater", “Hello, Pushkin!”, "Echo of Centuries", "Book Week";
Intergroup e.g. "Mathematical collages", "World of Animals and Birds", "Seasons";
Creative, for example "My friends", “In our non-boring garden”, "We love fairy tales", "Natural World", "Rowan berries of Russia";
Group, for example "Tales of Love", "Know Thyself", "Undersea world", "Fun Astronomy";
Individual, for example "I and my family", "Family tree", "Secrets of Grandma's Chest", "Fairytale Bird";
Research, for example "World of Water", "Breath and Health", "Nutrition and Health".
Other classification features are:
List of participants (group, subgroup, personal, family, couples, etc.);
- duration: short-term - several lessons, 1-2 weeks; average duration - 1-3 months; long-term - up to 1 year (for example, "Pushkin's creativity"- for the academic year).
Main goal project activities in kindergarten is the development of the free creative personality of the child, which is determined by the tasks of development and the tasks of research children's activities.
Development objectives:
Ensuring the psychological well-being and health of children;
Development of cognitive abilities;
Creative development imagination;
Development of creative thinking;
Development of communication skills.
Tasks project activities specific for each age.
In junior preschool age is:
Children's entry into problematic play situations (leading role of the teacher);
Activating the desire to look for ways to resolve a problem situation (together with the teacher);
Formation of the initial prerequisites for the search engine activities(practical experiments).
Lines of personality development.
Physical development:
stimulation of the natural process of development of motor abilities and qualities;
formation of conscious ideas about the need to take care of one’s health (role-playing project"The ABC of Health");
Social-communicative development:
formation of communication methods (vernissage "I and my family", individual family projects"Family tree");
Cognitive development:
enrichment and expansion of ideas about the world around us;
expansion and qualitative change in methods of orientation in the surrounding world;
conscious use of sensory sensations in solving practical problems (mathematical collages, intergroup project"World of Animals and Birds", "Creative projects"My friends", "Natural World", "We love fairy tales");
Artistic and aesthetic development:
development of an emotional-value attitude towards works of art and artistic images;
mastery of artistic activities(complex projects"World of Theater", “Hello, Pushkin!”, role-playing games projects"Favorite toys").
In senior preschool age is:
Formation of search engine prerequisites activities, intellectual initiative;
Developing the ability to identify possible methods solving the problem with the help of an adult, and then independently;
Developing the ability to use data methods, contributing to the solution of the task, using various options;
Stimulating the desire to use special terminology, conducting a constructive conversation in the process of joint research activities.
Lines of personality development.
Social-communicative development:
development of self-knowledge and positive self-esteem;
mastering methods of non-situational and personal communication;
high level of communicative competence;
awareness of speech functions (individual project"I and my family", "Family tree", project"Tales of Love", group projects"Know Thyself");
Physical development:
development of a conscious attitude towards one’s health;
formation of the need for healthy lifestyle;
improvement of the process of development of motor abilities and qualities (role-playing projects"The ABC of Health", "Secrets of Ilya Muromets").
Cognitive development:
systematization of knowledge, stimulating the development of cognitive and creative abilities;
development of abilities for practical and mental experimentation and symbolic modeling, speech planning, logical operations (book lovers club "Wonderland", group projects"Ural Gems", "Undersea world", "Fun Astronomy", intergroup project"Seasons", complex projects“Hello, Pushkin!”, "Bogatyrs of the Russian Land");
Artistic and aesthetic development:
in-depth introduction to art, variety of artistic images;
mastering various types of art. activities;
development of abilities for aesthetic evaluation (role-playing project"Visiting a fairy tale", complex projects"Echo of Centuries", "Book Week", "World of Theater").
In the process of implementation project method in a preschool educational institution, the teacher acts as an organizer children's productive activities, he is a source of information, a consultant, an expert. Educator- main manager project and subsequent research, gaming, artistic, practice-oriented activities, coordinator of individual and group efforts of children in solving the problem.
Transition preschool institution using the project method of activity, as a rule, is carried out according to the following stages:
Classes including problematic situations of children's experimentation, etc.;
Complex block-thematic lessons;
- integration: partial or complete;
- project method like shape organization of educational space; How method development of creative cognitive thinking.
Work plan teacher for preparing the project can be like this:
1. Based on the studied problems of children, set a goal project.
2. Develop a plan to achieve the goal (plan is discussed with parents).
3. Involvement of specialists in the implementation of relevant sections project.
4. Drawing up a diagram project.
5. Collection, accumulation of material.
6. Inclusion in the plan lesson project, games and other types of children's activities.
7. Homework for independent completion.
8. Presentation project, open lesson.
Main stages project methods include:
1. Goal setting: the teacher helps the child choose the most relevant and feasible task for him for a certain period of time.
2. Development project - an activity plan to achieve a goal:
To whom ask for help(adult, teacher);
What sources can you find information from?
What items to use (accessories, equipment);
What objects should you learn to work with to achieve your goal?
3. Execution project- practical part.
4. Summing up - identifying tasks for new projects.
Stages of work on project:
Activities of a teacher
Children's activities
First stage:
Formulates the problem (target). Product is determined project.
Introduces into the gaming room (plot) situation.
Formulates the task.
Getting into the problem.
Getting used to the game situation.
Acceptance of the task.
Addition of tasks project.
Second phase
Helps in solving a problem.
Helps you plan activity, organizes activities.
Uniting children into work groups.
Third stage
Practical help (of necessity). Directs and monitors implementation project.
Formation of specific knowledge and skills.
Fourth stage
Preparing for the presentation.
Presentation.
Product activities preparing for presentation.
Present (spectators or experts) product activities.
So way, project method in working with preschoolers today is optimal, innovative and promising method, which should take its rightful place in the system preschool education. Discussed above methodological foundations of project activities give an idea of the high degree of adaptability of innovative technologies to the specifics of preschool educational institutions.
Usage project method in preschool education as one of the methods integrated learning preschoolers, allows you to significantly increase the independent activity of children, develop creative thinking, the ability of children to independently find information about an object or phenomenon of interest in different ways and use this knowledge to create new objects of reality. And he does the same educational the preschool educational system is open to the active participation of parents.
Specifics of use project method in preschool practice is what adults need "to direct" child, help detect a problem or even provoke its occurrence, arouse interest in it and "pull in" children in a joint project. Based on a student-centered approach to learning and education, ultimately, it should contribute to the development of individual creative activities teachers in the development of strategy, tactics and technology educational process, promote personal development pupils, ensure quality results of pedagogical activities.
Prospects project method in the preschool education system is that it provides the opportunity to develop observation and analysis of phenomena, comparison, generalization and the ability to draw conclusions, creative thinking, logic of knowledge, inquisitiveness of mind, joint cognitive-search and research activities, communication and reflective skills and much more, which are components of a successful personality.
Implementation stages project
Activities of the teacher Activities of children
Formulates the problem Entering the problem
Introduces into the gaming room (plot) situation Getting used to the game situation
Formulates the problem (not hard) Accepting the task
Addition of tasks project
Helps in solving the problem of uniting children into work groups
Helps you plan activity Role distribution
Organizes activities
Practical help (of necessity) Formation of specific knowledge, skills and abilities
Directs and monitors implementation project
Preparation for presentation Product activities preparing for presentation
Presentation Present (spectators or experts) product activities
Bibliography
1. Evdokimova E. S. Technology design in preschool educational institution / E. S. Evdokimova. - M.: TC Sfera, 2006. - 64 p.
2. Prokofieva L. B. A look at quality education from the perspective of a methodological approach. Collection of scientific works / L. B. Prokofieva, G. A. Voronina; edited by I. M. Osmolovskaya. - M.: ITiIP RAO, 2004. - P. 503.
3. Timofeeva L. L. Project method in kindergarten / L. L. Timofeeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing House LLC "Childhood-press", 2011. - 80 p.
4. Veraksa N. E., Veraksa A. N. Project activities for preschoolers. Manual for teachers preschool institutions. - M.: Mosaic - Synthesis, 2008. - 112 p.
5. Educational projects in kindergarten. Benefit for educators/N. A. Vinogradova, E. P. Pankova. – M.: Iris-press, 2008. – 208 p. – (Preschool education and development) .
6. Project method in the activities of a preschool institution: A manual for managers and practical workers of preschool educational institutions / Author. -comp.: L. S. Kiseleva, T. A. Danilina, T. S. Lagoda, M. B. Zuikova. – 3rd ed. pspr. and additional – M.: ARKTI, 2011. – 96 p.
7. Problems preschool education on modern stage: Issue 5 / Comp. O. V. Dybina, O. A. Yenik. – Tolyatti: TSU, 2007. – 116 p.
8. Solodyankina O. V. System design in a preschool institution. // Toolkit. - M.: ARKTI, 2010. - 80 p.
9. Shtanko I. V. Project activities with children of senior preschool age. // Control preschool educational institution. 2004, №4.
Moscow Department of Education
Moscow Institute of Open Education
Moscow City Psychological and Pedagogical University
institutions
In accordance with the approval and implementation of Federal state requirements for the structure of the basic general education program of preschool education (Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation No. 655 of November 23, 2009), the form and structure are changing Educational program Preschool educational institution of the city of Moscow.
Currently, based on federal requirements, the following are being developed:
an approximate basic general education program for preschool education;
an approximate basic general education program of preschool education for children with disabilities.
Until these two programs are implemented, these recommendations are temporary. These recommendations will help preschool educational institutions quickly make additions and changes to existing educational programs and improve the quality of preschool education. The educational program of a preschool educational institution is considered as a model for organizing the educational process focused on the personality of the pupil and taking into account the type of preschool educational institution, as well as priority areas of activity.
The basic general educational program of preschool education (hereinafter referred to as the Program) is developed, approved and implemented in an educational institution on the basis of approximate basic general educational programs of preschool education.
The program determines the content and organization of the educational process for preschool children and is aimed at the formation of a general culture, the development of physical, intellectual and personal qualities, the formation of prerequisites for educational activities that ensure social success, the preservation and strengthening of the health of preschool children, the correction of deficiencies in physical and (or ) mental development of children. The content of the Program includes a set of educational areas that ensure the diversified development of children, taking into account their age and individual characteristics in the main areas - physical, social-personal, cognitive-speech and artistic-aesthetic.
The program should:
comply with the principle of developmental education, the goal of which is the development of the child;
combine the principles of scientific validity and practical applicability;
meet the criteria of completeness, necessity and sufficiency;
ensure the unity of educational, developmental and training goals and objectives of the education process for preschool children, in the process of implementation of which such knowledge, skills and abilities are formed that are directly related to the development of preschool children;
be built taking into account the principle of integration of educational areas in accordance with the age capabilities and characteristics of students, the specifics and capabilities of educational areas;
be based on a comprehensive thematic principle of constructing the educational process;
provide for the solution of program educational tasks in the joint activities of adults and children and independent activities of children, not only within the framework of direct educational activities, but also during routine moments in accordance with the specifics of preschool education;
assume the construction of the educational process on age-appropriate forms of work with children. The main form of work with preschool children and the leading activity for them is play.
The educational program of the preschool educational institution consists of two parts:
1) mandatory part;
2) the part formed by participants in the educational process.
1. The mandatory part of the Program must be implemented in any educational institution that implements the basic general education program of preschool education. Ensures that pupils achieve school readiness, namely the necessary and sufficient level of child development for their successful mastery of basic general education programs of primary general education. In compensatory and combined groups, the mandatory part of the Program includes activities for qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities.
Part II of the Program, formed by participants in the educational process, reflects:
1) type diversity of institutions, the presence of priority areas of activity, including ensuring equal starting opportunities for teaching children in general education institutions, carrying out sanitary and hygienic, preventive and health-improving measures and procedures, physical, social-personal, cognitive-speech, artistic and aesthetic development of children (except for activities for qualified correction of deficiencies in the physical and (or) mental development of children with disabilities);
2) the specifics of the national-cultural, demographic, climatic conditions in which the educational process is carried out.
Time, necessary for the implementation of the Program is from 65% to 80%) of the time spent by children in groups with a 12-hour stay, depending on the age of the children, their individual characteristics and needs. Volume The mandatory part of the Program is at least 80%) of the time required to implement the Program, and the part formed by participants in the educational process is no more than 20% of the total volume of the Program.
The structure of the educational program of the preschool educational institution. Title page
1 Name of preschool educational institution;
2. “I confirm: the head of the preschool educational institution...”
3. “Adopted at a meeting (scientific and methodological council, pedagogical council, small pedagogical council), date, protocol number.
4. “Agreed” (MA or CMC)
6. The contents (table of contents) of the educational program are given on the back of the title page.
Explanatory note
The general education program of preschool educational institution No.____ ensures the diversified development of children aged from ___________________________ to ________________________
years, taking into account their age and individual characteristics in the main areas - physical, social,
personal, cognitive-speech and artistic-aesthetic. The program ensures that students are ready for school. The explanatory note should disclose:
1. Age and individual characteristics of the contingent of children brought up in an educational institution, information about the qualifications of teaching staff and information about the families of students.
The main priority areas in the activities of the educational institution are: (formulate)
3. The goals and objectives of the activities of the preschool educational institution for the implementation of the main educational program are determined on the basis of analysis
the results of previous teaching activities, the needs of parents, the society in which the preschool is located
educational institution.
Considering that the institution has developed a “Preschool Educational Development Program”, which defines conceptual ideas, a development strategy for the entire educational institution and mechanisms for its implementation, the Educational Program prescribes the goals and objectives of organizing the pedagogical process for its participants (children, teachers, parents of students)
4. Features of the educational process.
We remind you that they can be: organizational, national-cultural, demographic, climatic, etc. When organizing the educational process, the principles of integration of educational areas should be taken into account (physical education, health, safety, socialization, labor, cognition, communication, reading fiction, artistic creativity, music) in accordance with the age capabilities and characteristics of the students. Indicate this position, as well as the fact that “the basis for organizing the educational process is a complex thematic principle with leading play activity, and the solution of program problems is carried out in various forms of joint activity of adults and children, as well as in the independent activity of children.” 5. Principles and approaches to the formation of a general education program (open in accordance with the above).
PART 1 (compulsory)
1. Organization of the regime of stay of children in preschool educational institutions.
In this section, the DOU must submit:
Flexible mode of activity depending on the social order of parents, the availability of specialists, teachers, medical workers, approaches to the training and education of preschoolers, to the organization of all types of children's activities;
Interaction schedules for teachers, specialists and educators;
A model of the educational process using various forms, and taking into account the time of year and age-related psychophysiological capabilities of children, the relationship of planned activities with the daily life of children in kindergarten (Appendix No. 3);
System of hardening measures;
A system of physical education and health activities; (Appendix No. 2)