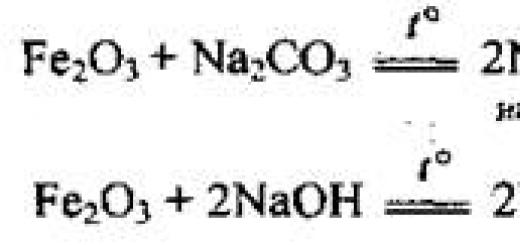In psychology, there is a special approach called the principle of determinism.
This scientific position allowed the development of a whole range of teachings.
What is rigidity of thinking and should it be overcome? Learn about it from ours.
Definitions
What does the principle of determinism in psychology say? scientific principle based on a number of concepts operated by scientists.
Determinism in psychology
Allocate three key methodological principles psychology: determinism, consistency and development.
The principles of consistency and development are unambiguous for understanding.
Under consistency refers to the existence of links between various manifestations of the psyche, and under development- change of stages, types of ongoing processes.
concept determinism not so clear. This is the recognition of a direct relationship between phenomena and the factors that give rise to them.
That is, when studying any mental phenomenon, it is necessary to analyze the conditions for its occurrence. Only in this case can we talk about creating a complete picture of the present. Not all scientists agree with this opinion.
Deterministic approach
This is a scientific approach, according to which everything that happens processes are not random, but have some specific cause.
Determinism considers causality as a set of circumstances that determines all processes. At the same time, it is recognized that it is impossible to explain all phenomena by causality alone.
Other forms of determinism that are of key importance are:

Determination of behavior
What is the definition of behavior? Human behavior is determined not only by his individual character traits and the current situation in which it functions, but also by the specifics of its surrounding social environment.
The immediate environment (family, friends, acquaintances) influence the formation of life attitudes.
It is in the child in the family and in society that he learns moral and ethical norms, comprehends the principles of behavior. His personal qualities are supplemented by information coming from outside.
In addition to the immediate environment (microenvironment), the individual is influenced by society as a whole(macro environment). Political, economic, sociocultural and historical processes form rules of conduct, typical processes and phenomena.

This leads to the fact that certain stereotypes of behavior, habitual views and opinions are developed in a particular society.
To become a full-fledged citizen and achieve social well-being, these stereotypes and rules must be observed.
Cultural determinism assumes that all human behavior is explained purely social and cultural reasons. It is the level of a person's culture that determines his emotional reactions, behavior, etc.
Thus, internally "I" under the influence of life in society is supplemented and transforms into "I-image". Under the inner "I" is understood the totality of individual personality traits - ideas about oneself and about the world.
But often a person in the course of his social life encounters phenomena that conflict with his inner personality.
In this case, the “I-image” comes first - this is the one that a person demonstrates to communicate effectively with others.
That is, he says and does exactly what his members expect from him. Even if it goes against his internal position.
Determinism and freedom of behavior are possible only if a person is able to adapt to the requirements of the environment and accept all existing rules without internal discomfort.
Determinants of mental development
The study of the problem of the mental development of an individual involves the analysis of three main factors:

Determinist - who is it?

Determinists are adherents of the corresponding doctrine.
Proponents of this scientific approach speak of a person's lack of freedom of choice.
All our actions are determined by motives that underlie the causality of phenomena.
These motives may be due to external circumstances or internal characteristics of a particular individual.
Any act of a person does not depend on his specific choice, but on the fact what motive is predominantly influencing him at the current time.
As a rule, determinists in practical life are not guided by their theory in its pure form. In modern social conditions, it is not possible to fully function, showing complete apathy and lack of initiative.
But people successfully apply the principles of the approach when it becomes necessary to justify their own behavior. In this case, negative actions are explained by the influence of the environment, the biological characteristics of the psyche, the negative impact of the environment, etc.
Theory - briefly

The basis of the psychological approach lies in the philosophical theory, according to which there is a universal relationship and interdependence between the phenomena of the surrounding reality.
The first aspects of determinism were formulated as early as ancient Greek materialists-atomists.
Then the principle was considered by representatives of the classical school of philosophy.
In the 17th century, the existence of the causality of all phenomena in society is determined. With the development of science comes the understanding that any event or phenomenon is a pattern of any causes.
At present, the theory is actively used to explain the development and functioning of various phenomena.
AT social sciences the approach makes it possible to analyze the laws of social development, the degree of influence of social norms and principles on human behavior.
AT special sciences the principle is used to designate constant connections in various processes, mechanisms, equations, etc. That is, processes or mechanisms that lend themselves to a strictly unambiguous description and forecasting are deterministic.
The presence of the aspect of probability, variability, instability indicates the operation of the opposite principle - indeterminism(lack of patterns and dependencies in nature, in society).
Principle

The Problem of Determinism occupies an important place in psychological science, since it directly affects the issues of will, freedom of choice, responsibility for one's own destiny.
Self determination is the ability of a person to choose and have their own opinion. It is this skill that distinguishes people from other living beings.
The complexity and paradoxical nature of the issue often leads many scientists to go in the direction of indeterminism.
Among Russian and foreign scientists, however, there are representatives of a strictly deterministic approach, which substantiate the relevance of this doctrine.
The authors
Eminent psychologist and philosopher S.L. Rubinstein developed an activity approach in psychology, based on the general philosophical principle: external causes have an impact through internal conditions.
So, according to the scientist, the brain activity of an individual develops under the influence of external environmental conditions. As a result of the relationship of a person with the outside world, the formation of the nervous system occurs.
L.S. Vygotsky argued that there is a certainty of mental processes based on causality. Nothing can happen randomly without some reason. Thus, the manifestation of a person's will is based on the principles of regularity and necessity.

According to K. Höfer, any event arises on the basis of previous phenomena and conditions, the laws of nature.
Determinism manifests itself not only in our understanding of the sciences and objective phenomena, but also in the formation of ideas about life: freedom of choice, manifestation of will.
Examples
The best example of determinism from a scientific point of view is combination of the laws of mechanics and gravity developed by Newton. It is possible to apply these laws to the planet Earth.
If our planet is launched from a given place at a certain speed, then it is possible to predict its location at any given time in the future.
Another example the operation of the psychological principle can often be observed in daily life. A child who devotes a lot of time to studying and constantly improves his level of knowledge always learns for good grades.
A lazy person who does not want to engage in self-development turns out to be a loser. On the face of the obvious causality of phenomena: mastered the knowledge - received a good mark, did not master the knowledge - received a bad mark.

Explicit Interaction of Determining Factors can be seen in the example of raising children in foster families and in public institutions.
Often, children from the same family, who initially have the same biological aspects of development (parental genes, pregnancy conditions, etc.), fall under the influence of various social factors.
One child is brought up in an orphanage, and the second child is taken up by a family from an early age.
As a result, the conditions of socialization can lead to the formation of two personalities with completely different social attitudes, life values and mental characteristics.
So the principle of determinism is important philosophical and psychological concept. Causal patterns can be found in all aspects of social life and science.
Free will and determinism:
Introduction
Psychological science is currently in a state of methodological crisis. There are a number of contradictions between the representatives of psychological schools, referring themselves to two different scientific paradigms. The first paradigm is scientistic (explanatory) psychology, which considers mental phenomena in a natural scientific way, but is far from studying subjective reality. The second paradigm - humanitarian (descriptive) - studies the unique individuality of a person, while periodically breaking away from the material foundations.
Determination of personality development
Representatives of the first paradigm tend to see a person as an object that is formed under the influence of external factors, representatives of the second paradigm see a person as a subject with a desire for self-development, capable of changing and changing the world around. Understanding the human personality is the main stumbling block in this scientific struggle.
The development of the problem of the human personality in its various manifestations was carried out by representatives of various schools of psychology: psychoanalysis (Z. Freud, K. G. Jung), humanistic psychology (A. Maslow, K. Rogers), even behaviorists came to the concept of an independent variable that determines the behavior of the subject . But only in Russian psychology did scientists (L. S. Vygotsky, A. N. Leontiev) approach the understanding of personality as a result of socialization, without breaking away from the biological roots of Homo sapiens. An attempt to combine the data of representatives of the natural science and humanitarian paradigms was made by B. F. Porshnev.
This study is based on the concept of personality as a system of self-control, which is formed in the process of socialization. The personality includes 3 levels, and the specificity of the levels is determined by the peculiarities of the second-signal interaction with others.
The first level is the level of unconscious regulation (0 - 3 years), at which secondary signal stimuli are insignificant, behavior is guided by instincts, and in the pursuit of satisfaction, the individual is capable of uncontrolled actions that can be regarded as aggressive. In phylogeny, according to the theory of B. F. Porshnev, these qualities are characteristic of suggestors, persons who influence others in order to immediately satisfy their own needs.
The second level is the level of consciousness (3-7 years), at which human behavior is controlled by additionally reinforced second-signal stimuli from the outside, both received from other people and arbitrarily generated through a system of loud and then egocentric speech. The need for external reinforcement causes increased social anxiety. In phylogenesis, these qualities are inherent in suggerends, persons subject to external influence, suggestion, and when exposed from outside, interrupt the satisfaction of their own needs in order to satisfy the needs of other members of the community.
The third level is the level of self-awareness (7 - 15-16 years old), at which behavior begins to be regulated with the help of internal speech that does not require external reinforcement. With the formation of abstract thinking necessary for reflection, the puberty crisis of identification ends. In phylogeny, according to the theory of B. F. Porshnev, the ability to abstract (on the basis of diplasty) leads to the formation of the psyche of Homo Sapiens Sapiens and the emergence of the ability to choose whose needs - one's own or others to satisfy at a given moment in time.
After the pubertal crisis, one of the structural levels of the personality begins to dominate in the process of self-regulation. Depending on which level prevails, a person's behavior changes either towards suggestiveness (not enough conscious regulation with influencing others), or towards suggestion (conscious regulation of behavior with submission to others), or towards diplasty (regulation at the level of self-awareness, the manifestation of the ability to freely manage one's behavior, expressed in a high level of subjective control).
Neurophysiologically, suggestiveness can be expressed by a sharp dominance of the left hemisphere, which is responsible for generating speech and building behavior programs, while suggestiveness can be expressed by a sharp dominance of the right hemisphere, which is responsible for perceiving speech intonations that have semantic meaning. A high level of adequate self-control is possible only when the activity of the hemispheres is integrated without a sharp dominance of one over the other.
On the basis of the Russian State University named after S. A. Yesenin, a study was conducted on a sample of students numbering 50 people. Interhemispheric asymmetry was studied (the Dobrokhotova-Bragina method), the level of subjective control (J. Rotter's test adapted by E.F. Bazhin, S.A. Golynkina, A.M. Etkind), performance and dominance (according to the scales of the Rogers-Diamond questionnaire) , as well as the level of anxiety and aggressiveness (scales of the test of self-assessment of mental states by G. Eysenck).
The students with right hemisphere dominance had the highest levels of anxiety (average 10.5) and the statements (average 13.95), as well as the lowest level of dominance (average 7.32). That is, the signs of personality suggestion in social interaction are revealed.
Students with left hemisphere dominance had the lowest levels of anxiety (average 7.62) and statements (average 13.04), as well as the highest level of dominance (average 9.27). That is, the signs of suggestive personality in social interaction are revealed.
In students with a high level of subjective control, the levels of anxiety (8.09), aggressiveness (9.73), statement (13.09) and dominance (8.91) turned out to be average. In general, the average severity of these characteristics is adaptive, since it excludes extremes in reflection (high or low anxiety) and extremes in the area of control (lack of self-control or excess control over others). The level of subjective control is positively related simultaneously to the level of anxiety (moderate correlation 0.425097) and the level of dominance (moderate correlation 0.40938), that is, its formation of self-control is influenced by factors associated with the activity of both the right and left hemispheres. This may indicate a higher level of integration of the activity of the hemispheres, a closer interaction between the first and second signaling systems, diplasty, which ensures adequate functioning of self-consciousness and high self-control.
The place and significance of psychological knowledge in the study of personality
At present, due to the increase in the birth rate in the country, it is a task of prime national importance. Ensuring the future of Russia with healthy generations of full-fledged people is impossible without taking into account the knowledge about the uniqueness of the process of intrauterine development and its impact on the entire subsequent life of the individual, the development of large-scale state programs based on them, aimed at changing the practice of obstetric care, pregnancy management. Psychological developments of these topics are carried out by psychologists and psychotherapists working in line with perinatal psychology. These specialists work both in state institutions - antenatal clinics, maternity hospitals, etc., and in non-state institutions - medical centers, pregnancy training centers, schools for parents, etc.
Perinatal psychology is a new field of knowledge that studies the circumstances and patterns of development of the human psyche in the early stages (antenatal, intranatal, neonatal) and their impact on the entire subsequent life of the individual. The object of study is the dyad "mother-child", and the object of influence of the psychologist-practitioner is the expectant mother, family.
The history of the emergence and development of perinatal psychology and psychotherapy is associated with the development of the psychodynamic approach and a number of its areas and practical applications: object relations theory, attachment theory, transpersonal psychology and psychosomatics.
In the last years of the twentieth century. there was a turn towards scientific theoretical and methodological understanding of the problems of the prenatal and perinatal period of development of the human psyche. In domestic psychology and psychotherapy, the concepts of psychophysiology of the maternal dominant were proposed (Batuev A.S., Vasilyeva V.V.); psychology of motherhood and psychology of the reproductive sphere (Filippova G.G.), perinatal psychotherapy (Dobryakov I.V.), theoretical justification and practical application of perinatal psychology to the correction of pregnancy (Kovalenko N.P.) and preparation for parenthood (Lantsburg M.E. .) and others. Since 1993, scientific sections and associations have been formed, thematic conferences and congresses are regularly held, symposiums are organized at psychological and psychotherapeutic conferences and congresses.
At present, in our country, we can state the penetration of evidence-based methods into the practical work of perinatal psychologists and psychotherapists; there is a growing mutual understanding between perinatal psychologists, psychotherapists and obstetricians (evidence of this is the large number of collections of joint scientific papers published in recent years).
The growing trend of mutual respect and mutual understanding between physicians and psychologists is also reflected in the emergence of interest in perinatal psychology among managers and organizers of obstetric, maternity and childhood services.
More and more doctors are becoming not only loyal to perinatal psychologists, but also actively interested in psychology, improving their education in this area, and thinking about how to apply this knowledge in their own practice. New special psychotherapeutic techniques are being developed to accompany and treat pregnant women, infants, and members of their families. We can talk about a new direction in psychotherapy - perinatal. Perinatal psychotherapy is a practical application of perinatal psychology - as an independent area of psychology that has developed in the last quarter of a century.
PSYCHOLOGY AND PEDAGOGY
V. V. Kazanevskaya
Doctor of Philosophy, Professor, Tomsk
The study of the category of "determination" in the general scientific and philosophical aspect (as a causal connection), the concept of Laplace's mechanical determinism in the social aspect (identification of causal goals) pursued the main goal - the selection of cause-and-effect chains from the apparent chaos of historical events. In modern Western sociology, one of the leading places is occupied by the concepts of "technological determinism", representing the progress of mankind as a result of the rapid development of science and technology.
The insufficiency of such generalized and therefore simplified ideas about determination in the course of scientific research was revealed quite early. The positivist philosopher D. S. Mill (1806-1873) expressed the idea of the multifactorial nature of determination.
Bypassing many mediations in the development of this thought, one can immediately proceed to the assumption that in the process of studying determination, the initial ideas about causation were ideas about linear causation; and only with the development of these studies did the idea arise of the possibility of structured connections, of the structural nature of these connections. Strictly speaking, such a train of thought is inherent in any study, when one moves from the idea of linear connections to the study of more complexly organized connections, that is, to the study of structured connections.
A significant place in the development of ideas about structured relationships is occupied by the so-called systemic ideas. System representations, as a rule, are based on a certain system of concepts, suggesting certain relationships. Systemic representations at the initial stage of development were called the systemic approach, the essence of which is that the object under study is considered as a system. Obviously, it comes down to what is meant by a system, and this is not at all a simple question. The fact is that the systems approach, as it develops in various branches of knowledge, has turned into a vast sphere with dozens of separate theories, separate fundamental principles manifested in various branches of knowledge, separate very popular concepts that are “included” in various branches of knowledge, etc. e. Therefore, at present, a systematic approach can be understood as any of the existing systemic concepts, or principles, or theories, and their choice will have a determining influence on the object under study.
In this article, not a categorical general theory of systems, but a psychological theory, in terms of which the problem of mental determination is discussed, will be used as its systemic basis - this is an integral theoretical psychology of personality.
If we continue the logic of the development of ideas about the structural nature of the connections of the external world, then we come to the assumption that different objects are inherent
and different link structures and different elements that connect those links. Obviously, here the determination of objects begins, that is, the general contours of the determination of an object depend on the choice of a theory to describe it, if there is a theory, or on the development of an appropriate theory, if the theory has not yet been developed. As such a general psychological theory, as mentioned above, this article adopted the integral theoretical psychology of personality.
Thus, the determination of any object can be considered at its various levels and in a more or less generalized form. The determination of an object can mean causality as such, or general methodological principles, or, finally, this or that theory. As you know, the determination of a personality problem in the conditions of an abundance of psychological theories of personality can be based on any of them, and then in each case a different picture will be obtained.
In this article, we are talking about the intrapsychic determination of personality, ideas about which are developed as part of the integral psychology of personality.
According to the provisions of the integral psychology of personality, the human psyche can be represented by two components - objective and subjective. Both components have a determining function, but the processes of determination look different in them. This article discusses the problem of mental determination in its subjective aspect. the concept of determination is of great importance for the psychology of individuality, for differential psychology, for the psychology of the subject. The general statement that we put forward from the very beginning of the discussion is that the difference between people consists, first of all, in their different determination. The theoretical idea of this article is that the principle of determinism should take its place in the study of personality psychology. The article discusses the question of what this role consists of, in what concepts it is expressed, in the solution of which problems it will find its constructive application, etc.
The concept of determination can be found in various fields of knowledge. Without pretending to complete coverage of this issue, let us dwell on the field of sociology, since the closest to the topic of this article are the developments of this concept in the field of sociological sciences. It should be noted that this concept plays a much greater role in sociology than in psychology. Therefore, the experience of developing the concept of determination in the field of sociology may be applicable in the field of psychology.
It cannot be said that the concept of determination is not used in modern psychology. Determination as a principle of causality, determination as statements of a theoretical nature, etc. However, this concept is used in modern psychology in the most general sense.
In itself, the concept of determination has a vast scale and in each case, depending on the level of its location, it has its own separate content. We can say that this concept can be used in its various statuses, from more general to strictly specific. Therefore, it is necessary to speak of determination not only in its general sense, but also in its specific sense. In this article, we are not talking about determination in general, as a principle, but about specific determination - determination at the level of the inner psyche, and this determination has a number of specific expressions, specific knowledge. We are talking here about mental determination, about the determination of the psyche. In the monograph, this problem, as part of other theoretical problems of personality psychology, is discussed and substantiated as a whole, on the basis of the principle of nature. This article is devoted specifically to the concept of determination, the content of personal mental determination. The main provisions of personal mental determination are as follows:
The personal level of the psyche has its own intrapsychic functioning; this means that a person not only responds to stimuli and works out
needs, but it also has proper mental functional needs, the realization of which in a functional form constitutes the inner mental life; it is emotional functioning, mental functioning, volitional functioning; in a similar way, that is, functionally, the personal properties of the categorical composition of the personality are manifested, which constitute the most important personal determination;
Structural personal determination is carried out through the mechanisms of formation of associative formations and is the most important reason for the subjectivity of the personality structure;
Constant determination is quite subjective and individual.
Thus, the concept of determination in integral psychology is the main expression of the individuality of each person, the difference between each specific person and all others. Further, these basic provisions of personal mental determination are considered in somewhat more detail.
It should be noted about the terms "mental" and "psychological" that their difference may play a big role in a certain context, but in this article the term "psychological" will be used only when it is about psychology, and not about psyche. In cases where the psyche is spoken of, the term "psychic" will also be used. Therefore, the determination of the properties, states and functions of the psyche will be called mental determination, the role and significance of these concepts for psychology will be called psychological.
The basis for the interpretation of all concepts and the entire content of the article, as already indicated above, is the integral theoretical psychology of personality. This theory has its own distinctive features, some of which will be mentioned in this article. One of them is the idea of mental functioning, which can be called internal and which belongs to the personal level. This mental functioning constitutes the mental determination of the personality. The determining role of mental functioning, according to the provisions of integral psychology, is that the very fact of functioning and the main composition of mental functioning processes is general, characteristic of a “person in general”, but as for the specific content and constants of these general functionings, they are individual, personal, as a staffer might say; they are personal, subjectively personal, as a categorical psychologist would say, based on the concepts of integral categorical psychology of personality.
It is precisely the properties of personal determination, the individual determination of a separate personality, that make it possible for integral psychology to speak not about the psyche in general and not about a person in general, but about a given, specific person, a given specific personality, allow "calculating" a personality. Let us note that this problem and its formulation constitute not only an unsolved, but also an unformulated task of personality psychology. Let us also note that the term "determination" is absolutely necessary for the formulation of this problem, that it directly answers this problem and makes it possible to discuss and solve it.
Further, the main forms of functioning act as personal determinants - the functioning of will-activity (activity), the functioning of the emotional and the functioning of the intellectual. All types of functional determination are concretized for a particular person. The most important task is the introduction into the functional determination of ideas about the forms of functioning, about the forms of mental movement. The main one is the form of "difference-identity" movement or oscillatory movement.
The most important determinant is also a constant determination. the listed personal determinants underlie a holistic individual determinant
nation of a particular individual, which fully explains the differences between individuals - both objective and inevitable.
But that's not all. Among the mental mechanisms that ensure the individuality of the individual, we see the mechanism of association. It is this mechanism that not only builds associative links, which are the structural links of the psyche, but also builds them absolutely individually. Structural connection is experienced - writes Dilthey. This means that human experiences underlie the structuring of the psyche, the individuality of which is thereby ensured. Thus, mental structure is another individual personality determinant.
As we can see, in the field of terminology of the processes of individual structuring of the psyche, the problem of the correct or incorrect formation of the personal sphere, including the emotional, mental, volitional, and actually personal, can be posed.
Surprisingly, when discussing the phenomenon of associativity, attention is usually drawn to the manifestation of associativity, to the manifestation of previous experience; at the same time, the essence of the formation of an associative connection remains in the shadows. The multidimensionality of the categorical concepts of psychology leads to the fact that from one categorical concept it is possible, and quite reasonably, to move on to a dozen different concepts related to it. Thus, the phenomenon of association supported in Wundt's school the idea of a vicious circle of psychic phenomena. Meanwhile, attention to the logic of association formation can put this phenomenon in its proper place and give it its own psychological role and significance.
Considering the mechanism of formation of associative connections as a way of fixing the connections of the external world, we will inevitably come to the question of how a person distinguishes the connections of the objective world from the connections that express his personal experience, the connections are subjective, objectively subjective. It can be assumed that at first a person perceives all connections as subjective, while the selection of objective connections occurs on the basis of special studies.
the psychological significance of the mechanism of associations lies in the fact that the processes of formation of associative formations, including elements, underlie the formation of personal structures and the basis of complete subjectivity, individuality of these structures; subjectivity, the individuality of the individual, depends on them as a whole.
Subjectivity, individuality of personality structures underlies individual differences, differences between individuals. It is the personal structures that are responsible for the composition of the functional spheres and for the way the individual reacts.
In connection with the question of the mutual influence of intrapsychic and social determination, let us dwell only on what is new in the concept of intrapsychic determination.
An important issue of social determination of personality is the philosophical question of free will. As a social being, a person realizes his activity not in isolation, but in the process of interaction not only with other people, but also with society as a whole. It is society as a whole, its social institutions that have a concretizing influence on the activity and life of a person, on the form of his life, starting from the formation of feelings and ending with family and industrial relations. Society serves as the framework that has a concretizing influence on all manifestations of man. How does intrapsychic determination affect this sphere? First of all - on its goal-setting. As you know, in his cooperation with society, a person consciously sets the goals of his life and activity. But the goals of a person, the way of their realization and aspirations of a person are closely and necessarily consciously connected with his intrapsychic determination. Lack of awareness of intrapsychic determination can be the cause of general personal distress. For example, you-
The choice of a profession that does not correspond in its emotional characteristics to a person’s own emotionality can lead him to a state of permanent emotional deficit and to serious consequences. Even more clearly manifested is the situation when an intrapsychic determining characteristic forces a person to choose not only a form of behavior or activity, but also goals.
Thus, intrapsychic determination has a mediating but very serious influence on social determination and social behavior. But the main thing is that intrapsychic determination has an extensive influence on all manifestations of the personality, including the social manifestations of the personality and on itself, that is, on its composition, structures, functions, goals, behavior, etc. As well as the concept of intrapsychic determination, these influences have not yet been studied and it can be expected that their study will significantly deepen the understanding of social and socio-psychic mechanisms.
The meaning of the concept of determination for practical psychological work should be considered not in itself, but as part of an integral categorical personality psychology, the features of which, as shown above, reveal the individual determinism of the personality and allow working with an individual specific person. At the same time, this theory has the means to study the psychological properties of groups of people. The very construction of an integral categorical psychology of personality is focused on an individual personality, its description and research. This requires a description of the functional spheres of the personality - volitional - active, emotional and intellectual - according to the composition of the foundations of functioning and according to the parameters of the function itself; that is, the mentioned composition of the three functional areas is, by definition, individual; it must be borne in mind that not only the composition of the foundations of functioning is individual, but the structures that connect this composition are also individual; this applies both to individual structural connections and to large structural formations - concepts of personality. In addition, the properties of the mental system "personality", as well as many other concepts of the integral psychology of personality, are individual.
Literature
1. Kazanevskaya VV Systems and system laws: Categorical theory of systems. - Kemerovo: Kuzbassvuzizdat, 1992. - 272 p.
2. Kazanevskaya VV Integral Theoretical Psychology of Personality. - Tomsk: Publishing House Vol. un-ta, 2000. - 526 p.
L. V. Miroshnichenko
Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Associate Professor, Head. Department of Pedagogy and Psychology Kemerovo State University of Culture and Arts
INTERACTION OF THE STUDENT AND TEACHER IN THE EDUCATIONAL PROCESS: NEW PROBLEMS AND TRENDS
The formation of a high-class professional with a system of qualities required by modern society and specified by the State Educational Standards of Higher Professional Education is possible only if there is an optimal interaction between the main subjects of the pedagogical process at the university - the student and the teacher.
The question of the determination (causation) of mental development was originally raised in philosophy. There is a long history of disputes about which factors (driving forces) - biological (internal, natural, related to heredity) or social (external, cultural, environmental) - play the most important role in development.
Traditionally, there are two extreme points of view on the conditionality of development - nature (heredity) or environment (upbringing, training).
Natural...
Distracting from the content of certain specific behavioral acts, their underlying values and motives, we can try to identify the most important factors that determine role behavior in business communication. The cognitive value of this approach is explained by the fact.
That the behavior of any individual is determined not only by a set of personal qualities, the characteristics of a particular situation, but also by the specifics of the social environment, which is not always taken into account, within which his business is implemented ...
In literary sources, the term "self-determination" is used in various meanings. So, they talk about cultural, national, political, religious, economic self-determination, etc. At the same time, one cannot but agree that personal self-determination determines the development of social and professional self-determination.
Personal self-determination occurs at the level of values. Value, on the other hand, is fundamentally timeless; giving a person an idea of the future, it does not correlate it with the time ...
Raising the question of the nature of man, people at all times assumed the existence of something that constitutes his essence. Erich Fromm on this occasion notes that no one doubted the specific nature of man, but at the same time, very different opinions were expressed about its content.
Hence the many definitions of a person: either he is a “rational being” (animal rationale), then a “social animal” (zoon politikon), then a “handy man” (homo faber), then a being capable of creating symbols, finally, for everyone ...
Jack Engler is an American psychotherapist, supervisory psychologist at Harvard Medical School, Buddhist researcher, and Zen teacher.
In this article from Buddhism and Psychotherapy, he writes about why meditation alone is often not enough; the ten unhealthy motivations of Western practitioners; and how the practice can be transformed from a path of liberation into an ego-strengthening tool.
Translation by Anastasia Gosteva and Olga Turukhina
Having accumulated a certain experience of practice, in particular, in ...
The study of the characteristics of group and individual behavior cannot be successful without taking into account the general cultural and historical background, called the macroenvironment of the individual.
The study of the macroenvironment of the individual involves the identification and analysis of objective factors that to some extent determine the behavior of the individual.
It is important to note that determination can be both direct and indirect. At the same time, the effect of certain factors is ambiguous and depends both on the features ...
Using the language of synergetics itself, one can say that at least some of the sciences are today at the point of bifurcation, at the point of transition to a new level of development, redefining the subjects and methods of studying those sectors of “objective reality” that until now seemed so self-evident subjects of research.
When the view of the world order and the mechanisms of the world order changes, it is difficult to expect a calm (evolutionary) development of sciences. Scientific revolutions are inevitable - at least for...
2.5. Poetae nascuntur, oratores fiunt
(Poets are born, speakers become)
I graduated from the Military Medical Academy. I didn't take a pedagogy course. However, I was lucky in my life: I saw “how it is done”, I was lucky to listen to the speeches of brilliant teachers. When I studied at the Military Medical Academy, its head was the outstanding Soviet physiologist Academician L.A. Orbeli. I will probably never forget his lecture on the adaptive-trophic role of the sympathetic nervous system. For...
The structure of social systems and activities are very different in Eastern and Western countries. One can see how in the history of Europe the destabilization of ethno-tribal social systems gradually occurred, which manifested itself in the active mixing of peoples, in migrations and social revolutions.
The external reason for this was the accumulating mismatch of traditional ethno-clan systems with the destructible biospheric environment. This was especially active in the regions of the Mediterranean, which attracted masses of peoples...
DETERMINISM- the concept according to which people's actions are determined - determined and limited by heredity and the previous events of their lives. In psychology, the natural and necessary dependence of mental phenomena on the factors that give rise to them. Includes causality as a set of circumstances that precede the investigation in time and cause it; however, the explanatory principle of causality is not exhausted, since there are other forms of determinism:
1) systemic determinism - the dependence of individual components of the system on the properties of the whole;
2) determinism of the feedback type - the consequence affects the cause that caused it;
3) statistical determinism - for the same reasons, different effects occur within certain limits, subject to statistical patterns;
4) target determinism - the goal that precedes the result as a law determines the process of achieving it, etc. The development of scientific knowledge about the psyche is associated with the development of various forms of determinism. For a long time, it focused on mechanical determinism, which represented the conditionality of mental phenomena by material factors in the manner of the interaction of objects in mechanics, or the operation of technical devices. Despite the limitations of this view, it gave psychology the most important teachings about reflexes, associations, affects, etc. In the middle of the 19th century. biological determinism arose, which discovered the peculiarity of the behavior of living systems (Ch. Darwin's theory of natural selection) and approved the view of the psyche as a function necessary for survival. If mechanical determinism represented the psyche as a side effect - an epiphenomenon, now it has acted as an integral component of life activity. Later, when it was established that this component has an independent causal significance, psychological determinism arose; however, he received an inadequate theoretical interpretation in the doctrine of a special mental causality, supposedly opposed to the material one. A different understanding of psychological determinism was developed in the works of natural scientists, who showed that mental phenomena (image, reaction of choice, etc.) caused by the influence of external objects on the body are formed according to laws different from physical and biological ones, and act as special regulators of behavior. The introduction of the ideas of natural-science psychological determinism into psychology led to its separation into an independent field of knowledge that studies processes that are subject to special laws. In domestic psychology, an interpretation of determinism was put forward as the action of external causes through internal conditions, and as the action of the internal through the external. But both of these formulas are one-sided. The basic principle of explaining the human psyche from the positions of materialism is outlined by the position that, changing the real world with its objective activity, its subject changes itself. Thanks to this activity, both the “external” - the products of material and spiritual culture, in which the essential forces of a person are embodied, and the “internal” - the essential forces of a person, formed in the process of their objectification in these products, are simultaneously generated.
(Golovin S.Yu. Dictionary of practical psychologist - Minsk, 1998)