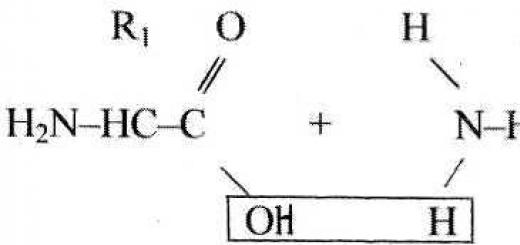
Periodization of the Great Patriotic War
1st period – June 22, 1941 – autumn 1942 –
German attack on the USSR. Red's defeats
Armies in the first months of the war. Defeat of the Nazis
near Moscow. The failure of the German Blitzkrieg plans.
2nd period – autumn 1942 – 1943 – indigenous
turning point during the war. Battles of Stalingrad and Kursk.
The collapse of Germany's offensive strategy and its
satellites.
3rd period – January 1944 – May 9, 1945 –
end of WWII. Liberation of Europe from invaders.
The defeat of Nazi Germany.
4th period – August 8 – September 2, 1945 – Defeat and
Japanese surrender. The end of World War II.
Results of the Great Patriotic War
- Victory of the USSR and defeat of Germany and its allies.- Preservation of territorial integrity and
sovereignty of the USSR.
- Liberation of the peoples of Europe from German rule
occupation and restoration of their statehood.
- Eradication of fascism and Nazism as a state
ideology and politics.
- Entry into the USSR of new territories
(East Prussia, southern Sakhalin,
Kurile Islands).
- Increasing the international authority of the USSR.
- The USSR has the most powerful army in the world.
- Huge human and material losses. Human losses during the Second World War
wars (died on the battlefield, died from wounds,
died in death camps) German losses (killed, wounded,
missing persons and prisoners of war)
Reasons for the exorbitantly high losses of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War.
1. Wide scale of military operations inSoviet-German front.
2. The policy of genocide of German fascism in
regarding prisoners of war and civilians
population in the occupied Soviet
territories.
3. Low combat effectiveness of many units
Red Army, Soviet miscalculations
command.
4. Requirements of high command
carry out combat missions at any cost, do not
stopping at no sacrifice
(the nature of Soviet totalitarianism).
Reasons for the victory of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War.
- Huge mobilization opportunitiesSoviet society.
- Unity of the front and rear workers.
- Unity of the peoples of the USSR.
- Patriotism of the Soviet people, massive
heroism at the front and in the rear.
- Soviet military leadership talent
military leaders.
- Help from the allies in the anti-Hitler war
coalition.
- Huge spaces and unusual for
enemy natural and climatic
conditions.- World-historical significance of the victory
Soviet Union in the Great
The Patriotic War is
What:
1) the bloodiest was completed
war in human history;
2) the threat of establishing
world domination by states
Hitler's bloc;
3) the peoples of Europe gained freedom and
restored their statehood;
4) dictatorships were eliminated
fascist regimes.
RESULTS OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR
1. The defeat of Nazi Germany, fascist Italy and imperialistJapan - invader states where totalitarian regimes emerged.
Italy lost its position in the Mediterranean;
Germany, being occupied and divided into zones, stopped for a while
to be an independent subject of international relations;
Japan in the Far East and Asia has lost the positions it
conquered over a number of decades.
2. The anti-Hitler coalition won - countries with different
social systems that pursue exactly the opposite
goals that managed to find ways for coordinated actions during the war.
3. The USSR suffered the greatest losses and the greatest
victims. But by the end of the war, the USSR had enormous military power, and
Its international positions have strengthened and its authority has grown.
4. The victory over fascism contributed to the rise of the national liberation struggle of the peoples of colonial countries and the liberation
them from colonial dependence.
5. Europe, having gone through the war, overcame the traditional idea
about the limited political role of the state and recognized
responsibility of the state for maintaining a high level
economic growth for the vitality and security of the country.
CONSEQUENCES OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR
1. Huge casualties (60 million people). 12million people lost contact with their homeland.
2. Economic devastation.
3. Huge moral shock in
as a result of crimes against
humanity - mass extermination
civilians, bullying
prisoners, abuse
democratic principles and
human rights.
LESSONS OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR
1. The Second World War showed that the whole burdenwar falls on the shoulders of the peoples. They carried it all
hardships and hardships, tragedies of human loss
lives, grief and suffering.
2. It is much easier to start a war than to end it. War,
having begun, it further develops in its own way
own laws, and plan its outcome
almost impossible. It's not always a win
comes to the one who started the war.
3. A war cannot be planned either in scale or in
the nature of the means used.
4. War prevention requires unity
actions of peace-loving forces. During the preparation period
World War II it was possible
prevent. Measures have been repeatedly proposed to
this direction. Many agreed with them, but
unity of action was never achieved.
“Lessons of the Great Patriotic War” - Kursk today. Weapon of victory. Kyiv today. IL-2. IN AND. Chuikov. T-34. Coat of arms of Kursk. I.S. Konev. G.K. Zhukov. Stalingrad today. "Ferdinand". Creators of great victories. Battle of Stalingrad. Counter-offensive of the Red Army at Stalingrad. Sergius-Kazan Cathedral. "Katyusha". On the eve of the decisive battles. K.K. Rokossovsky.
“Participants in the Battle of Kursk” - Sonin Ivan Egorovich. Children. Historical meaning. Heroes of the Battle of Kursk. Stormy war years. Kurians. Troops of the Central Front. Panther. Tigers. Tank battle. Living Rylians. Troop leadership. Kursk defensive operation. Firework. Citadel. Lomakin Alexey Maksimovich. Soldier. Borovykh Andrey Egorovich.
“Battles of Stalingrad and Kursk” - Battle of Prokhorovka. The balance of forces also gradually improved in favor of the Soviet troops. These figures include those killed, wounded, sick, and missing. The first day. The Great Tank Battle of Prokhorovka. The Soviet armies, having suffered heavy losses, retreated. A crisis began in the pro-fascist regimes in Italy, Romania, Hungary, and Slovakia.
“Results of the Great Patriotic War” - Manchurian operation. Losses of the Red Army. Potsdam Conference. Conference of Heads of State. Tula. Brest Fortress. Rokossovsky K.K. General principles of policy. International Tribunal in Nuremberg. Reasons for victory. The act of unconditional surrender of Japan. Results of the war. Soviet delegation. Moscow.
“Kursk Bulge” - The enemy’s losses were even greater. In the Oryol and Belgorod directions, the Red Army went on the offensive. The decision was made to exhaust the enemy through defensive battles and then go on the offensive. Broken Panther. Battle of Kursk. Before the Battle of Kursk. After persistent, bloody battles, German troops advanced 10-12 km.
“Battle of Kursk” - 1. Battle of Stalingrad. Russian history. The liberation of Donbass began in February. Results of the second period of the war. Street fighting in Stalingrad. Battle of Stalingrad. Prove that the fundamental turning point in the course of the war took place in 1943? The defeat of German troops at Stalingrad. Within a month, Kharkov, Orel, and Belgorod were liberated.
There are a total of 22 presentations in the topic
May 9 – Victory Day Soviet people in the Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945
Prepared the presentation
student of 6th grade "B"
MBOU gymnasium No. 8
Kolomna
Galtsova Ariana
For 1418 days and nights, the Soviet people waged a bloody war against the fascist aggressors and crushed them. The people defended the freedom and independence of their Fatherland and saved world civilization from fascist enslavement. For 1418 days and nights, the Soviet people waged a bloody war against the fascist aggressors and crushed them. The people defended the freedom and independence of their Fatherland and saved world civilization from fascist enslavement.
The Great Patriotic War was an integral part and the main content of the entire Second World War, in the orbit of which more than 60 states were involved. The fighting took place over vast areas of Europe, Asia and Africa, in sea and ocean spaces. The German-Italian-Japanese fascist bloc, expanding its aggression, persistently strove to gain world domination. On the way to this goal, the Soviet Union stood as an insurmountable obstacle.
The fate of the entire Second World War was decided on the Soviet-German front - it was the main front of the fight against fascism. The USSR took upon itself and bore the brunt of the fight against the aggressor to the end. It was our country and its Armed Forces that played a decisive role in the victorious outcome of the Second World War.
Initially, fascist German troops managed to seize the strategic initiative. They desperately rushed to the vital centers of the Soviet Union. But the delusional plans for a lightning war were not destined to come true.
The Great Patriotic War was the largest armed conflict in human history. On a huge front stretching from the Barents to the Black Sea, from 8 to 12 million people fought on both sides at different periods, from 5 to 20 thousand tanks and self-propelled artillery units, from 150 to 320 thousand guns and mortars, from 7 to 19 thousand aircraft. The history of wars has never known such a huge scale of combat operations and the concentration of such a large mass of military equipment. The whole country stood up to fight the enslavers. At the front and in the rear, people of all nations and nationalities were united by one goal - to survive and win.
The history of the Victory Day holiday dates back to May 9, 1945, when in the suburbs of Berlin, the Chief of Staff of the Supreme High Command, Field Marshal General V. Keitel from the Wehrmacht, Deputy Supreme Commander-in-Chief Marshal of the USSR Georgy Zhukov from the Red Army and Air Marshal of Great Britain
A. Tedder from the allies signed an act of unconditional and complete surrender of the Wehrmacht.
Berlin was taken on May 2, but German troops offered fierce resistance to the Red Army for more than a week before the fascist command, in order to avoid unnecessary bloodshed, finally decided to surrender.
But even before this moment, Stalin signed a decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR that from now on May 9 becomes a public holiday, Victory Day, and is declared a day off. At 6 o'clock in the morning Moscow time, this Decree was read out on the radio by announcer Levitan.
The first Victory Day was celebrated in a way that, probably, very few holidays were celebrated in the history of the USSR and Russia. People on the streets congratulated each other, hugged, kissed and cried.
On May 9, in the evening, the Victory Salute was given in Moscow, the largest in the history of the USSR: thirty salvos were fired from a thousand guns.
However, May 9th was a public holiday for only three years. In 1948, it was ordered to forget about the war and devote all efforts to restoring the national economy destroyed by the war.
And only in 1965, already during the Brezhnev era, the holiday was again given its due. May 9 became a day off again, Parades, large-scale fireworks in all cities - Heroes and honoring of veterans - resumed.
Abroad, Victory Day is celebrated not on May 9, but on May 8. This is due to the fact that the act of surrender was signed in Central European time
May 8, 1945 at 22:43. When in Moscow, with its two-hour time difference, May 9 had already arrived.
On May 9, all veterans of the country accept congratulations on the Victory Day of the Soviet people in the Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945.
On this day I would like to repeat the lines of Olga Berggolts: “No one is forgotten, nothing is forgotten.”
After all, if there had not been that great victory, we would not have existed.
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!Government House. Enemy group. Losses of German troops. Major General of Aviation. Operation "Bagration". Masha Bruskina. Treaty on the Soviet-Polish border. Heroic deeds. Front. Troops. Bagration. Liberation of Belarus from fascist occupiers.
“Battle of Berlin” - It was decided to launch our attack two hours before dawn." Trying to inspire his troops, Hitler wrote in an appeal dated April 14: The Berlin garrison laid down their arms. The wounded did not leave the formation. Many had not yet healed the wounds from past battles . Battle for Berlin. Berlin will remain German...". With the end of the Berlin operation, the war in the West ended. The capture of the Reichstag had enormous political and moral significance.
“The end of the Great Patriotic War” - The trial of fascist war criminals. Battle for Berlin. Berlin in May 1945. Nuremberg trials. Banner of victory over the Reichstag. Party and government leaders are at the mausoleum. May 1945. 200 Nazi banners were thrown onto the platform at the mausoleum. Berlin. The end of the Great Patriotic War. Meeting of the leaders of the winning countries in Potsdam. June 24, 1945 - parade on Red Square. The parade is hosted by Marshal G.K. Zhukov.
“Battle of Kursk” - Enemy plan. Commander of the Central Front. Department of military-patriotic and civil education. Time to prepare for summer battles. The warriors constantly felt supported. Scorched throats. Prokhorovka. Hundreds of thousands of inhabitants. Unity of the rear and the front. Soviet soldiers fought bravely. Division commander. Pre-storm calm. Soviet soldiers. Hitler. Wehrmacht command. Prokhorovsk tank battle.
“Participants in the Battle of Kursk” - Rokossovsky Konstantin Konstantinovich. Victory in battle. Heroes of the Battle of Kursk. Panther. Soviet counteroffensive. Konorev Ivan Alekseevich. Kurians. The color of the German tank forces. Stormy war years. Lomakin Alexey Maksimovich. Tank battle. Tank battle. Igishev Georgy Ivanovich. Firework. Soviet medium tank. Battle of Kursk. Historical meaning. Soldier. Plans and strengths of the parties. Sonin Ivan Egorovich.
“Results of the Great Patriotic War” - Potsdam Conference. Brest Fortress. United Nations. Moscow. General principles of policy. International Tribunal in Nuremberg. I.S. Konev. The act of unconditional surrender of Japan. Volgograd. Memorial of Glory. Conference of Heads of State. Leningrad. Soviet delegation. Reasons, price and significance of the great Victory. Odessa. Rokossovsky K.K. Victory parade. Reasons for victory. The price of victory. Manchurian operation.
Slide 1
Slide 2
 Periodization of the Great Patriotic War Period 1 – June 22, 1941 – autumn 1942 – German attack on the USSR. Defeats of the Red Army in the first months of the war. Defeat of the Nazis near Moscow. The failure of the German Blitzkrieg plans. Period 2 – autumn 1942 – 1943 – a radical turning point in the course of the war. Battles of Stalingrad and Kursk. The collapse of the offensive strategy of Germany and its satellites. Period 3 – January 1944 – May 9, 1945 – end of the Second World War. Liberation of Europe from invaders. The defeat of Nazi Germany. 4th period – August 8 – September 2, 1945 – Defeat and surrender of Japan. The end of World War II.
Periodization of the Great Patriotic War Period 1 – June 22, 1941 – autumn 1942 – German attack on the USSR. Defeats of the Red Army in the first months of the war. Defeat of the Nazis near Moscow. The failure of the German Blitzkrieg plans. Period 2 – autumn 1942 – 1943 – a radical turning point in the course of the war. Battles of Stalingrad and Kursk. The collapse of the offensive strategy of Germany and its satellites. Period 3 – January 1944 – May 9, 1945 – end of the Second World War. Liberation of Europe from invaders. The defeat of Nazi Germany. 4th period – August 8 – September 2, 1945 – Defeat and surrender of Japan. The end of World War II.
Slide 3
 Results of the Great Patriotic War - Victory of the USSR and defeat of Germany and its allies. - Preservation of the territorial integrity and sovereignty of the USSR. - Liberation of the peoples of Europe from German occupation and restoration of their statehood. - Eradication of fascism and Nazism as state ideology and policy. - The entry into the USSR of new territories (East Prussia, the southern part of Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands). - Increasing the international authority of the USSR. - The USSR has the most powerful army in the world. - Huge human and material losses.
Results of the Great Patriotic War - Victory of the USSR and defeat of Germany and its allies. - Preservation of the territorial integrity and sovereignty of the USSR. - Liberation of the peoples of Europe from German occupation and restoration of their statehood. - Eradication of fascism and Nazism as state ideology and policy. - The entry into the USSR of new territories (East Prussia, the southern part of Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands). - Increasing the international authority of the USSR. - The USSR has the most powerful army in the world. - Huge human and material losses.
Slide 4

Slide 5
 Human losses during the Second World War (died on the battlefield, died from wounds, died in death camps)
Human losses during the Second World War (died on the battlefield, died from wounds, died in death camps)
Slide 6

Slide 7
 Reasons for the exorbitantly high losses of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War. The wide scale of military operations on the Soviet-German front. The policy of genocide of German fascism towards prisoners of war and civilians in the occupied Soviet territories. Low combat effectiveness of many units of the Red Army, miscalculations of the Soviet command. The demands of the high command to carry out combat missions at any cost, without stopping at any sacrifice (the nature of Soviet totalitarianism).
Reasons for the exorbitantly high losses of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War. The wide scale of military operations on the Soviet-German front. The policy of genocide of German fascism towards prisoners of war and civilians in the occupied Soviet territories. Low combat effectiveness of many units of the Red Army, miscalculations of the Soviet command. The demands of the high command to carry out combat missions at any cost, without stopping at any sacrifice (the nature of Soviet totalitarianism).
Slide 8
 Reasons for the victory of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War. - Huge mobilization capabilities of Soviet society. - Unity of the front and rear workers. - Unity of the peoples of the USSR. - Patriotism of the Soviet people, mass heroism at the front and in the rear. - The military leadership talent of Soviet military leaders. - Help from allies in the anti-Hitler coalition. - Huge spaces and climatic conditions unusual for the enemy.
Reasons for the victory of the USSR in the Great Patriotic War. - Huge mobilization capabilities of Soviet society. - Unity of the front and rear workers. - Unity of the peoples of the USSR. - Patriotism of the Soviet people, mass heroism at the front and in the rear. - The military leadership talent of Soviet military leaders. - Help from allies in the anti-Hitler coalition. - Huge spaces and climatic conditions unusual for the enemy.
Slide 9
 The meaning of the victory of the Soviet Union in the Great Patriotic War. - The world-historical significance of the victory of the Soviet Union in the Great Patriotic War lies in the fact that: 1) the bloodiest war in the history of mankind was completed; 2) the threat of establishing world domination from the states of the Hitler bloc was eliminated; 3) the peoples of Europe gained freedom and restored their statehood; 4) dictatorial fascist regimes were eliminated.
The meaning of the victory of the Soviet Union in the Great Patriotic War. - The world-historical significance of the victory of the Soviet Union in the Great Patriotic War lies in the fact that: 1) the bloodiest war in the history of mankind was completed; 2) the threat of establishing world domination from the states of the Hitler bloc was eliminated; 3) the peoples of Europe gained freedom and restored their statehood; 4) dictatorial fascist regimes were eliminated.
Slide 10
 RESULTS OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR 1. The defeat of Nazi Germany, fascist Italy and imperialist Japan - the invader states where totalitarian regimes emerged. Italy lost its position in the Mediterranean; Germany, being occupied and divided into zones, ceased for a time to be an independent subject of international relations; Japan in the Far East and Asia lost the positions it had gained over a number of decades. 2. The anti-Hitler coalition won - countries with different social systems, pursuing directly opposite goals, who managed to find ways for coordinated actions during the war. 3. The USSR suffered the greatest losses and the greatest casualties in World War II. But by the end of the war, the USSR possessed enormous military power, and its international positions were strengthened and its authority grew. 4. The victory over fascism contributed to the rise of the national liberation struggle of the peoples of colonial countries and their liberation from colonial dependence. 5. Europe, having gone through war, overcame the traditional view of the limited political role of the state and recognized the responsibility of the state to maintain high levels of economic growth for the viability and security of the country.
RESULTS OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR 1. The defeat of Nazi Germany, fascist Italy and imperialist Japan - the invader states where totalitarian regimes emerged. Italy lost its position in the Mediterranean; Germany, being occupied and divided into zones, ceased for a time to be an independent subject of international relations; Japan in the Far East and Asia lost the positions it had gained over a number of decades. 2. The anti-Hitler coalition won - countries with different social systems, pursuing directly opposite goals, who managed to find ways for coordinated actions during the war. 3. The USSR suffered the greatest losses and the greatest casualties in World War II. But by the end of the war, the USSR possessed enormous military power, and its international positions were strengthened and its authority grew. 4. The victory over fascism contributed to the rise of the national liberation struggle of the peoples of colonial countries and their liberation from colonial dependence. 5. Europe, having gone through war, overcame the traditional view of the limited political role of the state and recognized the responsibility of the state to maintain high levels of economic growth for the viability and security of the country.
Slide 11
 CONSEQUENCES OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR 1. Huge casualties (60 million people). 12 million people lost contact with their homeland. 2. Economic devastation. 3. A huge moral shock as a result of crimes against humanity - mass extermination of civilians, abuse of prisoners, outrage against democratic principles and human rights.
CONSEQUENCES OF THE SECOND WORLD WAR 1. Huge casualties (60 million people). 12 million people lost contact with their homeland. 2. Economic devastation. 3. A huge moral shock as a result of crimes against humanity - mass extermination of civilians, abuse of prisoners, outrage against democratic principles and human rights.