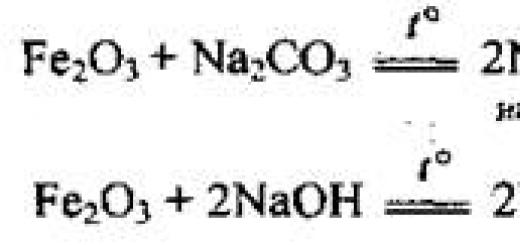Municipal educational institution
Sortavalsky municipal district of the Republic of Karelia
Secondary school No. 3
Diagnostic work in biology "Molecular level"
Grade 9
prepared
biology teacher of the highest category
Lappo Valentina Mikhailovna
Sortavala 2010
Molecular level
1 option
1. All living organisms:
a) have adaptations to the environment
b) develop
c) are heterotrophs
d) capable of metabolism
2. The distinctive function of fats from carbohydrates:
a) building
b) energy
c) storage
d) protective
3. Monomers of nucleic acids are:
a) amino acids
b) glucose
c) nucleotides
d) nitrogenous bases
4. DNA is different from RNA:
a) location in the cell
b) belonging to biopolymers
c) the remainder of H 3 RO 4 , which is part of the nucleotide
d) the presence of thymine in the nucleotide
5. Enzyme:
a) biocatalyst
b) participates in the process of synthesis and decay of substances
c) most active at t close to zero
d) has a protein base
6. Viruses are similar to non-living structures in that:
a) able to reproduce
b) unable to grow
c) have heredity and variability
d) do not produce energy
7. The composition of complex proteins - glycoproteins includes:
a) fats
b) nucleic acids
c) carbohydrates
d) inorganic substances
8. Vitamins:
a) are not used in the cage as a building material
b) are used as a reserve of nutrients
c) are biocatalysts
d) do not belong to biocatalysts
B. Determine the correct sequence.
9. Draw the nucleotide sequence of the second DNA strand, indicating the hydrogen bonds:
T-T-G-A-C-C-T-G-A-A.
10. Establish a correspondence between the types of nucleic acids and their characteristics.
Nucleic acids Characteristic
A) RNA 1. biopolymer
B) DNA 2. deoxyribose as part of the monomer
3. H 3 RO 4 in the monomer
4. monomers contain ribose
5. consists of monomers
6. contains uracil
7. Nucleotides contain nitrogenous bases
8. a nucleotide has three components
9. Contains Thymine
10. located in the cytoplasm and ribosomes
11. located in the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids
12. contains adenine
Diagnostic work in biology
Molecular level
Option 2
A. Select all correct answers.
1. All living organisms:
a) capable of metabolism
b) have the same structure
c) they are an open system
d) develop
2. Monomer versus polymer:
a) has a more complex structure
b) has a complex structure
c) consists of repeating links
d) is a link in the polymer chain
3. The same functions of fats and proteins:
a) protective
b) construction
c) storage
d) energy
4. Protein denaturation is irreversible in violation of the structure:
a) primary
b) secondary
c) tertiary
d) quaternary
5. ATP is different from RNA nucleotides:
a) the presence of ribose
b) the absence of uracil
c) the presence of three residues H 3 ro 4
d) the presence of adenine
6. Viruses are similar to living organisms in that:
a) unable to grow
b) able to reproduce
c) form a crystalline form of existence
d) have heredity and variability
7. Nitrogenous bases characteristic of DNA:
a) guanine
b) thymine
c) uracil
d) cytosine
8. Carbohydrates include:
a) ribose and lactose
b) glycogen and starch
c) glycerol and lipids
d) cellulose and chitin
B. Make a diagram.
9. Write down the missing DNA nucleotides, indicating the hydrogen bonds:
A-G-*-C-C-T-*-*-G-C
T-*-T-*-*-*-A-C-C-*
10. Establish a correspondence between the structure of a protein molecule and its characteristics.
Structure of a protein molecule
A) primary 1. characteristic of all proteins
B) secondary 2. globule
C) tertiary 3. polypeptide chain
D) Quaternary 4. spiral
5. occurs as a result of the connection
several proteins
6. formed by a strong peptide bond
7. held by numerous hydrogen bonds
connections
8. is destroyed by reversible denaturation
ANSWERS
1 option
a) 1,3,4,5,6,7,8,10,12; b) 1,2,3,5,7,8,9,11,12 |
Option 2
a) 1,3,6, b) 1,4,7 c) 1,2,7 d) 5,7,8 |
Used materials
1. Biology. Introduction to general biology and ecology. Textbook for 9 cells. A.A. Kamensky, E.A. Kriksunov, V.V. Pasechnik M.: Bustard, 2007.
2. Frosin V.N., Sivoglazov V.I. Getting ready for the unified state exam: General biology. - M .: Bustard, 2004. - 216s;
3. Bolgova I.V. Collection of problems in General biology for entering universities. M .: "Onyx 21st century" "World and education", 2005;
4. Biology. Educational and training materials for the preparation of students. "Intellect-Center" 2007
Option 1.
1 . The chemical elements carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen are called...
2. Differences between animate and inanimate nature arise at the ... level.
3. Thyroid hormones contain trace element ….
4. Hemoglobin molecule contains ions….
5. Substances soluble in water are called ....
6. With the complete oxidation of 1 g of lipids, ... energy is released.
7. Amino acids that make up proteins differ from each other ....
8. The process of destruction of the primary structure of the protein is called ....
9. Monomers of nucleic acids are ....
10. Proteins that affect the rate of biochemical processes in the cell are called ....
11. Structural polysaccharide of plants ....
12. Reserve polysaccharide of animals and fungi ….
13. The secondary structure of a protein is ....
14. Proteins actin and myosin perform ... a function.
15. According to the characteristics of monomers, polysaccharides belong to the group of ... biopolymers.
16. The process of synthesis of a new DNA chain on a matrix is called ....
17. Instead of thymine, RNA nucleotides include a nitrogenous base ....
18. A fragment of a DNA molecule encoding one polypeptide is called ....
19. The secondary structure in the form of a clover leaf has a molecule ....
20. Quantitative patterns of the content of nitrogenous bases in the DNA molecule established ....
Open type biology tests (tasks - additions) on the topic:
"Molecular level of organization of life" Grade 10.
Instructions for performing tests:
- Read the sentences carefully.
-Choose the necessary words to the places where they are missing.
- Under the appropriate numbers in the notebook, write down only what is missing.
Option 2.
1. At the elemental level, the differences between animate and inanimate nature ....
2. The composition of chlorophyll molecules includes metal ions ....
3. The supporting structures of horsetails and diatoms contain compounds ....
4. Due to the mobility of molecules, water can perform ... a function.
5. In relation to water, lipids and lipoids belong to the group of ... compounds.
6. With the complete oxidation of 1 g of carbohydrates, ... energy is released.
7. Sex hormones and adrenal hormones are synthesized in the body from ...
8. High-molecular organic compounds, the molecules of which consist of a large number of residues of simple molecules, are called ....
9. Monomers of proteins are ....
10. The process of restoring the natural structure of a protein after reversible denaturation is called ....
11. Structural polysaccharide of animals and fungi ….
12. The main reserve polysaccharide of plants ....
13. The primary structure of a protein is held by ... bonds.
14. Collagen and elastin proteins perform ... a function.
15. Proteins and nucleic acids, according to the characteristics of monomers, belong to the group of ... biopolymers.
16. The process of doubling the DNA molecule is carried out by the enzyme ....
17. DNA polynucleotide chains are located opposite each other according to the principle ....
18. Adenine nucleotides of DNA and RNA are different ....
19. All types of RNA are synthesized in ....
20. Scientists established the macromolecular structure of DNA, and also built a model of the DNA molecule, scientists ... and ....
Answers to tests of an open type (tasks - additions) on the topic:
"Molecular level of organization of life" Grade 10.
| |
|
| option 1 | option 2 |
| 1. organogenic 2. molecular 3. iodine 4. iron. 5. hydrophilic 6. 38.9 kJ 7. radicals 8. destruction 9. nucleotides 10. enzymes 11. cellulose 12. glycogen 13. spiral 14. motor 15.regular (periodic) 16.replication (reduplication) 17. uracil 18. gene 19. tRNA 20. E. Chargaff | 1. absent 2. magnesium 3. silicon 4. transport 5. hydrophobic 6. 17.2 kJ 7. cholesterol 8. biopolymers 9. amino acids 10. renaturation 11. chitin 12. starch 13. peptide 14. structural 15.irregular (heteropolymers) 16. DNA synthetase (DNA polymerase) 17. complementarity 18. pentose 19. core 20. D. Watson and F. Crick |
Criteria for evaluating works:
score 5 with 18-20 correctly completed tasks;
score 4 with 15-17 correctly completed tasks;
score 3 with 12-14 correctly completed tasks;
score 2 with 11 or less correctly completed tasks.
Tests of such a plan make it possible to test knowledge in a short time, and the possibility of guessing is excluded.
Pasechnik N. V. MBOU School No. 17 in Feodosia
Municipal educational institution
Sortavalsky municipal district of the Republic of Karelia
Secondary school No. 3
Diagnostic work in biology "Molecular level"
Grade 9
Sortavala 2010
Molecular level
1 option
1. All living organisms:
a) have adaptations to the environment
b) develop
c) are heterotrophs
d) capable of metabolism
2. The distinctive function of fats from carbohydrates:
a) building
b) energy
c) storage
d) protective
3. Monomers of nucleic acids are:
a) amino acids
b) glucose
c) nucleotides
d) nitrogenous bases
4. DNA is different from RNA:
a) location in the cell
b) belonging to biopolymers
c) the remainder of H 3 RO 4 , which is part of the nucleotide
d) the presence of thymine in the nucleotide
5. Enzyme:
a) biocatalyst
b) participates in the process of synthesis and decay of substances
c) most active t close to zero
d) has a protein base
6. Viruses are similar to non-living structures in that:
a) able to reproduce
b) unable to grow
c) have heredity and variability
d) do not produce energy
7. The composition of complex proteins - glycoproteins includes:
a) fats
b) nucleic acids
c) carbohydrates
d) inorganic substances
8. Vitamins:
a) are not used in the cage as a building material
b) are used as a reserve of nutrients
c) are biocatalysts
d) do not belong to biocatalysts
B. Determine the correct sequence.9. Draw the nucleotide sequence of the second DNA strand, indicating the hydrogen bonds:
T-T-G-A-C-C-T-G-A-A.
10. Establish a correspondence between the types of nucleic acids and their characteristics.
Nucleic acids Characteristic
A) RNA 1. biopolymer
B) DNA 2. deoxyribose as part of the monomer
3. H 3 RO 4 in the monomer
4. monomers contain ribose
5. consists of monomers
6. contains uracil
7. Nucleotides contain nitrogenous bases
8. a nucleotide has three components
9. Contains Thymine
10. located in the cytoplasm and ribosomes
11. located in the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids
12. contains adenine
Diagnostic work in biology
Molecular level
Option 2
A. Select all correct answers. 1. All living organisms: a) capable of metabolism b) have the same structure c) they are an open system d) develop2. Monomer versus polymer: a) has a more complex structure b) has a complex structure c) consists of repeating links d) is a link in the polymer chain3. The same functions of fats and proteins: a) protective b) construction c) storage d) energy4. Protein denaturation is irreversible in violation of the structure: a) primary b) secondary c) tertiary d) quaternary5. ATP is different from RNA nucleotides: a) the presence of ribose b) the absence of uracil c) the presence of three residues H 3 ro 4 d) the presence of adenine6. Viruses are similar to living organisms in that: a) unable to grow b) able to reproduce c) form a crystalline form of existence d) have heredity and variability7. Nitrogenous bases characteristic of DNA: a) guanine b) thymine c) uracil d) cytosine8. Carbohydrates include: a) ribose and lactose b) glycogen and starch c) glycerol and lipids d) cellulose and chitinB. Make a diagram. 9. Write down the missing DNA nucleotides, indicating the hydrogen bonds:A-G-*-C-C-T-*-*-G-CT-*-T-*-*-*-A-C-C-*
10. Establish a correspondence between the structure of a protein molecule and its characteristics.
Structure of a protein molecule
A) primary 1. characteristic of all proteinsB) secondary 2. globuleC) tertiary 3. polypeptide chainD) Quaternary 4. spiral5. occurs as a result of the connection several proteins6. formed by a strong peptide bond7. held by numerous hydrogen bondsconnections8. is destroyed by reversible denaturation
ANSWERS1 option1
Used materials
1. Biology. Introduction to general biology and ecology. Textbook for 9 cells. A.A. Kamensky, E.A. Kriksunov, V.V. Pasechnik M.: Bustard, 2007.
2. Frosin V.N., Sivoglazov V.I. Getting ready for the unified state exam: General biology. - M.: Bustard, 2004. - 216s;
3. Bolgova I.V. Collection of problems in General biology for entering universities. M .: "Onyx 21st century" "World and education", 2005;
4. Biology. Educational and training materials for the preparation of students. "Intellect-Center" 2007
Molecular level 1 option
1. What is the name of an organic substance whose molecules contain C, O, H atoms, which perform an energy and building function?
A- nucleic acid B-protein B- carbohydrate G-ATP
2. What carbohydrates are polymers?
A-monosaccharides B-disaccharides C-polysaccharides
3. The group of monosaccharides includes:
A-glucose B-sucrose C-cellulose
4. nucleic acid monomers are:
A-amino acids B-fats C-nucleotides D-glucose
5. a substance necessary for all chemical reactions in a cell, playing the role of a solvent for most substances, is ...
A- polynucleotide B- polypeptide C- water D-polysaccharide
6. Fats perform a function in the cell:
A - transport B - energy
B - catalytic G- informational
7. What compounds in relation to water are lipids?
A- hydrophilic B- hydrophobic
8. What is the importance of animal fats?
A-structure of membranes B-thermoregulation
B- source of energy D- source of water E- all of the above
9. Protein monomers are:
A-nucleotides B-amino acids C-glucose G-fats
10. what is the name of the reversible process of disruption of the structure of one of the most important organic compounds of the cell, which occurs under the influence of physical and chemical factors?
A-polymerization of glucose B-protein denaturation
B- DNA duplication D- fat oxidation
11. The amount of adenine in DNA is always equal to the amount of ...
A - thymine B -guanine C -cytosine D-uracil
12. What order will the nucleotides be in?second strand of DNA and in i-RNA , if the DNA chain has the following composition: TAC - GGT-ATA-GCG-CTT-AAG-CCT-CAT-ATC
chain of amino acids the primary structure of the encoded protein. write down anticodons
tRNA, encoding these amino acids.
Molecular level 2 option
Choose one correct answer
1. How many of the known amino acids are involved in protein synthesis?
A-20 B-100 V-23 G-150
2. The highest energy value (in terms of the amount of energy released from 1 g) has:
A) fat B) starch; B) protein; D) cellulose
3. What compounds are included in DNA?
A - nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, phosphoric acid residue
B-guanine, ribose, phosphoric acid residue.
B-ribose, glycerol and any amino acid
4. Monomers of nucleic acids are:
A-amino acids B-fats B-nucleotides D-glucose
5. What class of chemicals does ribose belong to?
A-protein B - carbohydrate C-lipid
6. What nucleotide is not part of the DNA molecule?
A- adenyl B-uridyl B-guanyl D-thymidyl
7. Which of the nucleic acids has the greatest length?
A-DNA B-RNA
8. The nucleotide is complementary to the guanyl nucleotide:
A-thymidyl B-cytidyl B-adenyl G-uridyl
9. The process of doubling DNA molecules is called:
A-replication B-transcription
B-complementarity G-translation.
10. tRNA:
BUTHave an anticodonB.Carries nucleotides
C. Located in the cytoplasm D. The molecule consists of two chains
11. The amount of guanine in DNA is always equal to the amount of ...
A - thymine B -adenine C -cytosine G-uracil
12. According to the section of codogenic DNA
TAC - AAT-GCG-ATG-CTT-AGT-TTA-GGA -ATT
Build complementary chain
i-RNA
Using the genetic code table, make up chain of amino acids the primary structure of the encoded protein.
write down tRNA anticodons, encoding these amino acids.